S1. Fixed point iteration is a numerical method for solving equations of the form x = g(x) by making an initial guess x0 and repeatedly substituting xn into the right side to obtain xn+1.
S2. The method converges if |g'(α)| < 1, where α is the root and g' is the derivative of g. This ensures the error decreases at each iteration.
S3. Examples show the method can converge rapidly, as in Newton's method, or diverge, depending on the properties of g near the root. Aitken extrapolation can provide a better estimate of the root than the current iterate xn.

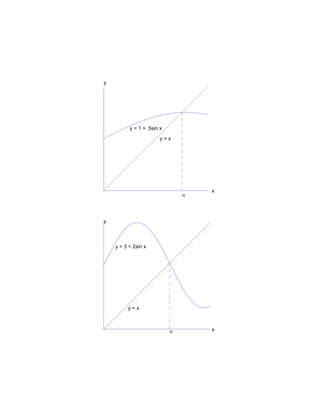

![EXISTENCE THEOREM
We begin by asking whether the equation x = g(x)
has a solution. For this to occur, the graphs of y = x
and y = g(x) must intersect, as seen on the earlier
graphs. The lemmas and theorems in the book give
conditions under which we are guaranteed there is a
fixed point α.
Lemma: Let g(x) be a continuous function on the
interval [a, b], and suppose it satisfies the property
a≤x≤b ⇒ a ≤ g(x) ≤ b (#)
Then the equation x = g(x) has at least one solution
α in the interval [a, b]. See the graphs for examples.
The proof of this is fairly intuitive. Look at the func-
tion
f (x) = x − g(x), a≤x≤b
Evaluating at the endpoints,
f (a) ≤ 0, f (b) ≥ 0
The function f (x) is continuous on [a, b], and there-
fore it contains a zero in the interval.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rootsequations-100720150107-phpapp02/85/Roots-equations-5-320.jpg)
![Theorem: Assume g(x) and g 0(x) exist and are con-
tinuous on the interval [a, b]; and further, assume
a≤x≤b ⇒ a ≤ g(x) ≤ b
¯ ¯
¯ 0 ¯
λ ≡ max ¯g (x)¯ < 1
a≤x≤b
Then:
S1. The equation x = g(x) has a unique solution α
in [a, b].
S2. For any initial guess x0 in [a, b], the iteration
xn+1 = g(xn), n = 0, 1, 2, ...
will converge to α.
S3.
λn
|α − xn| ≤ |x1 − x0| , n≥0
1−λ
S4.
α − xn+1
lim = g 0(α)
n→∞ α − xn
Thus for xn close to α,
α − xn+1 ≈ g 0(α) (α − xn)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rootsequations-100720150107-phpapp02/85/Roots-equations-6-320.jpg)
![The proof is given in the text, and I go over only a
portion of it here. For S2, note that from (#), if x0
is in [a, b], then
x1 = g(x0)
is also in [a, b]. Repeat the argument to show that
x2 = g(x1)
belongs to [a, b]. This can be continued by induction
to show that every xn belongs to [a, b].
We need the following general result. For any two
points w and z in [a, b],
g(w) − g(z) = g 0(c) (w − z)
for some unknown point c between w and z. There-
fore,
|g(w) − g(z)| ≤ λ |w − z|
for any a ≤ w, z ≤ b.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rootsequations-100720150107-phpapp02/85/Roots-equations-7-320.jpg)



![Corollary: Assume x = g(x) has a solution α, and
further assume that both g(x) and g 0(x) are contin-
uous for all x in some interval about α. In addition,
assume
¯ ¯
¯ 0 ¯
¯g (α)¯ < 1 (**)
Then any sufficiently small number ε > 0, the interval
[a, b] = [α − ε, α + ε] will satisfy the hypotheses of
the preceding theorem.
This means that if (**) is true, and if we choose x0
sufficiently close to α, then the fixed point iteration
xn+1 = g(xn) will converge and the earlier results
S1-S4 will all hold. The corollary does not tell us how
close we need to be to α in order to have convergence.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rootsequations-100720150107-phpapp02/85/Roots-equations-11-320.jpg)
![NEWTON’S METHOD
For Newton’s method
f (xn)
xn+1 = xn − 0
f (xn)
we have it is a fixed point iteration with
f (x)
g(x) = x − 0
f (x)
Check its convergence by checking the condition (**).
f 0(x) f (x)f 00(x)
g 0(x) = 1− 0 +
f (x) [f 0(x)]2
f (x)f 00(x)
=
[f 0(x)]2
g 0(α) = 0
Therefore the Newton method will converge if x0 is
chosen sufficiently close to α.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rootsequations-100720150107-phpapp02/85/Roots-equations-12-320.jpg)



![Usually, we write this as a modification of the cur-
rently computed iterate xn:
xn − λxn−1
α ≈
1−λ
xn − λxn λxn − λxn−1
= +
1−λ 1−λ
λ
= xn + [xn − xn−1]
1−λ
The formula
λ
xn + [xn − xn−1]
1−λ
is said to be an extrapolation of the numbers xn−1
and xn. But what is λ?
From
α − xn
lim = g 0(α)
n→∞ α − x
n−1
we have
α − xn
λ≈
α − xn−1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rootsequations-100720150107-phpapp02/85/Roots-equations-16-320.jpg)

![We combine these results to obtain the estimation
λn xn − xn−1
b
xn = xn+ [xn − xn−1] , λn =
1 − λn xn−1 − xn−2
b
We call xn the Aitken extrapolate of {xn−2, xn−1, xn};
b
and α ≈ xn.
We can also rewrite this as
λn
b
α − xn ≈ xn − xn = [xn − xn−1]
1 − λn
This is called Aitken’s error estimation formula.
The accuracy of these procedures is tied directly to
the accuracy of the formulas
α−xn ≈ λ (α − xn−1) , α−xn−1 ≈ λ (α − xn−2)
If this is accurate, then so are the above extrapolation
and error estimation formulas.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rootsequations-100720150107-phpapp02/85/Roots-equations-18-320.jpg)
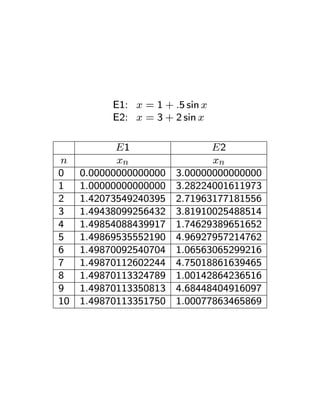
![EXAMPLE
Consider the iteration
xn+1 = 6.28 + sin(xn), n = 0, 1, 2, ...
for solving
x = 6.28 + sin x
Iterates are shown on the accompanying sheet, includ-
ing calculations of λn, the error estimate
λn
b
α − xn ≈ xn − xn = [xn − xn−1] (Estimate)
1 − λn
The latter is called “Estimate” in the table. In this
instance,
.
g 0(α) = .9644
and therefore the convergence is very slow. This is
apparent in the table.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rootsequations-100720150107-phpapp02/85/Roots-equations-19-320.jpg)
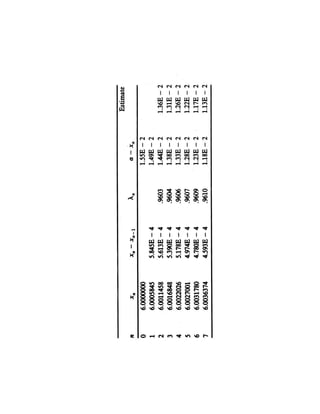
![AITKEN’S ALGORITHM
Step 1: Select x0
Step 2: Calculate
x1 = g(x0), x2 = g(x1)
Step3: Calculate
λ2 x2 − x1
x3 = x2 + [x2 − x1] , λ2 =
1 − λ2 x1 − x0
Step 4: Calculate
x4 = g(x3), x5 = g(x4)
and calculate x6 as the extrapolate of {x3, x4, x5}.
Continue this procedure, ad infinatum.
Of course in practice we will have some kind of er-
ror test to stop this procedure when believe we have
sufficient accuracy.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rootsequations-100720150107-phpapp02/85/Roots-equations-21-320.jpg)

