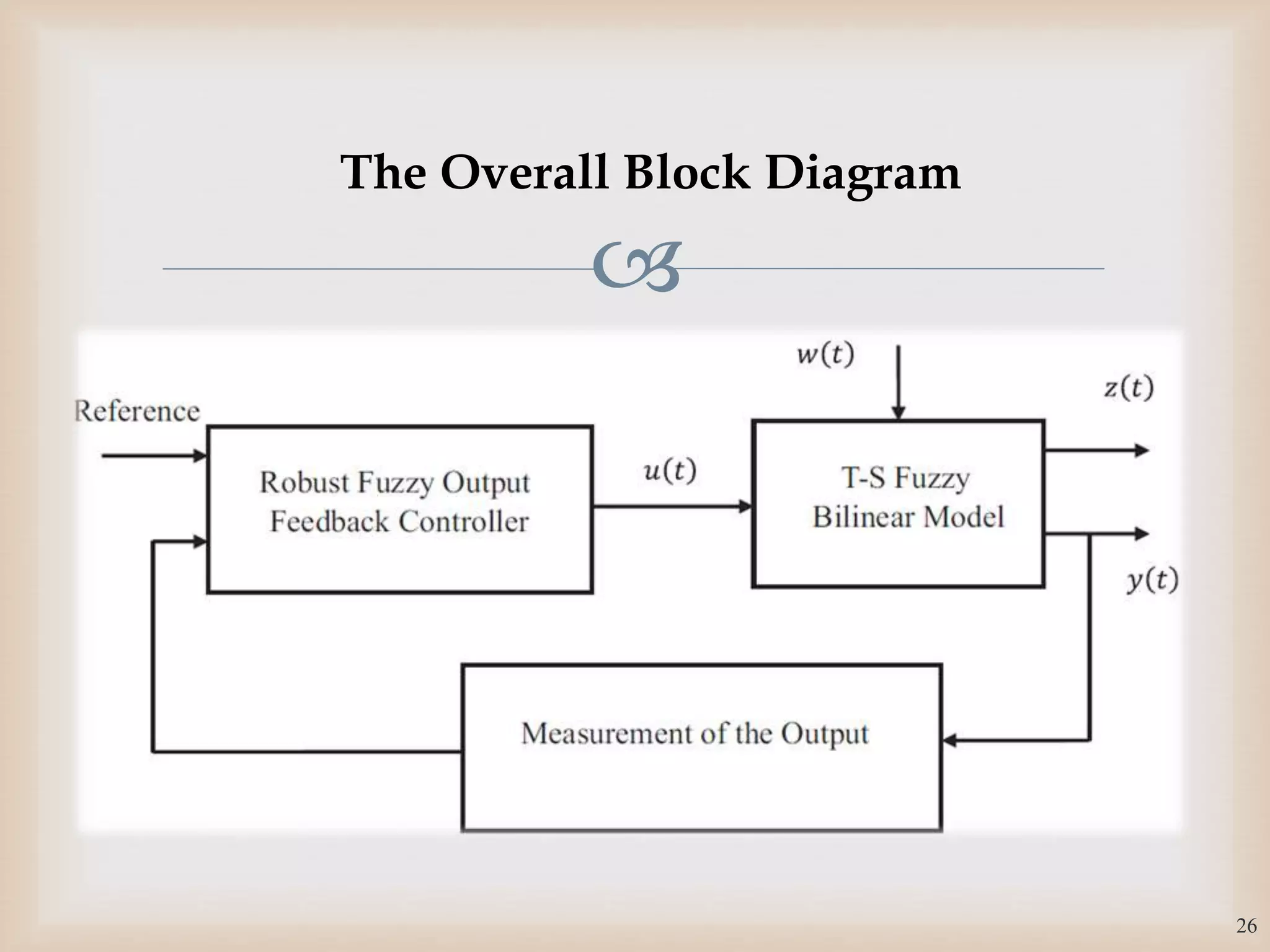
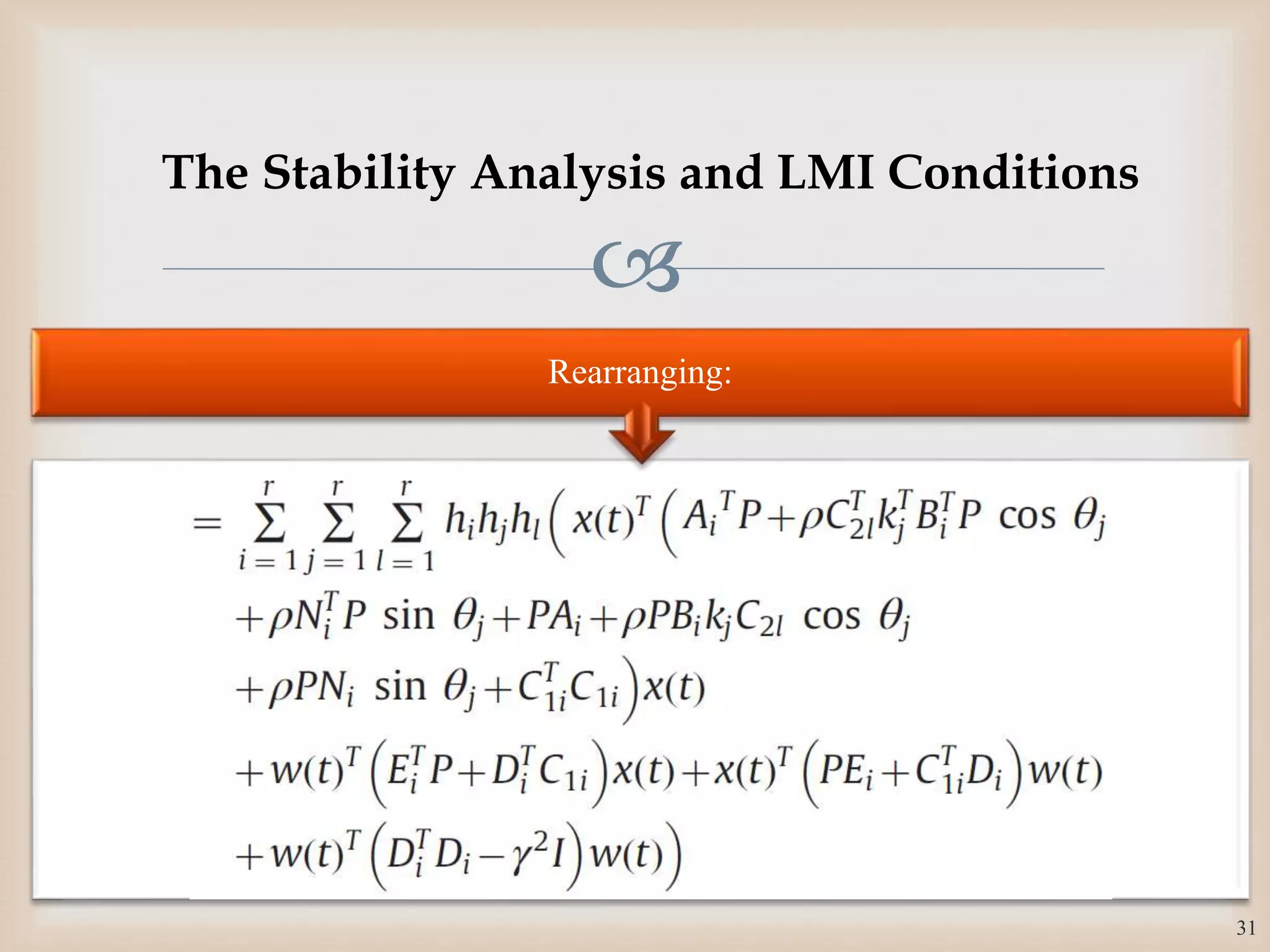
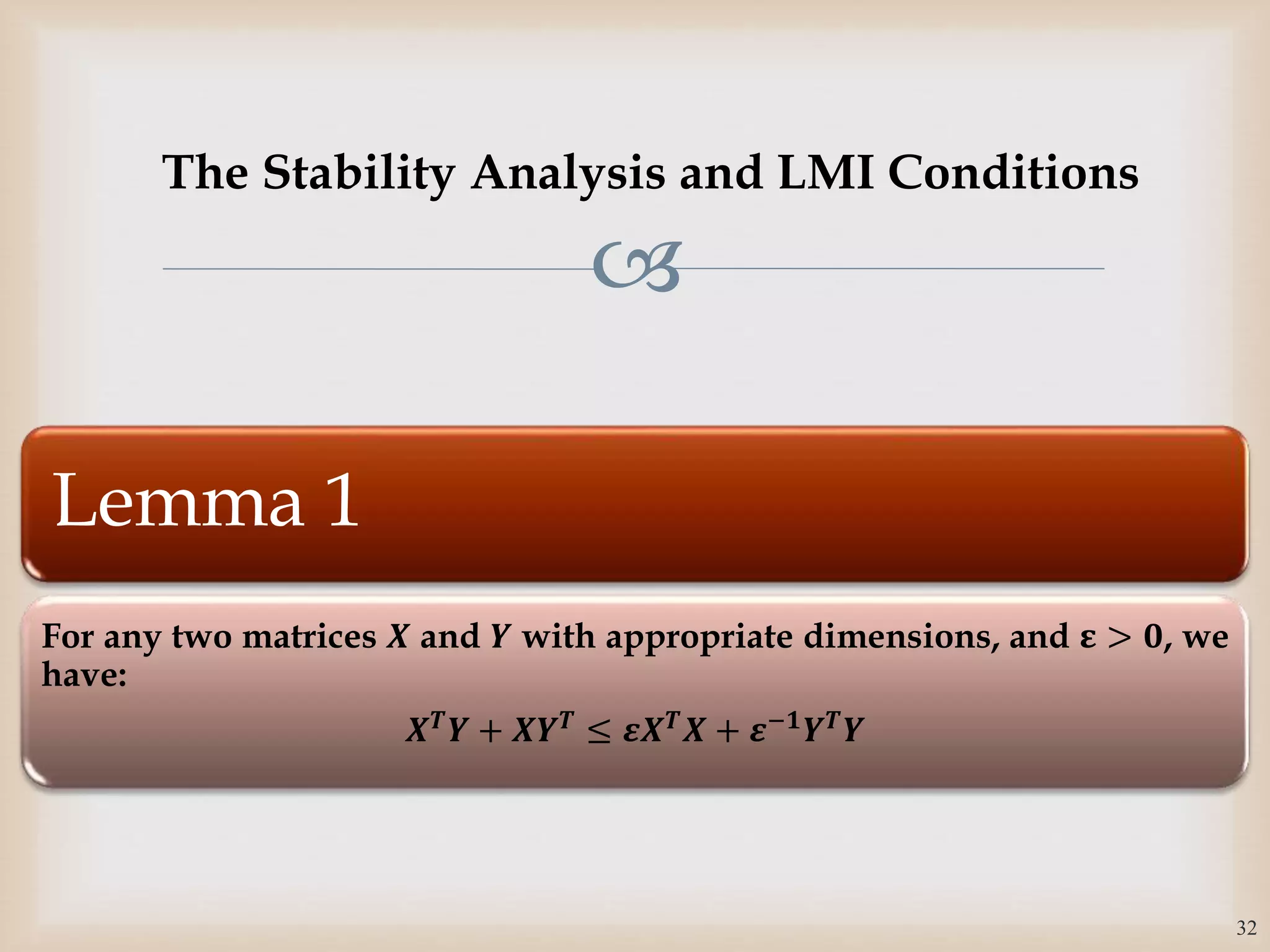
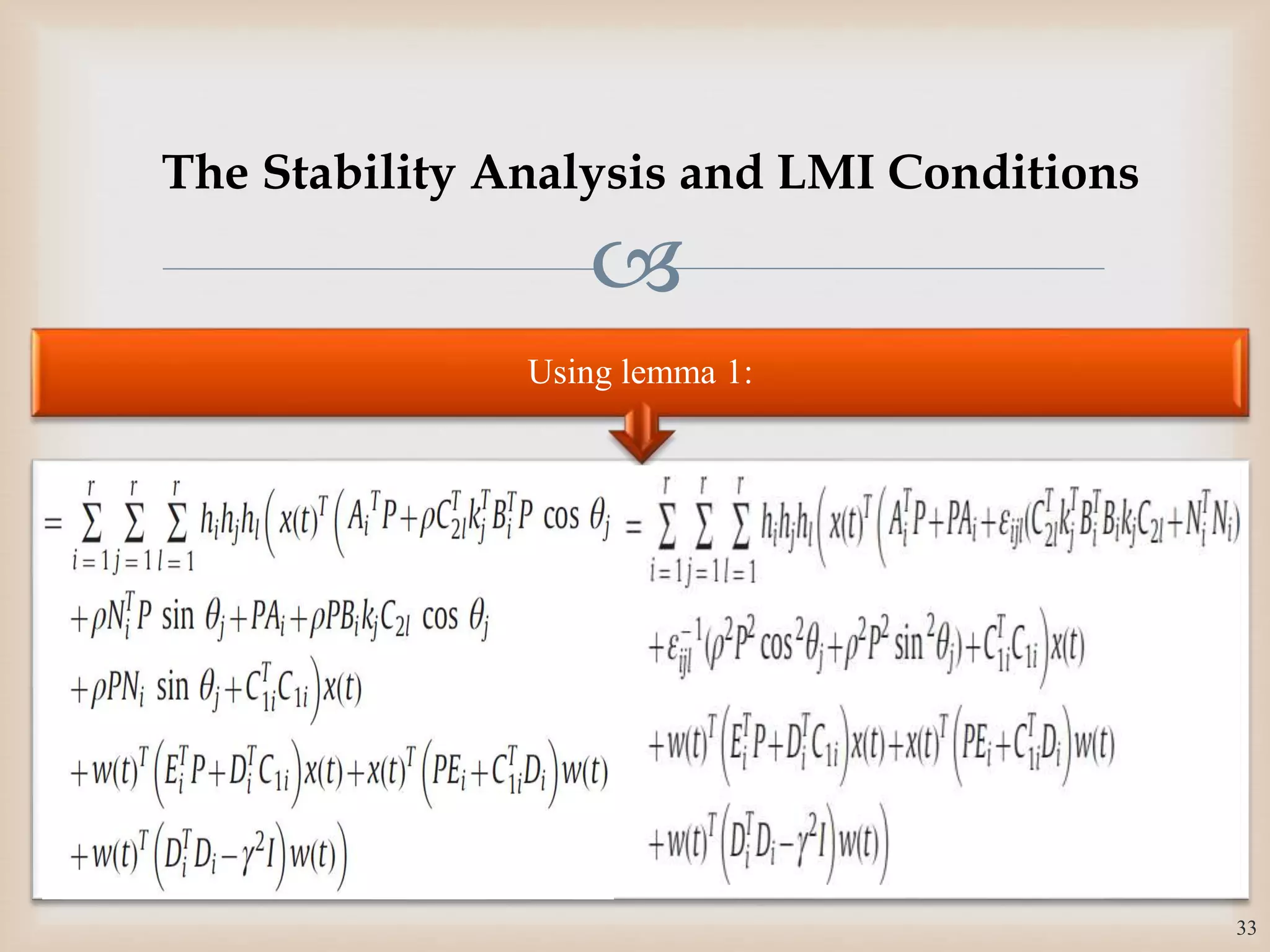
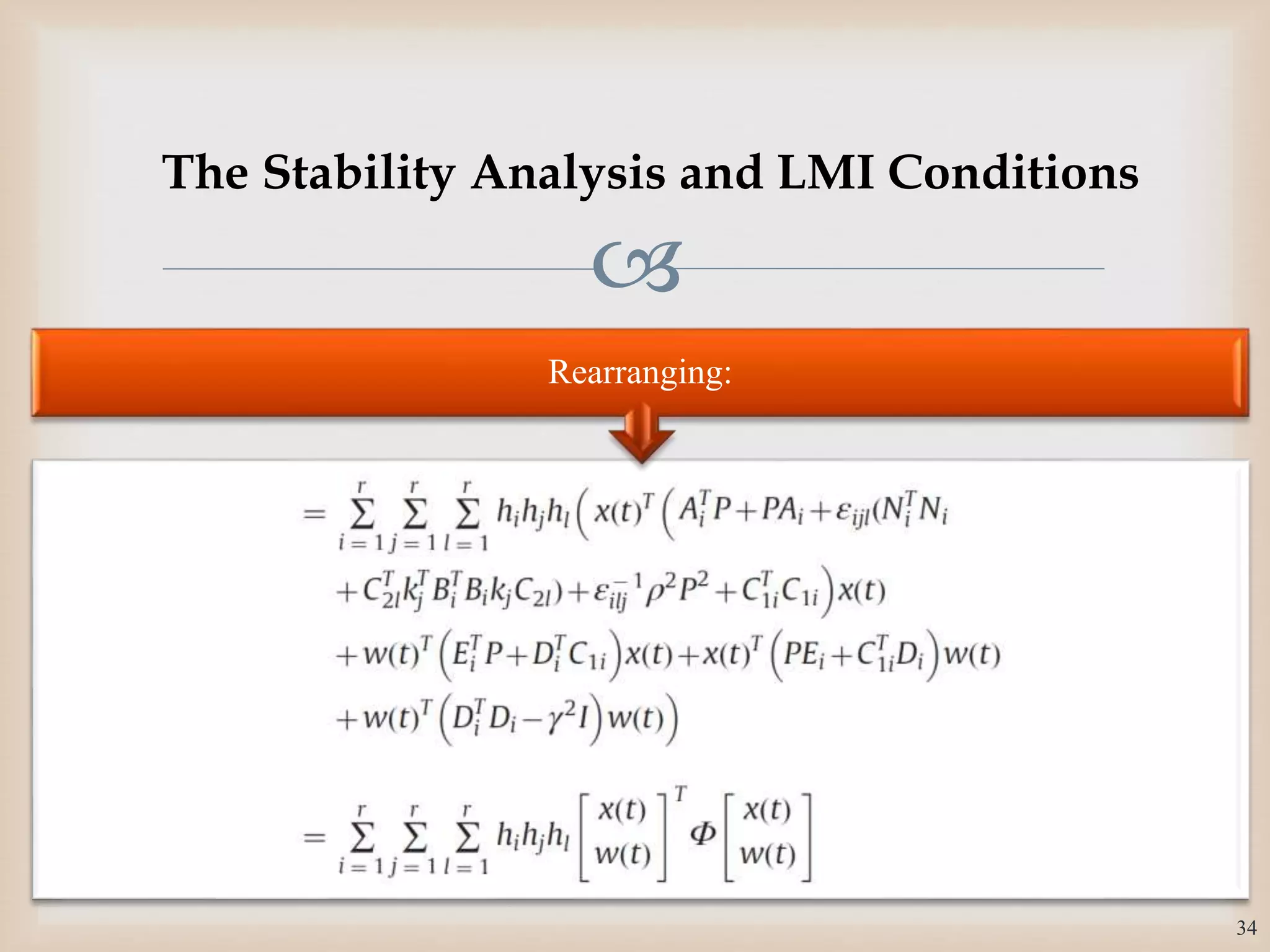
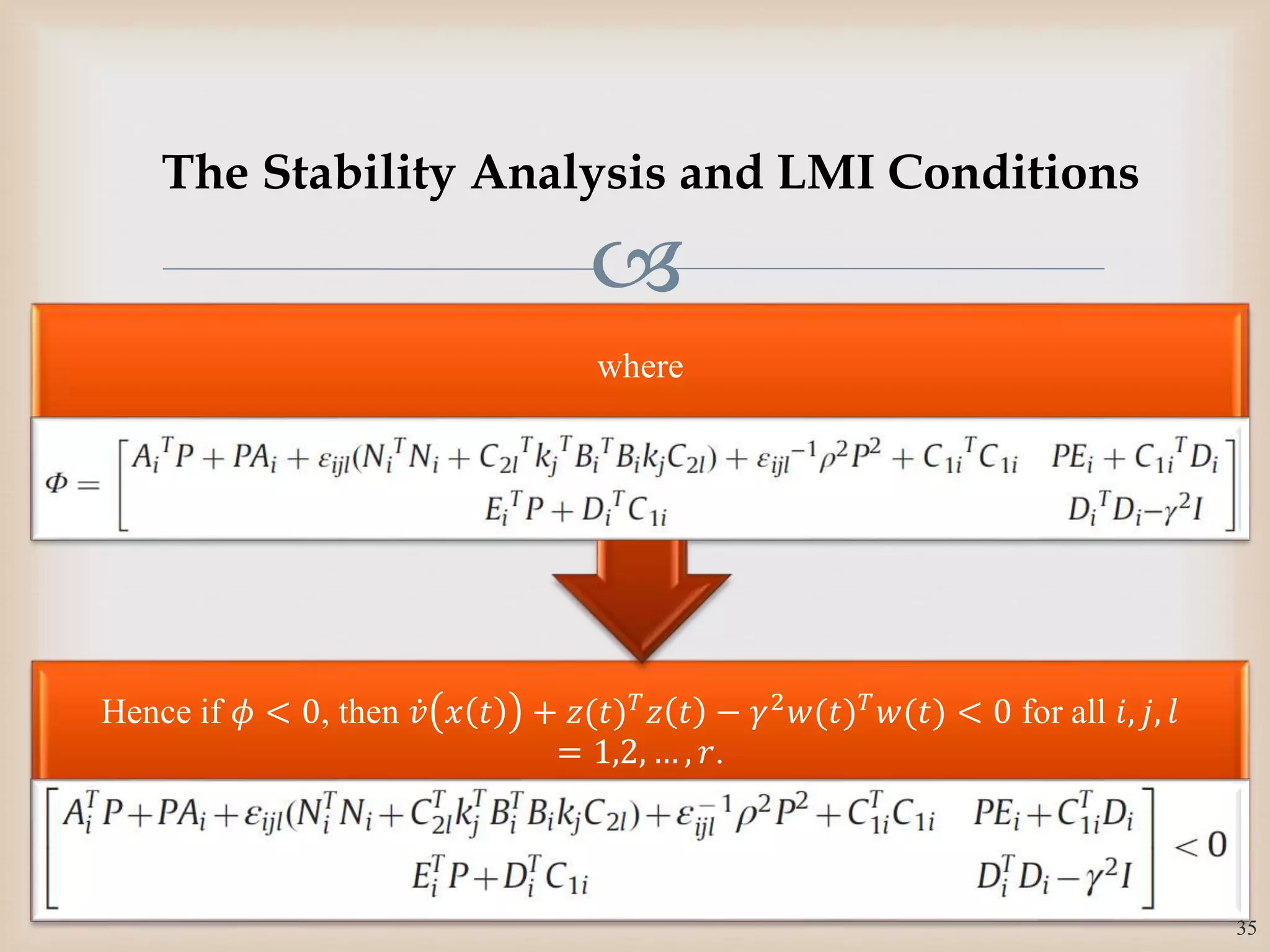
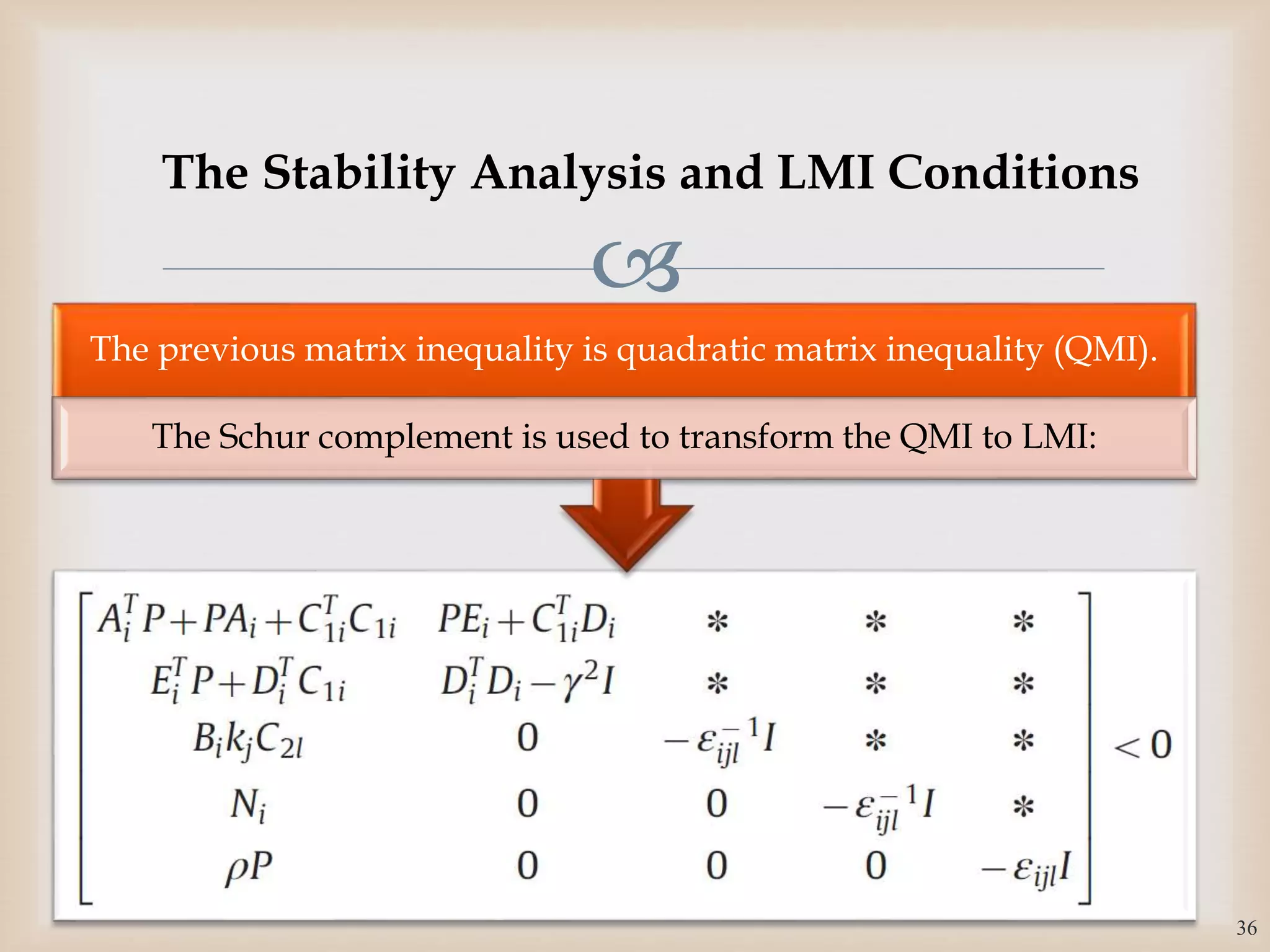
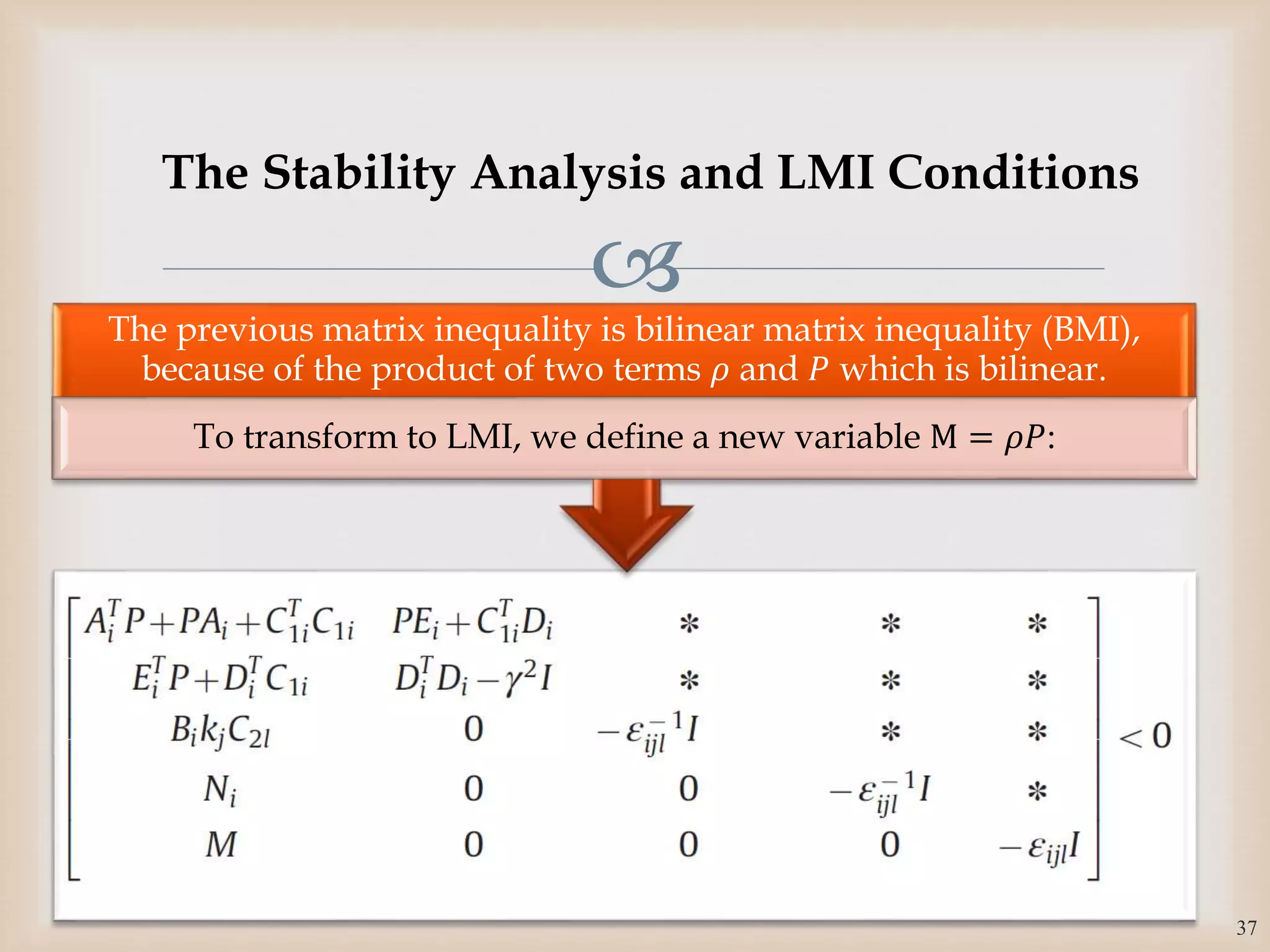
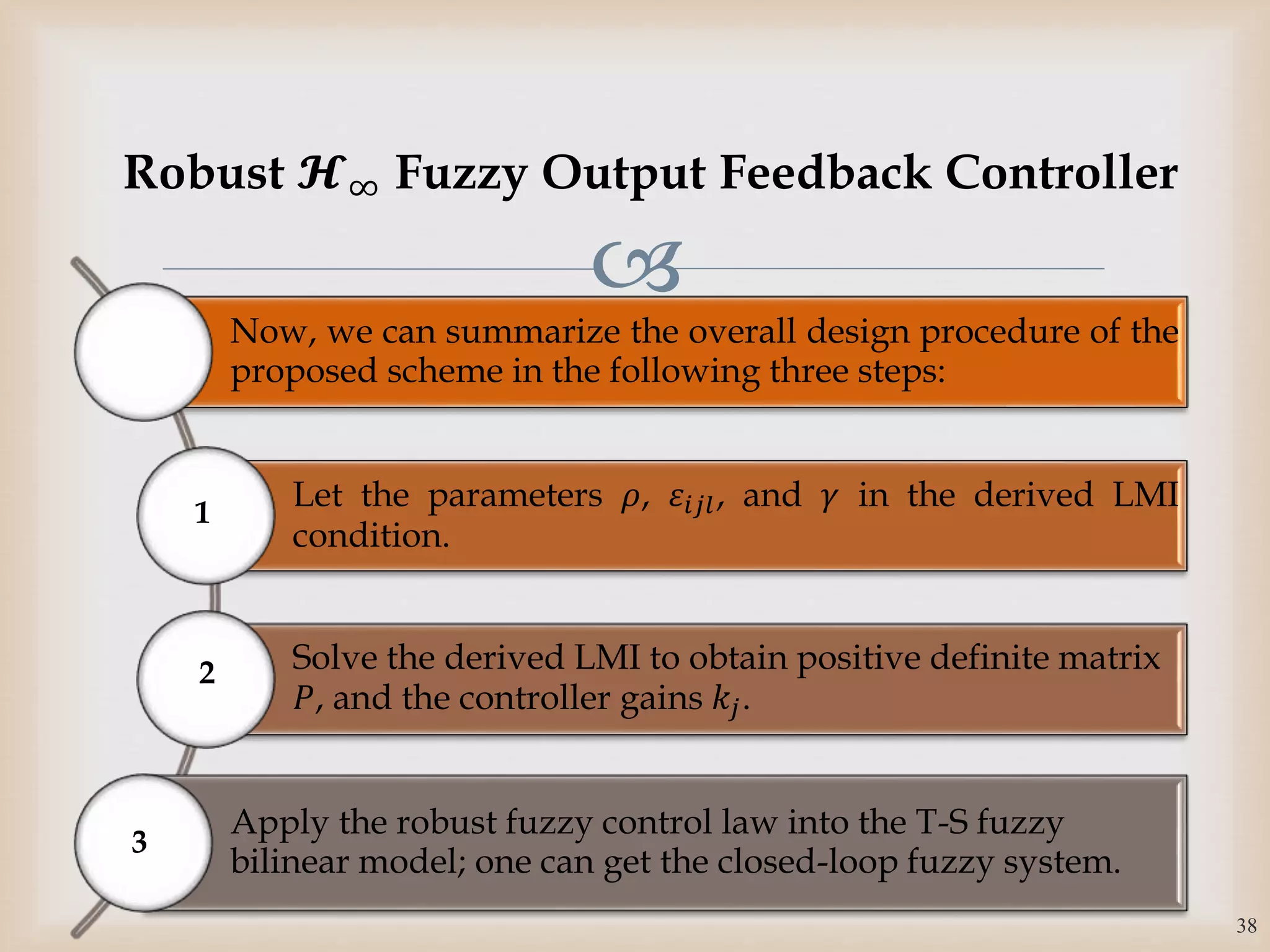
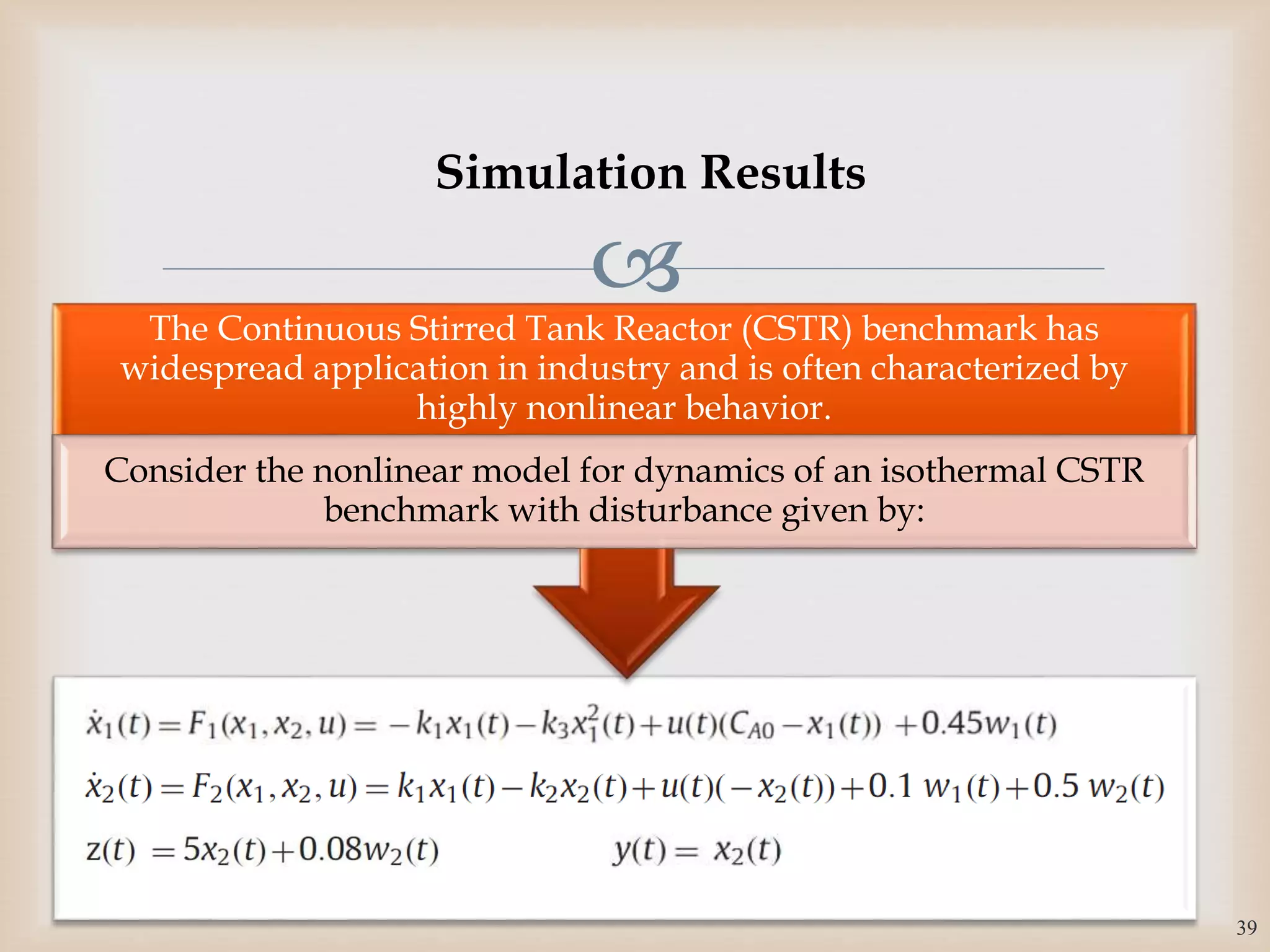
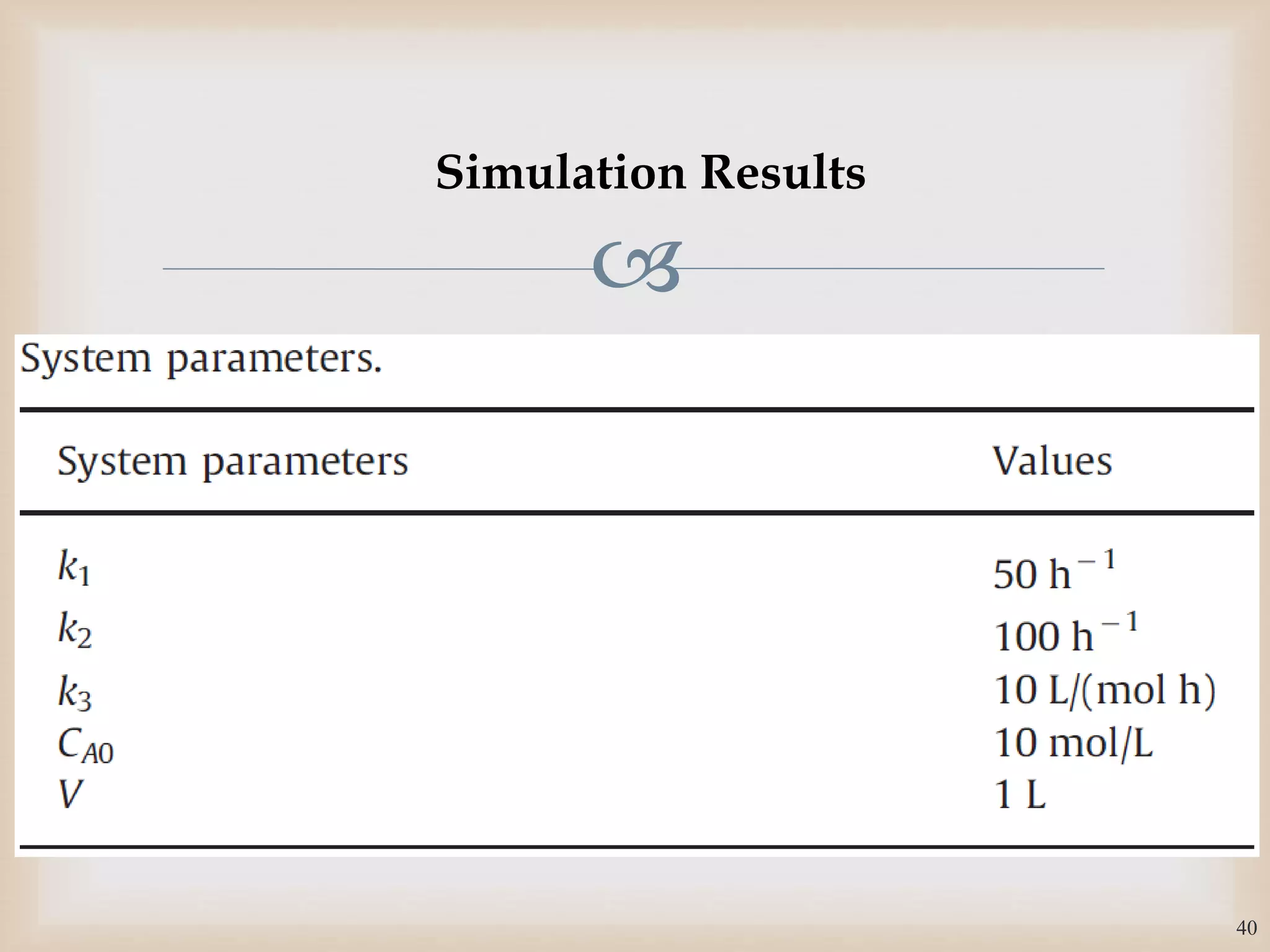
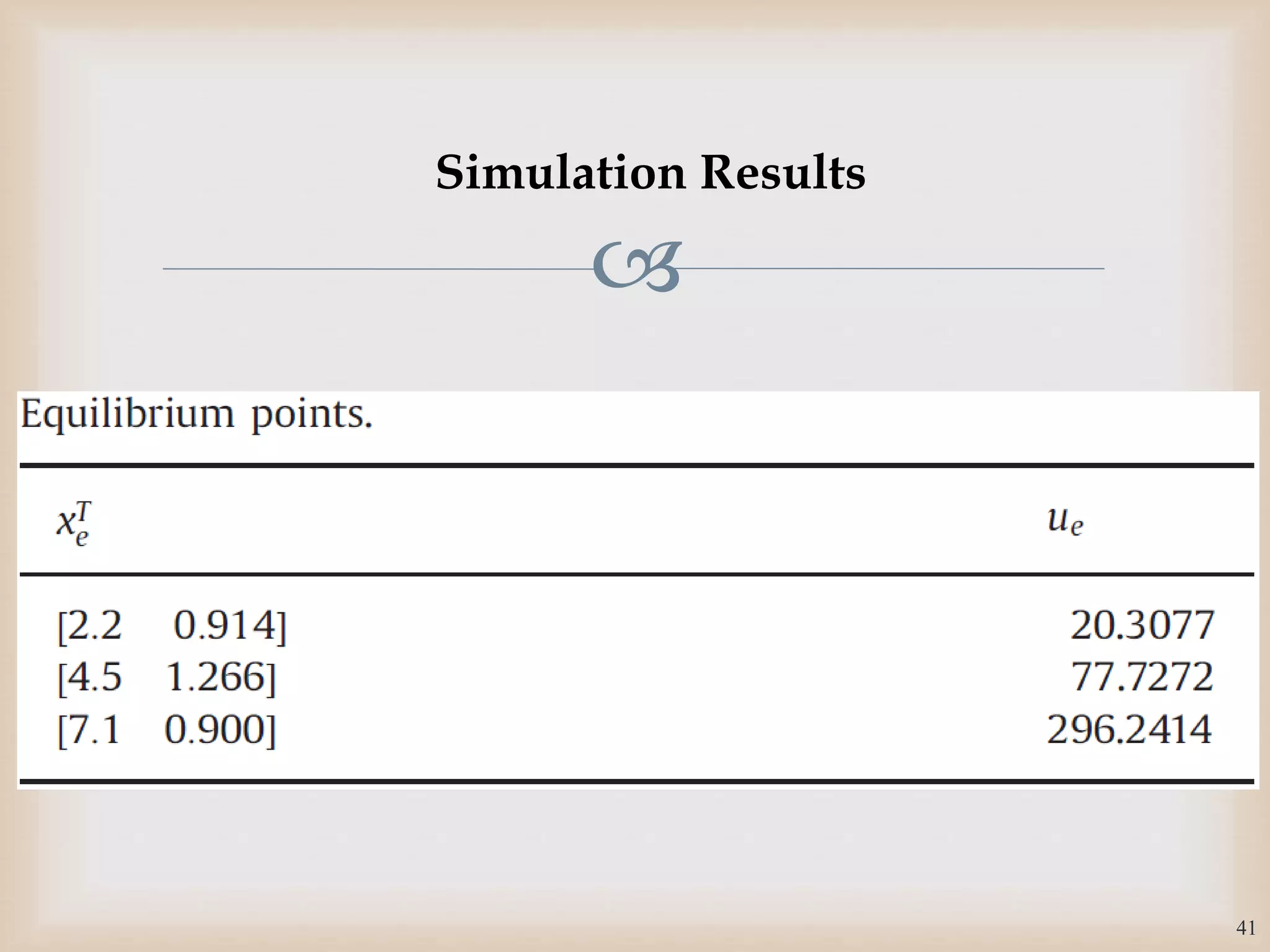
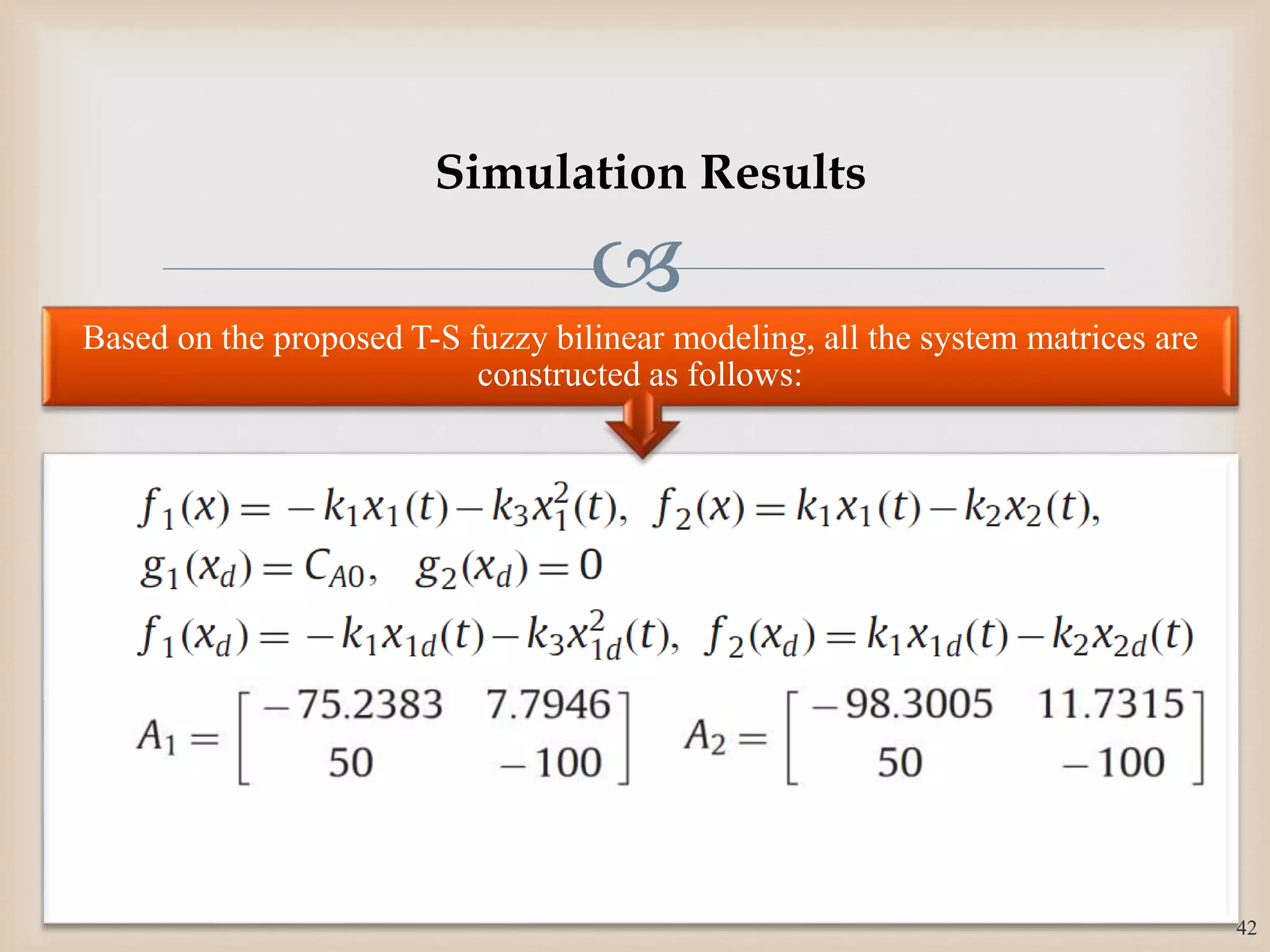
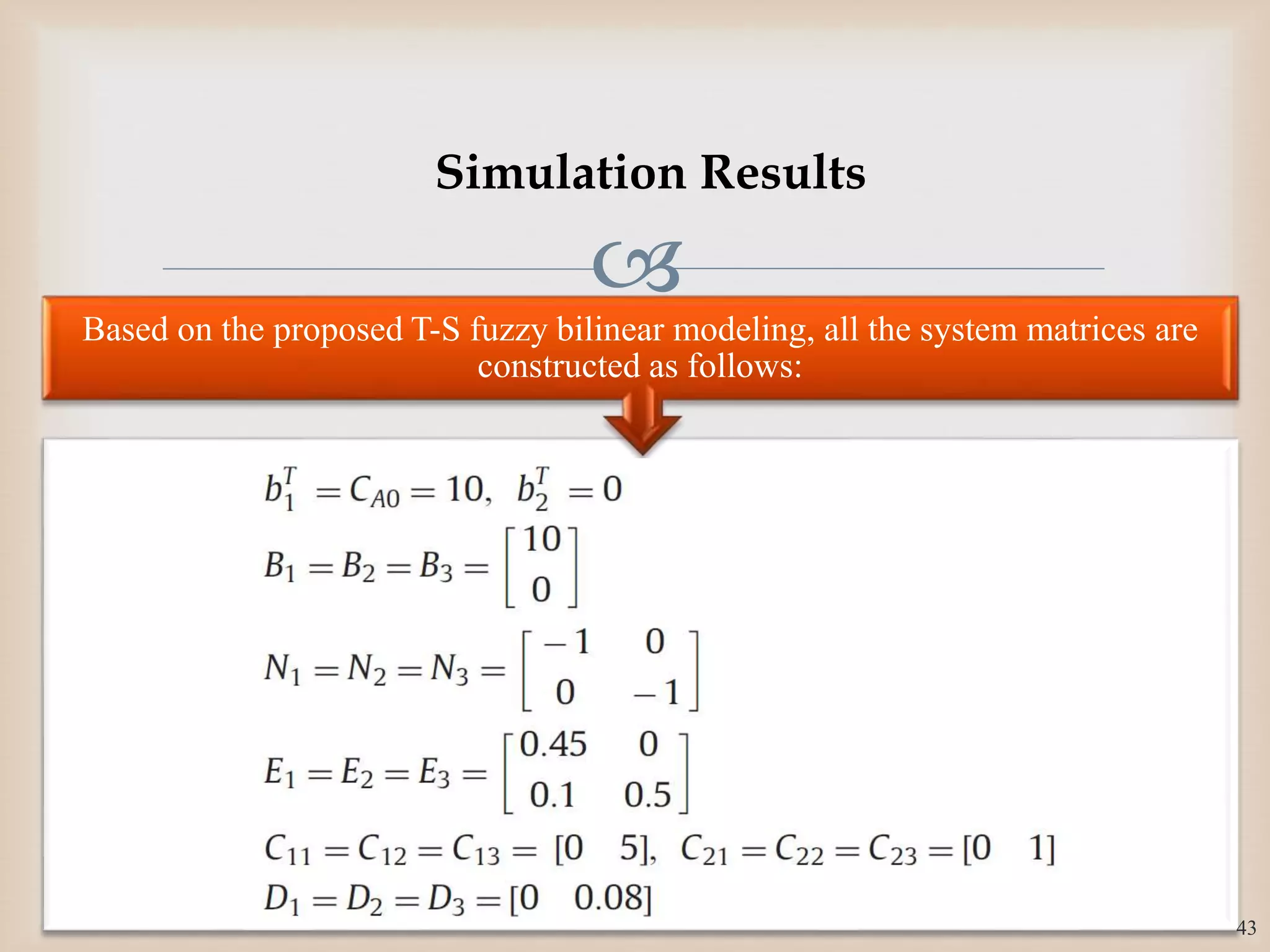
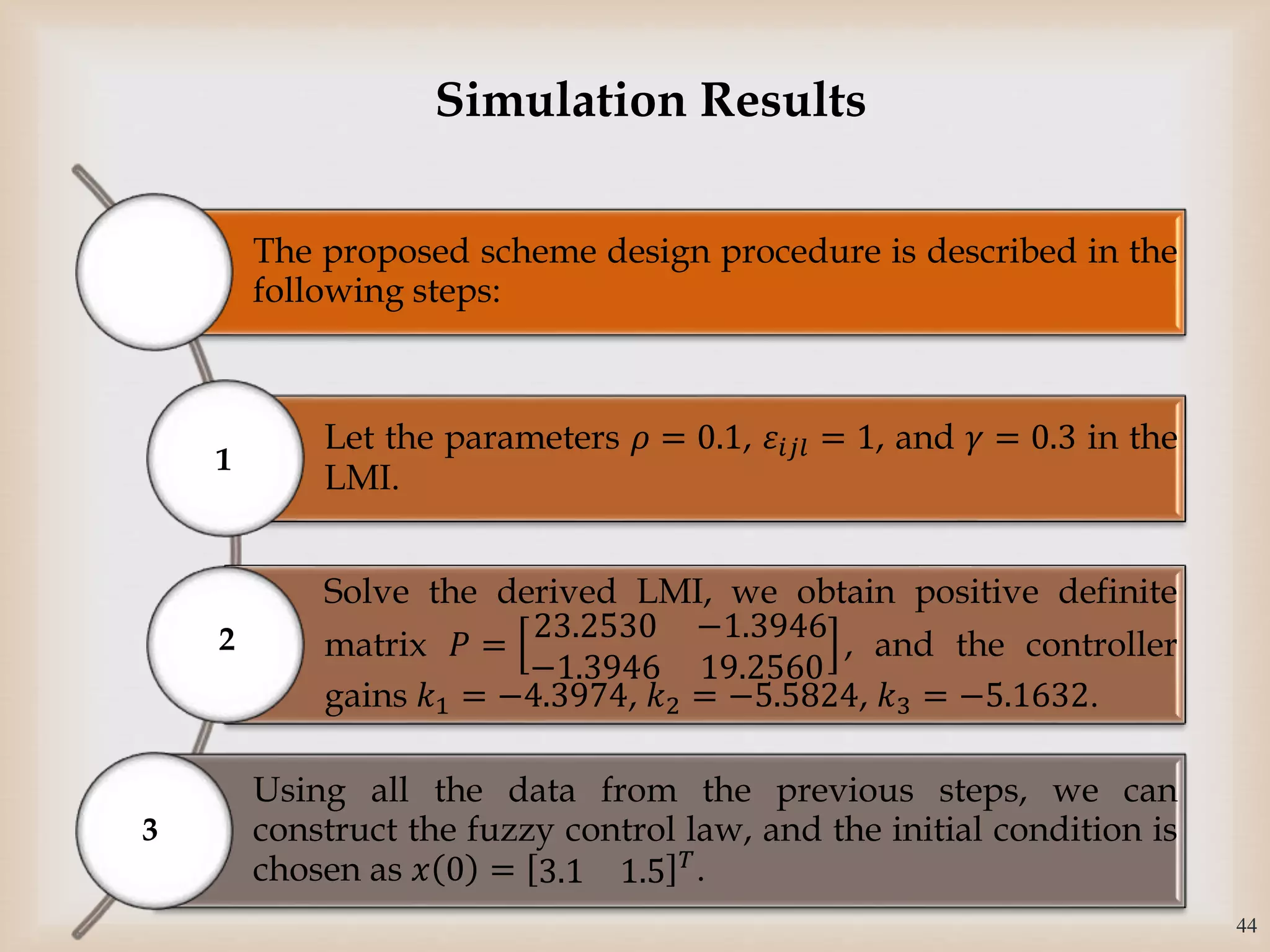
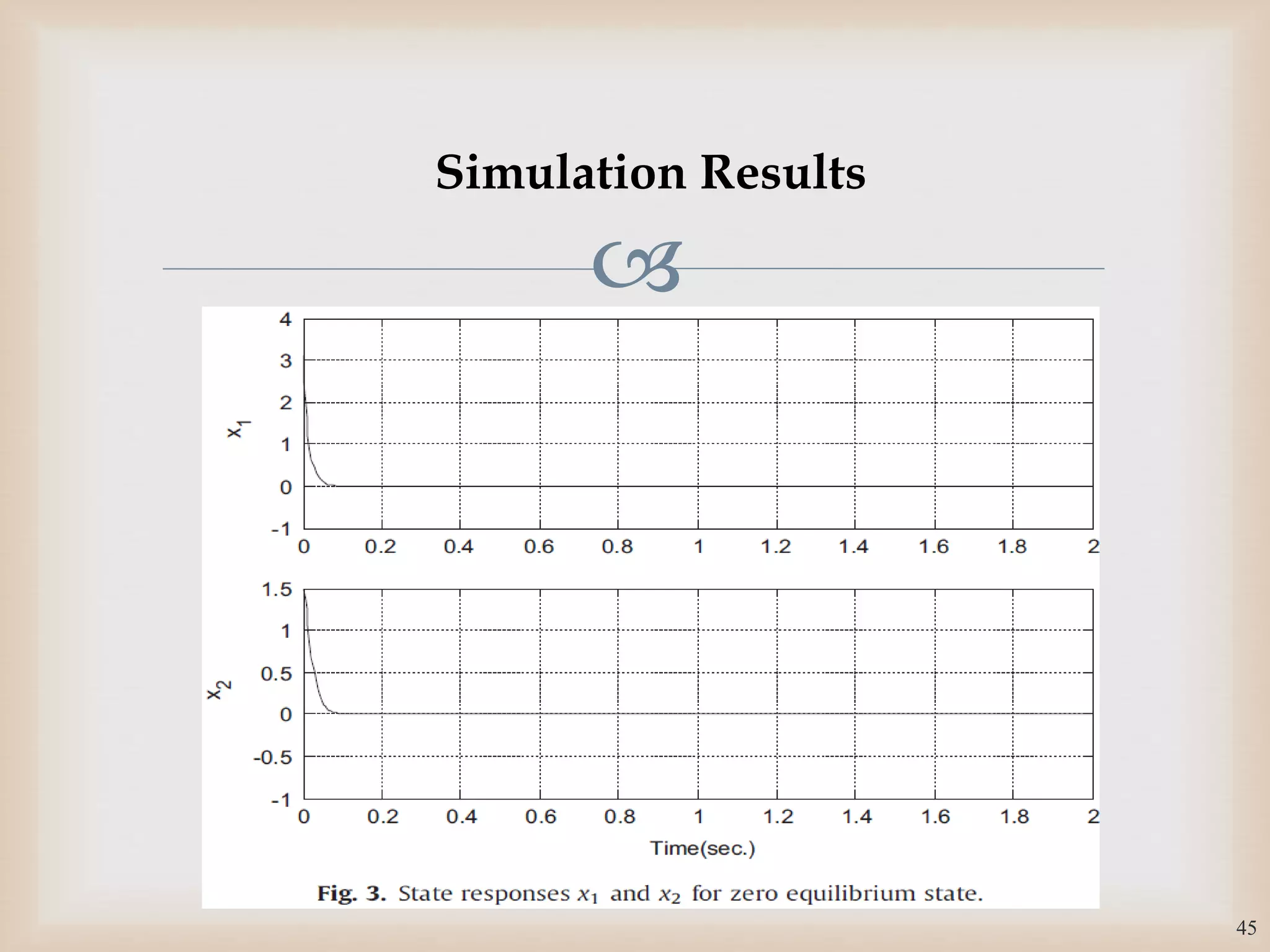
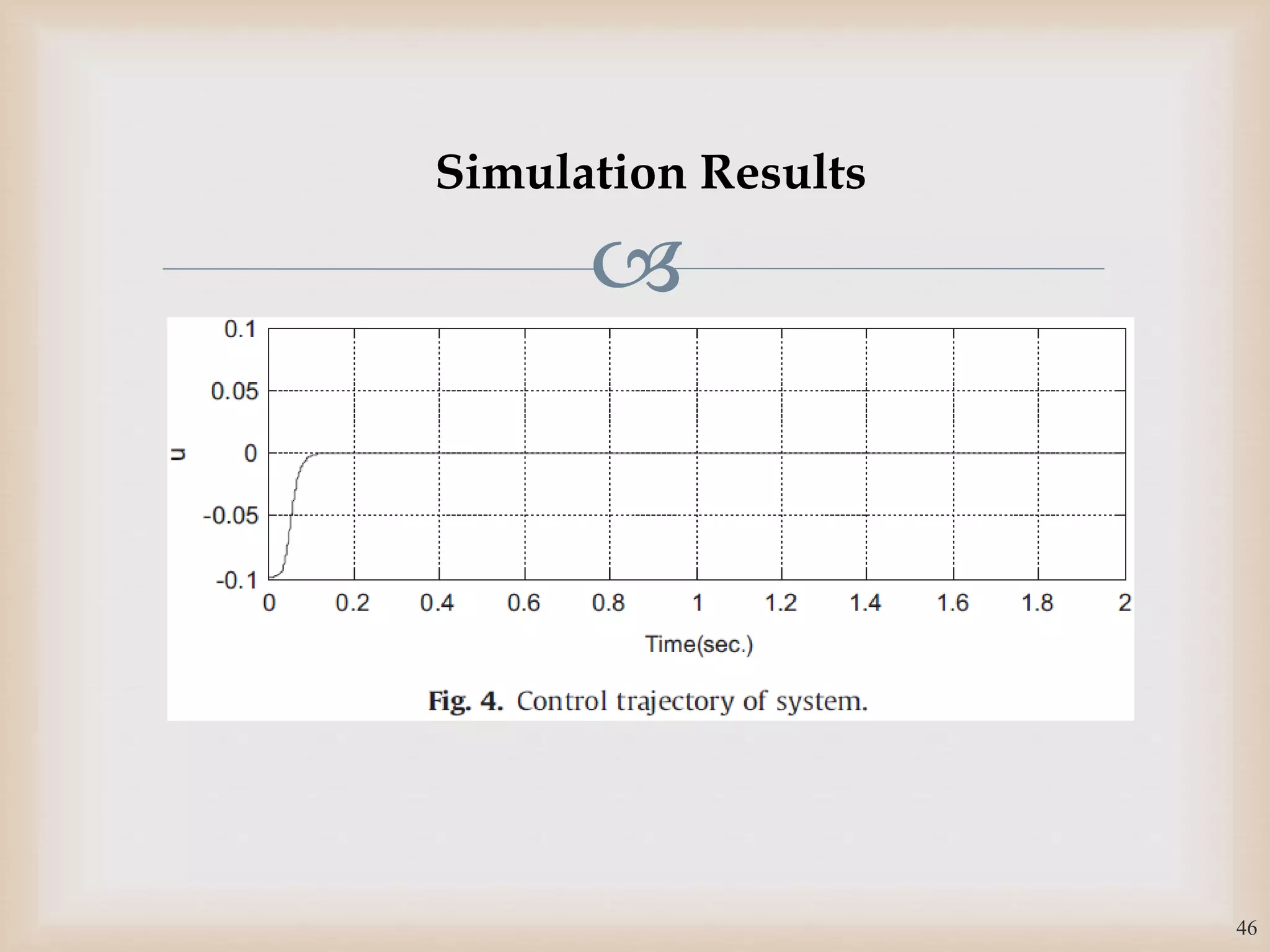
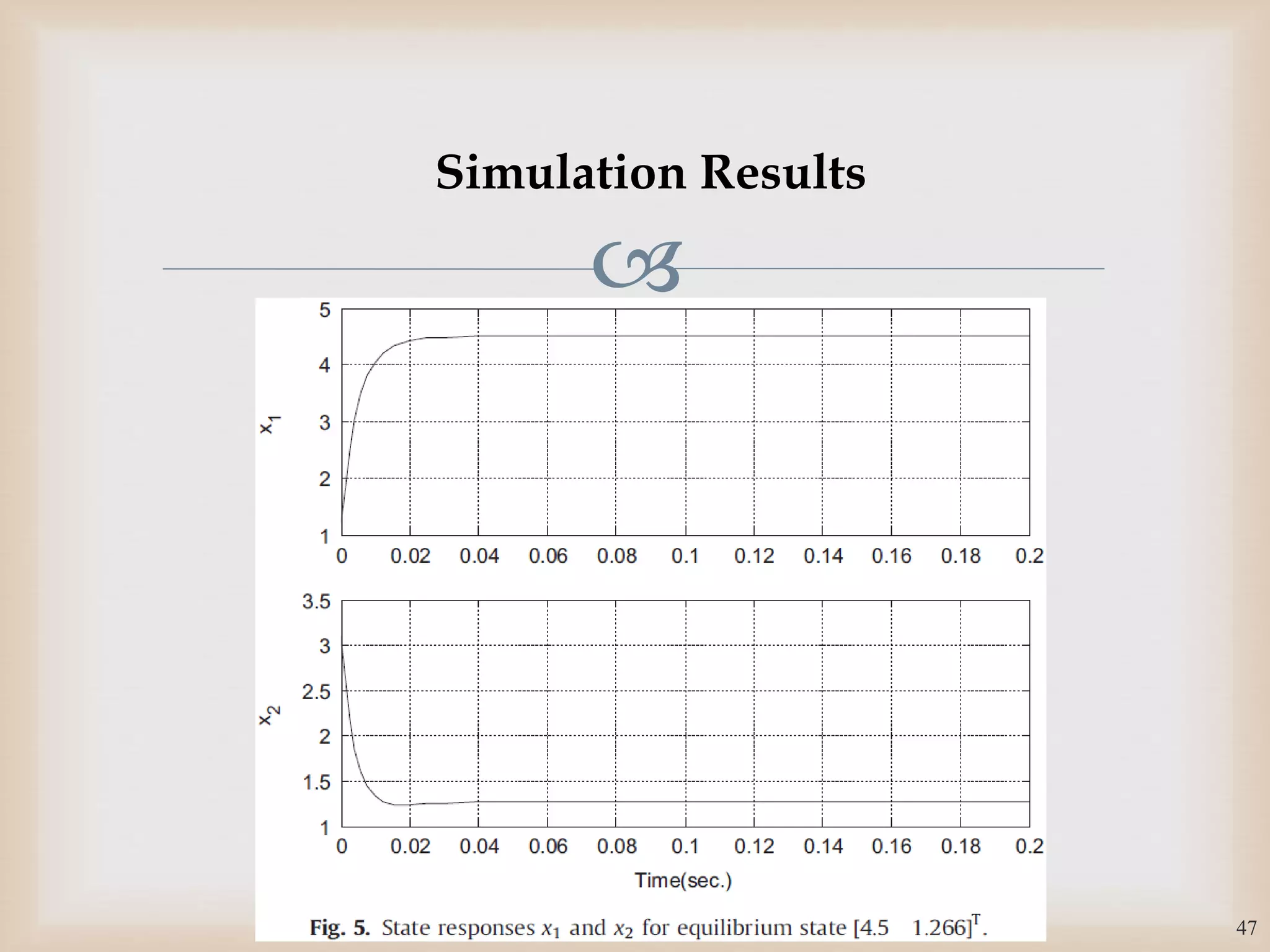
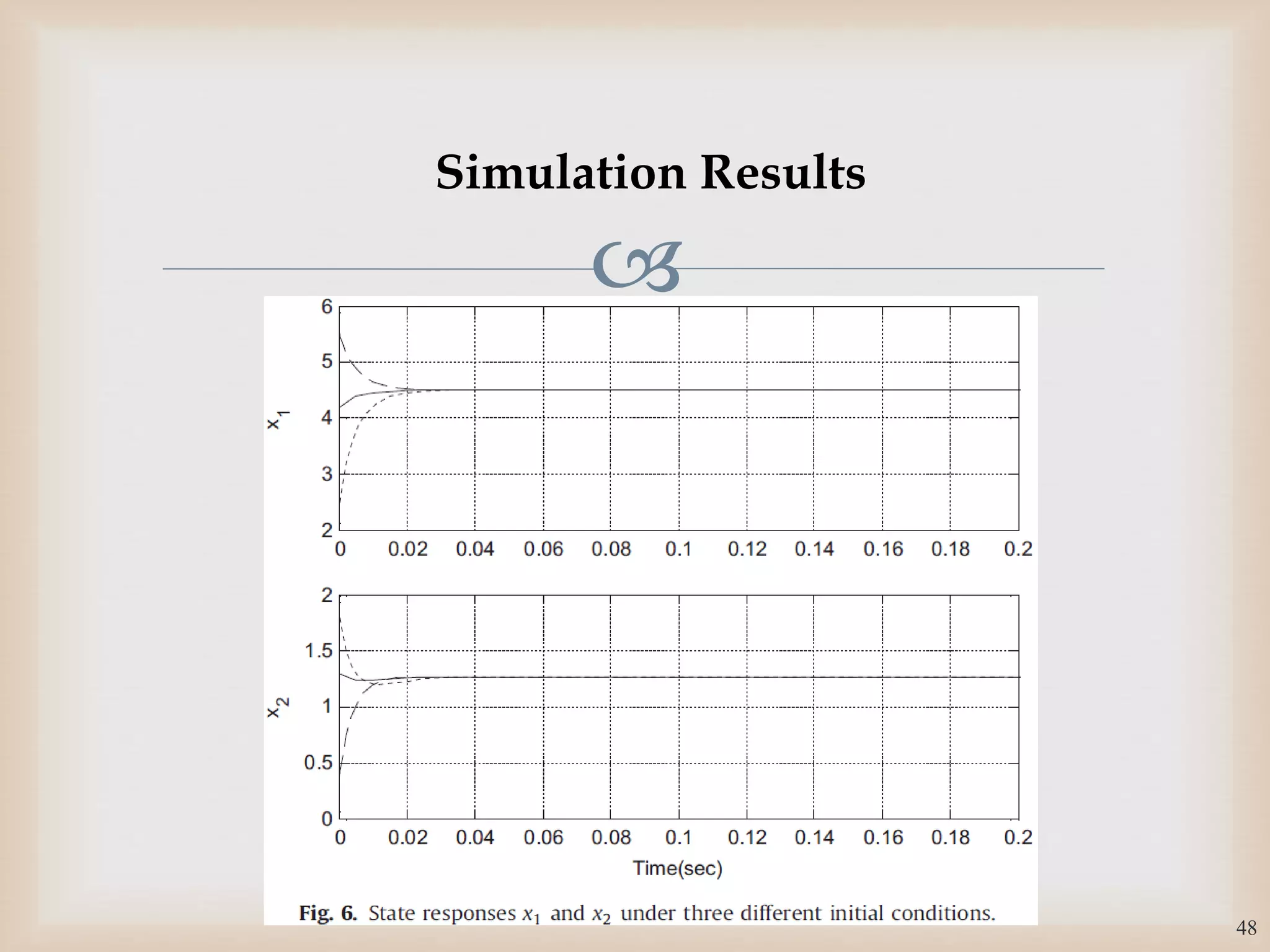
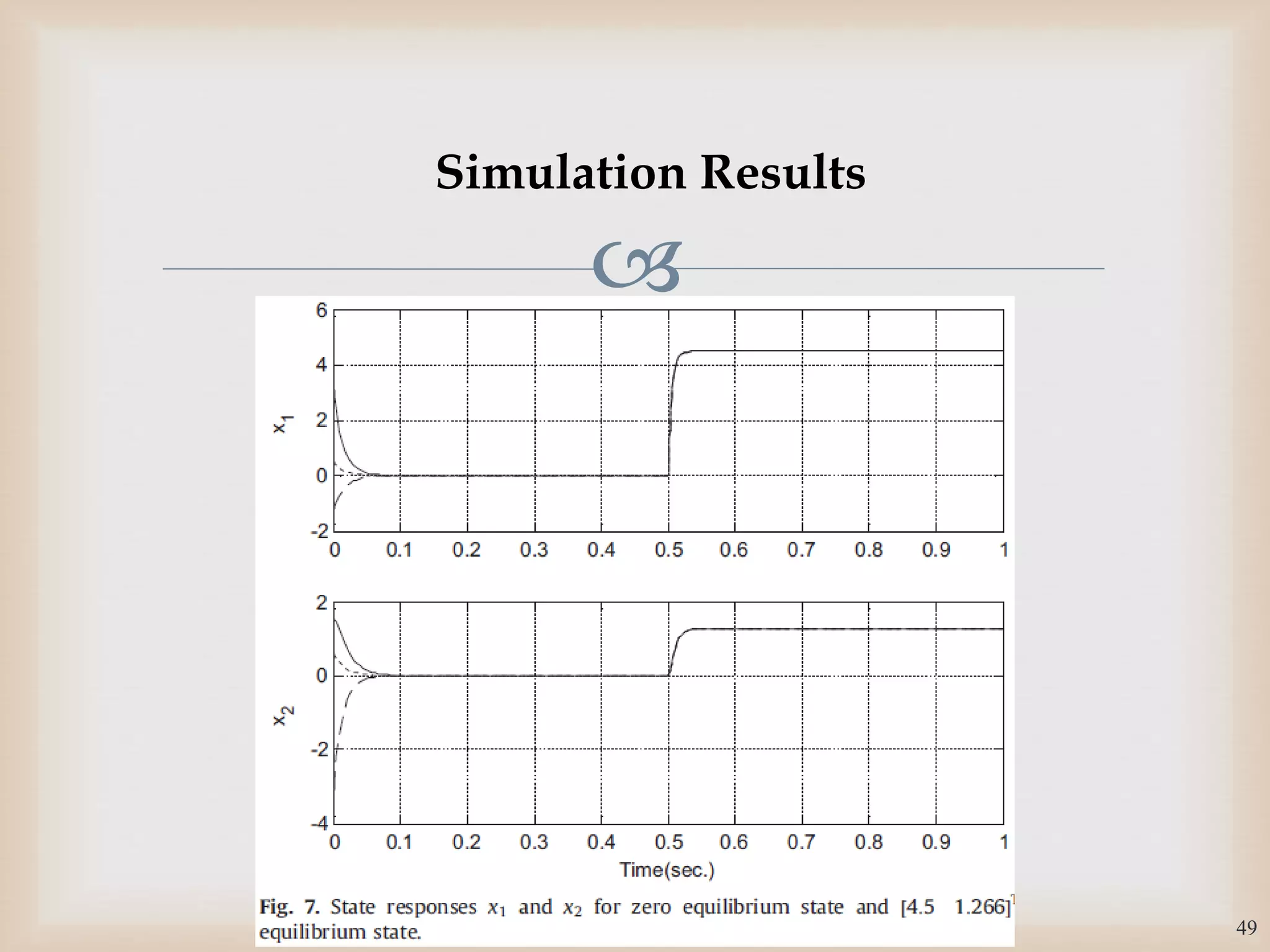
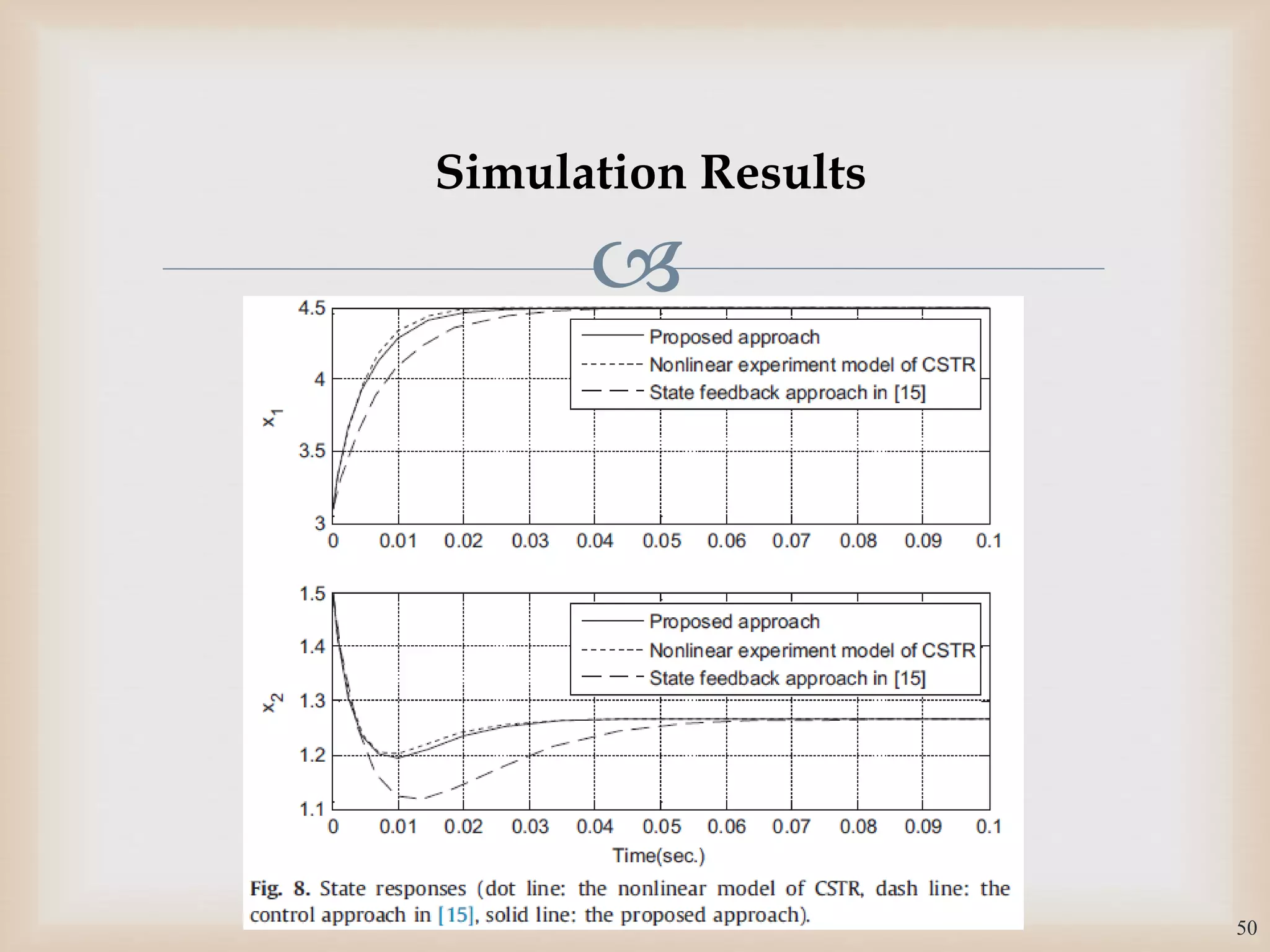
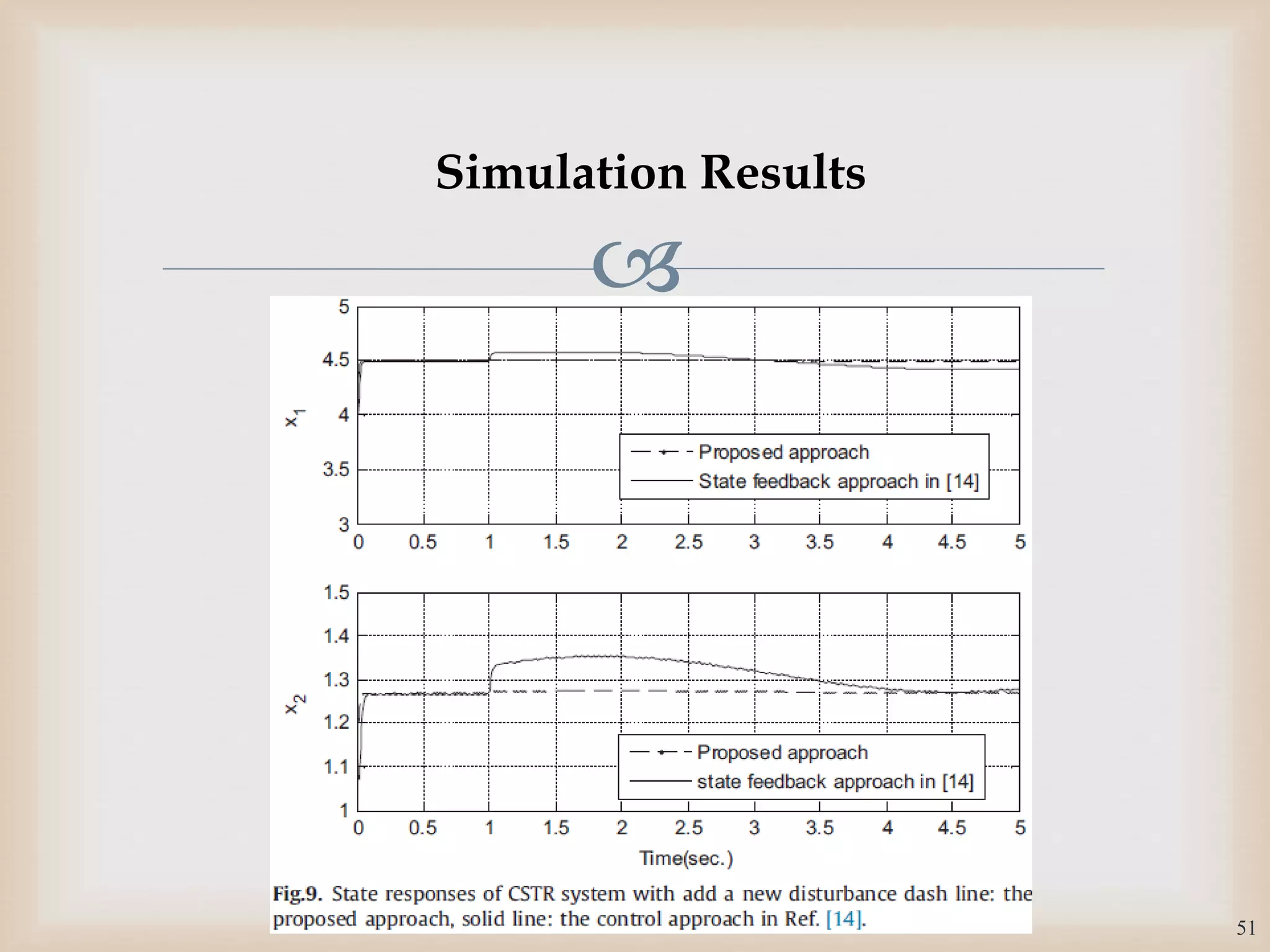
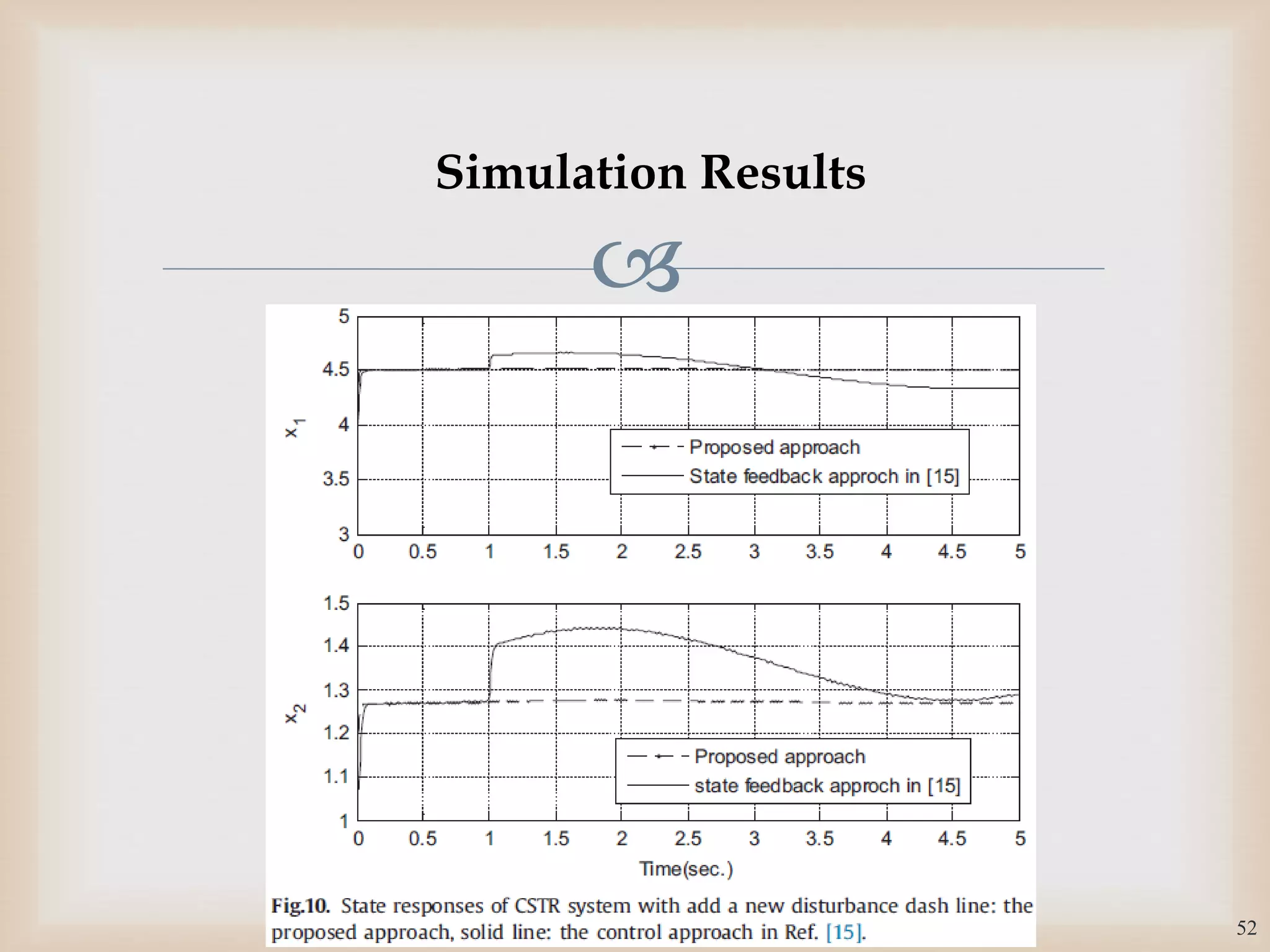
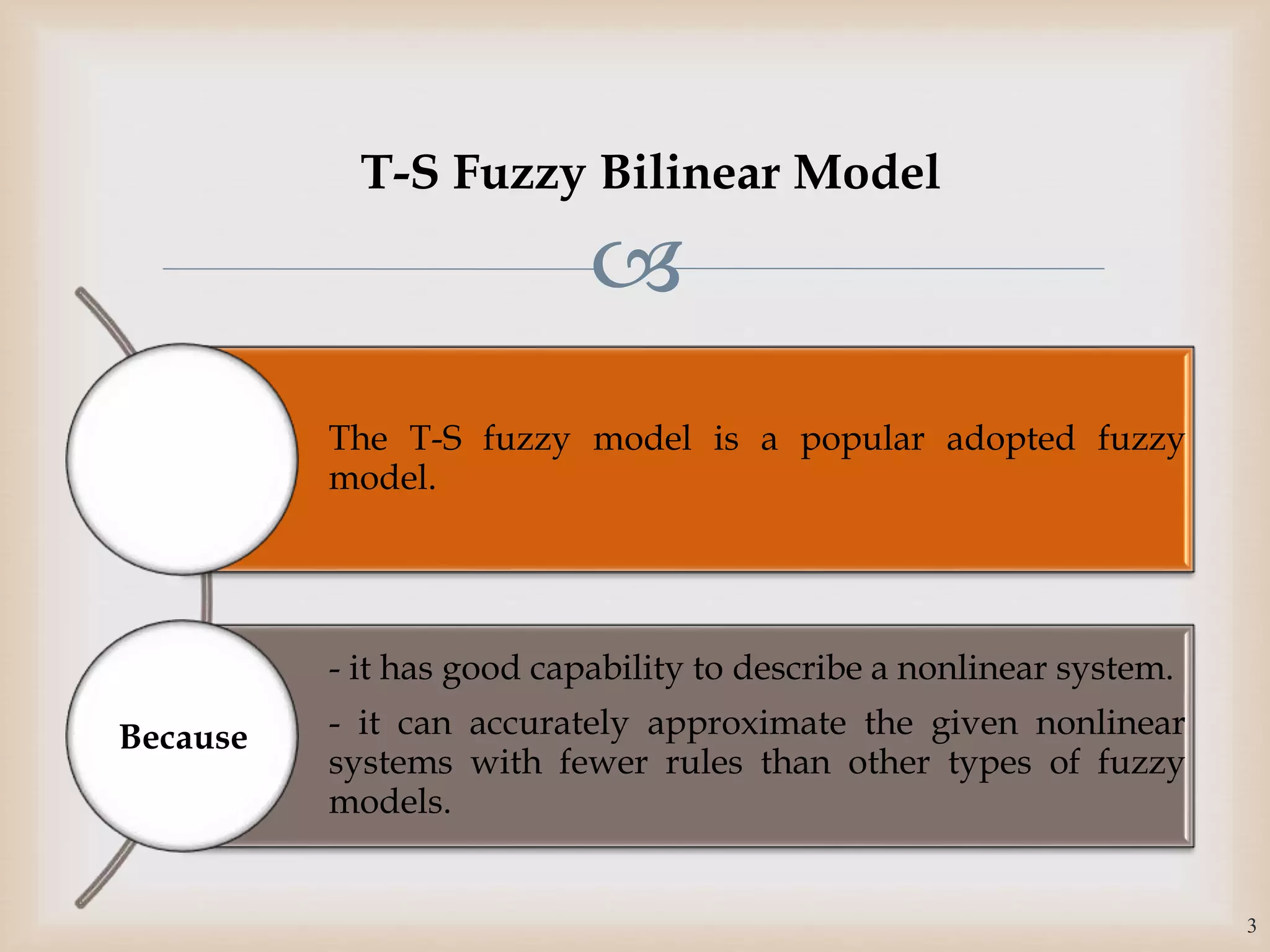
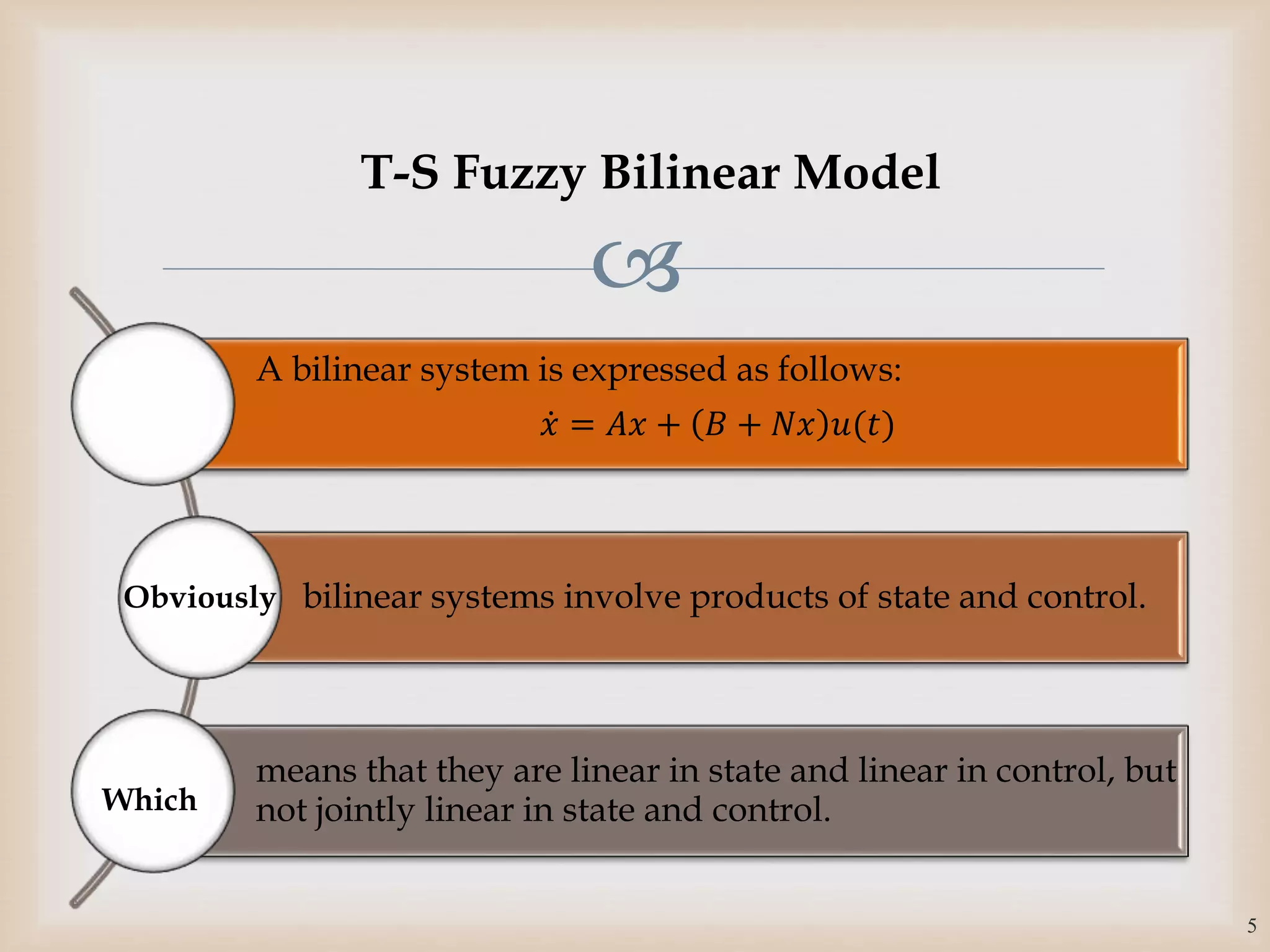
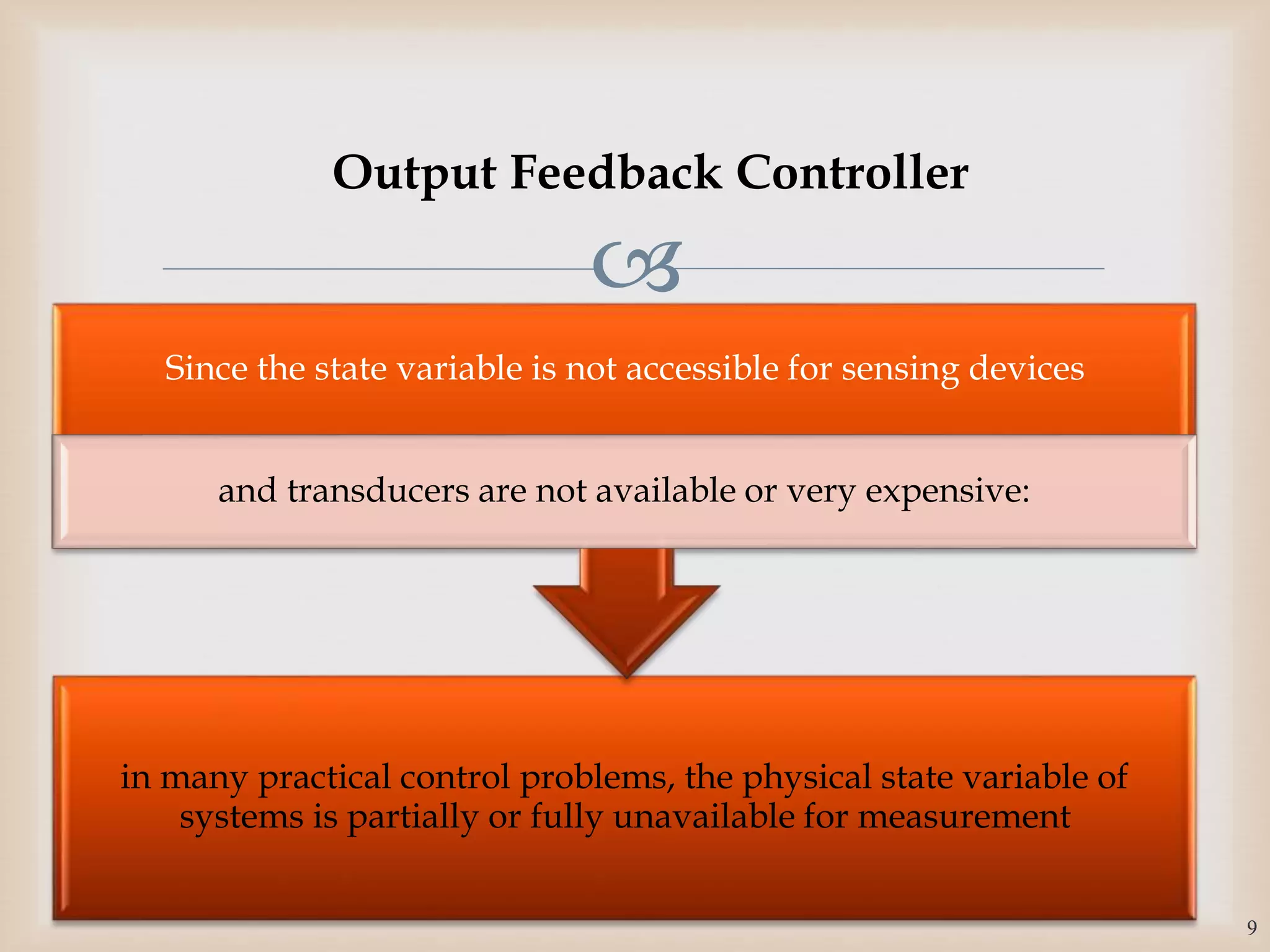
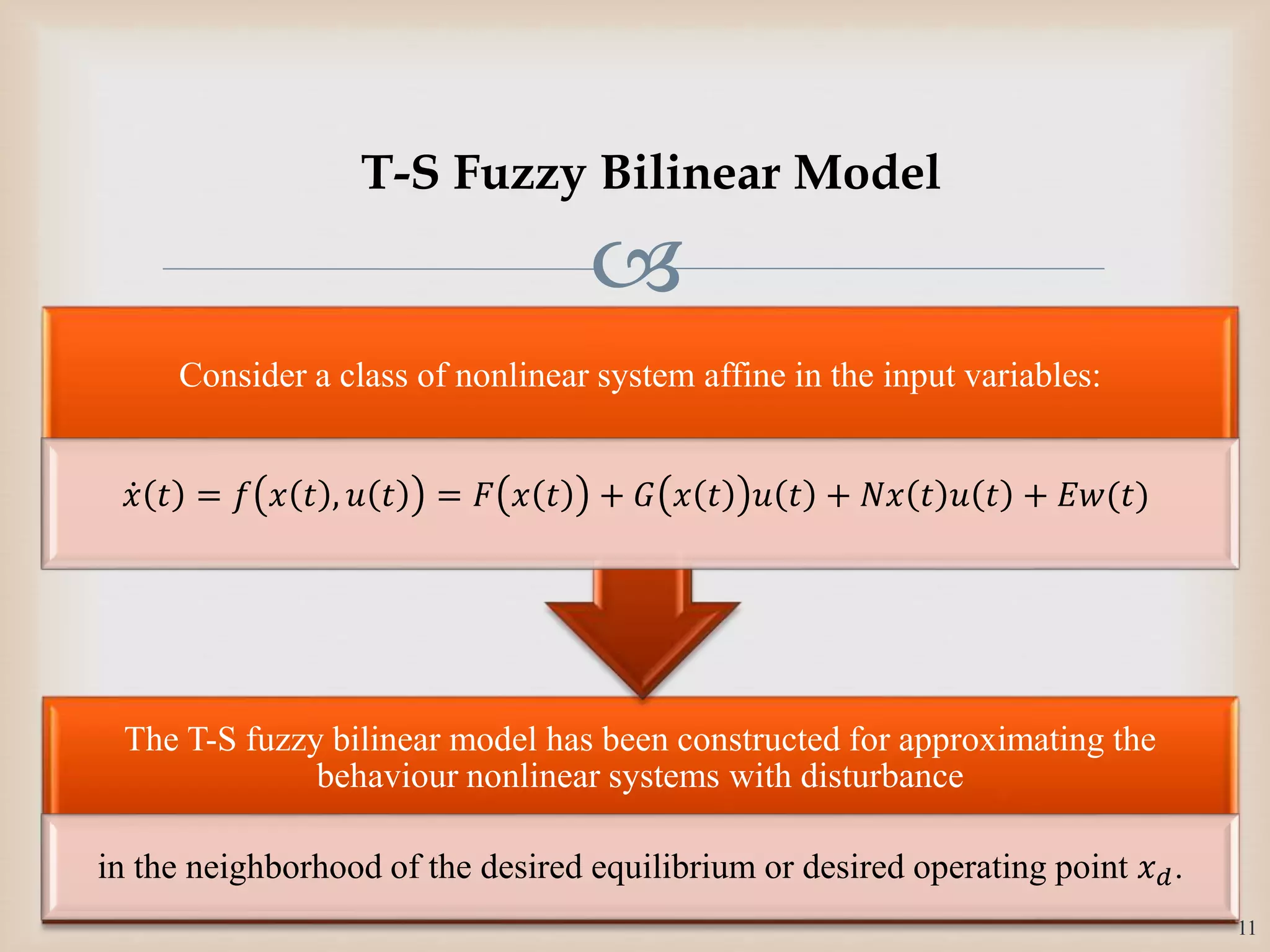
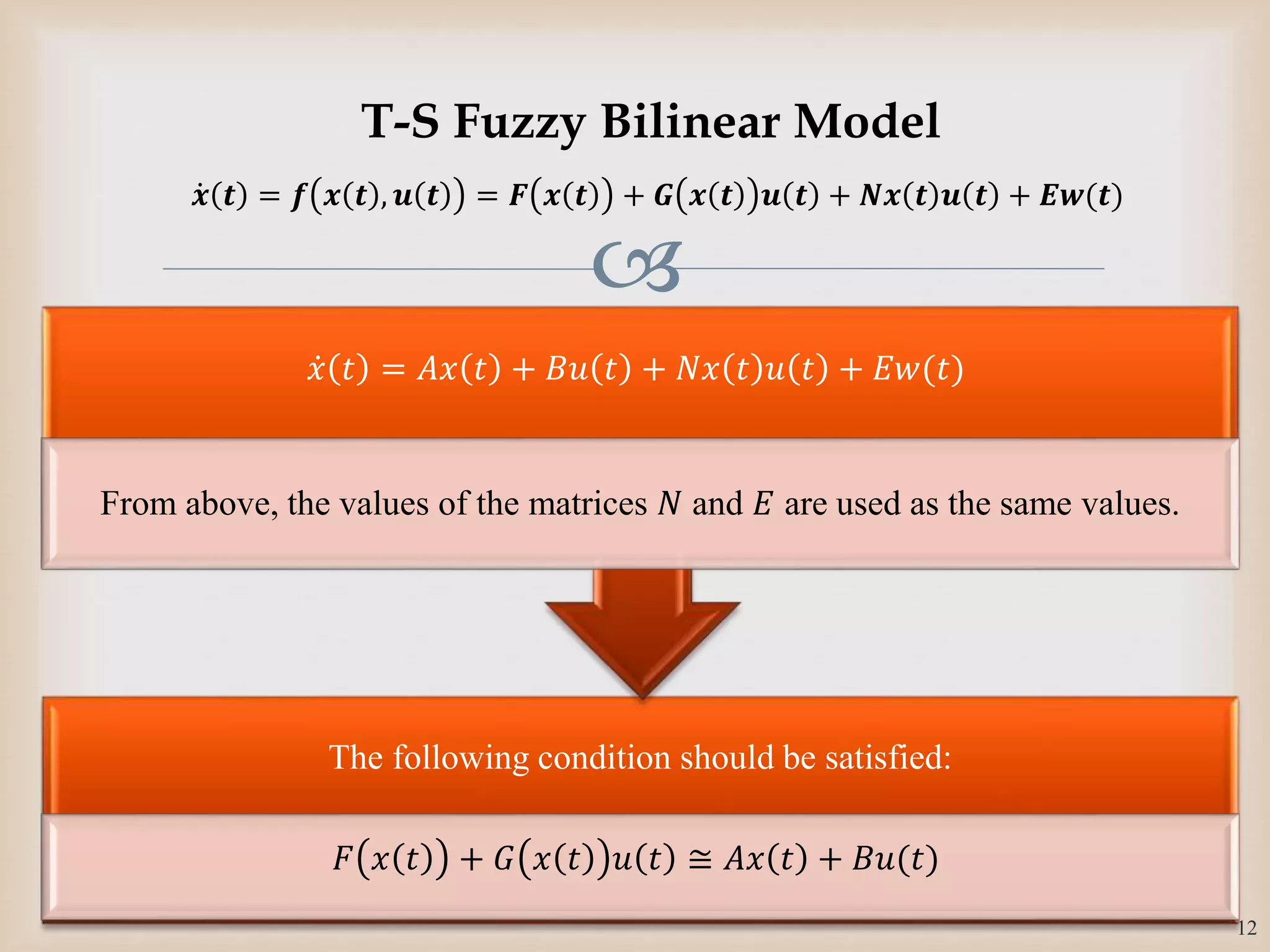
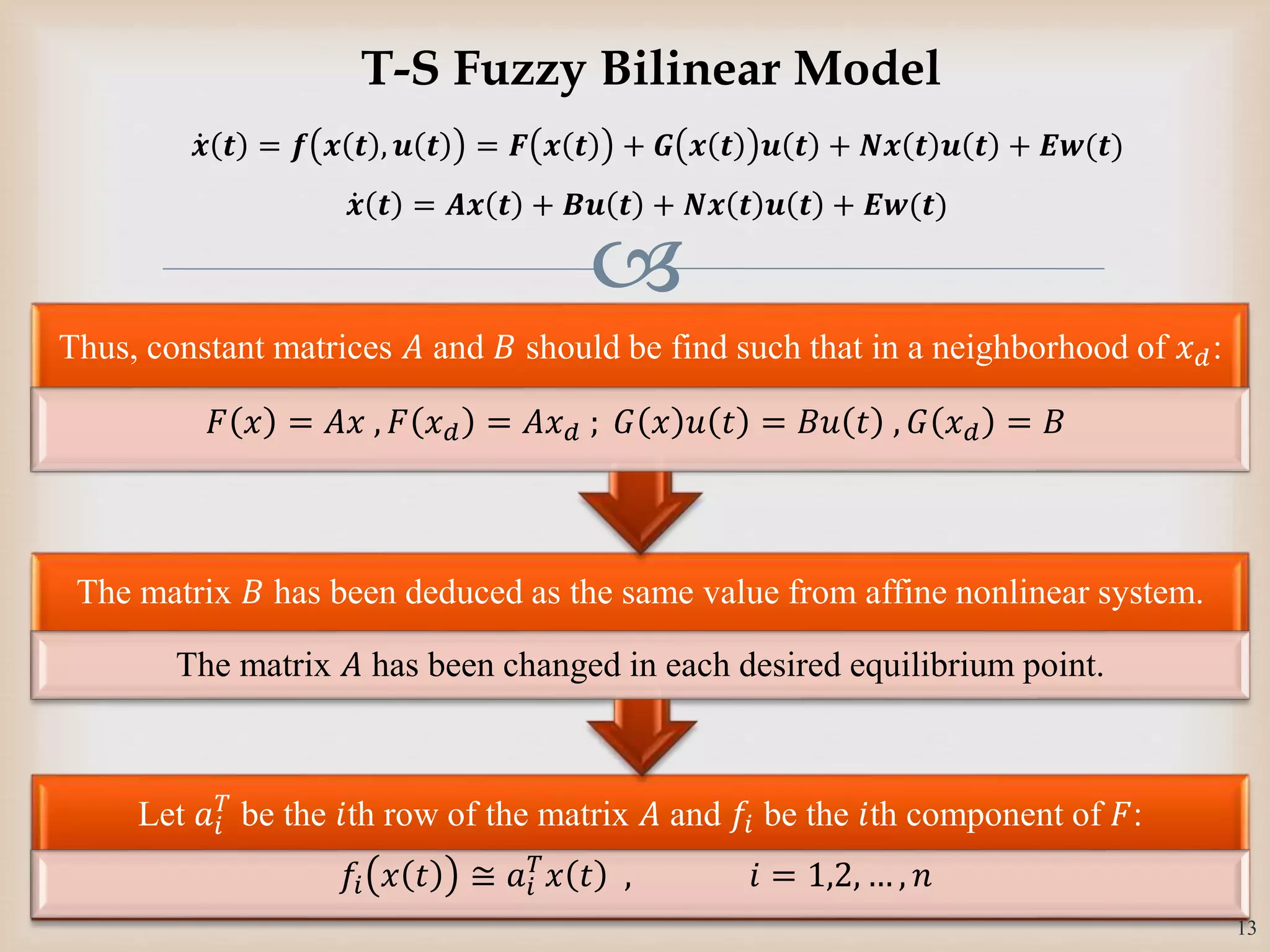
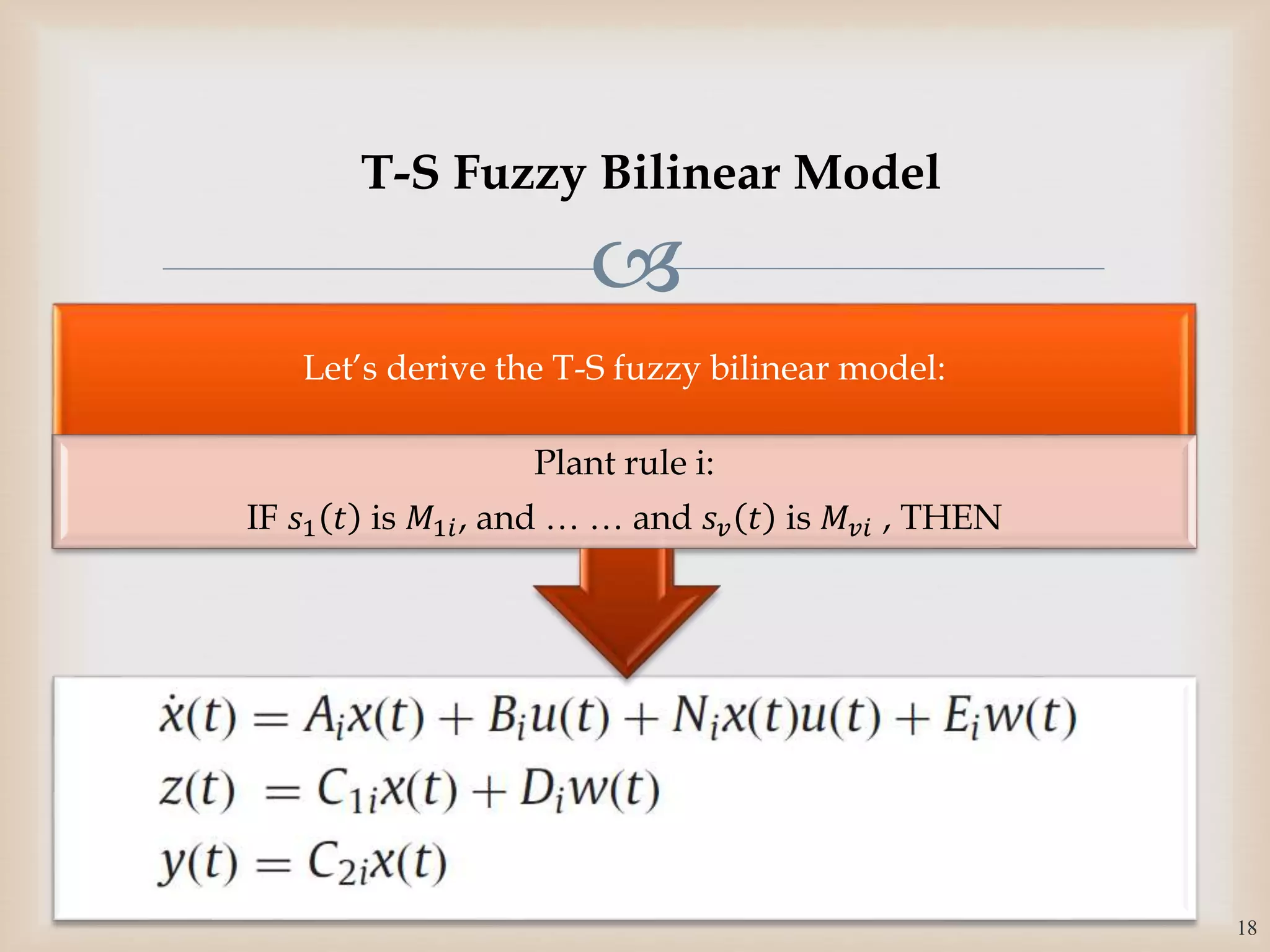
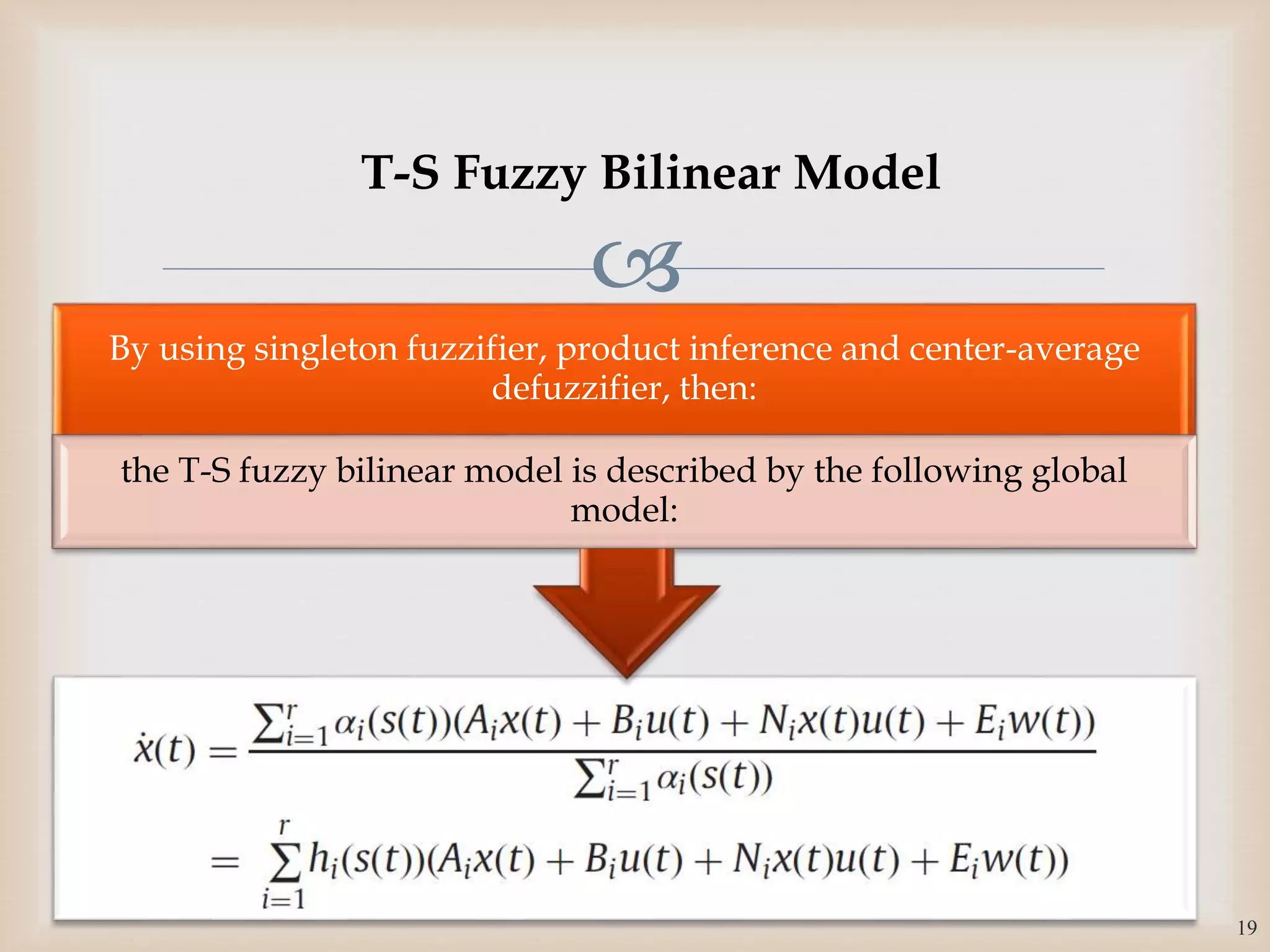
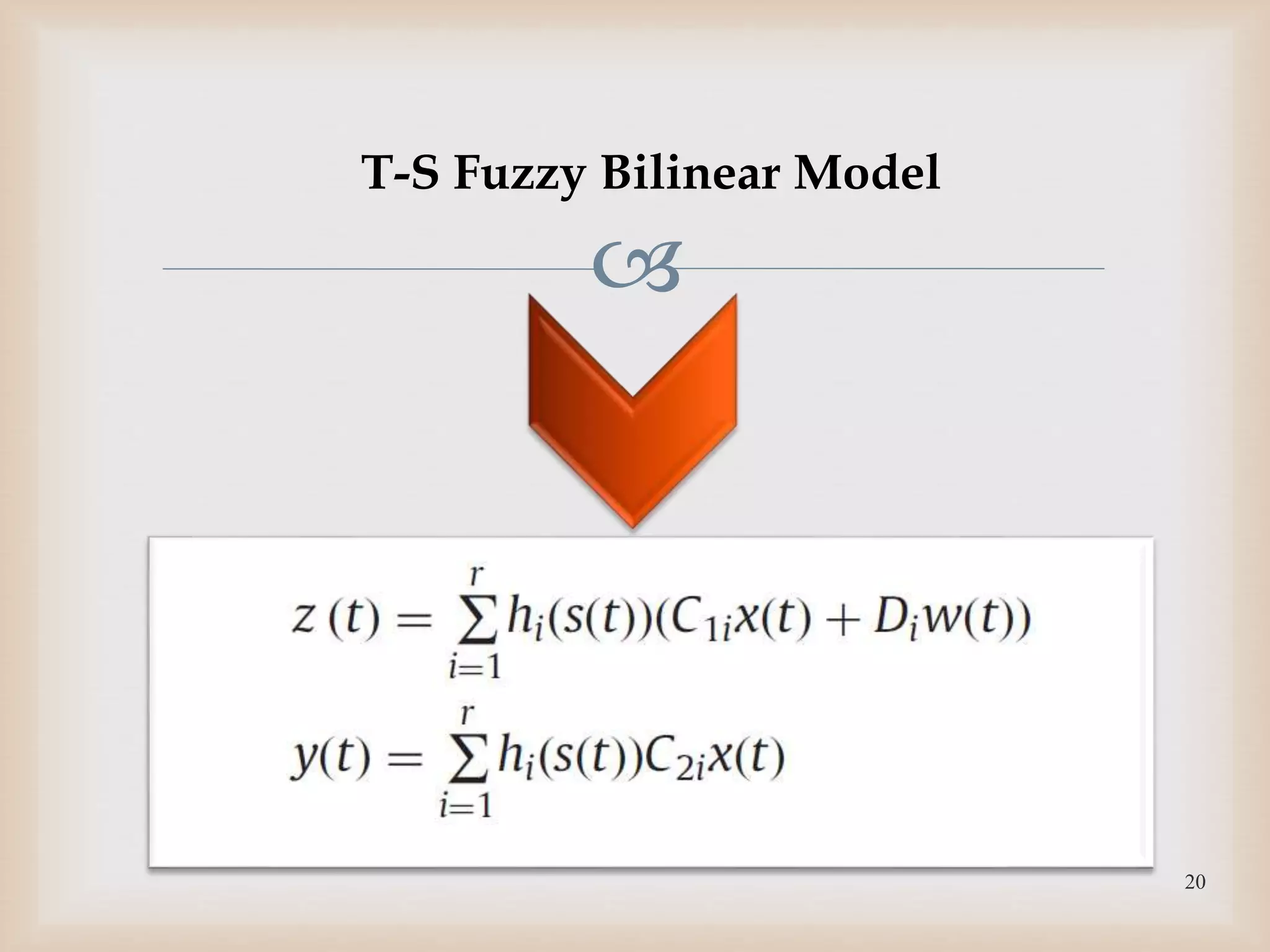
The document discusses the design and robustness of a fuzzy output feedback controller based on a Takagi-Sugeno (T-S) fuzzy bilinear model for affine nonlinear systems, specifically applied to a Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR) benchmark. It outlines the need for using a bilinear model when nonlinear systems cannot be adequately approximated by linear models and emphasizes the importance of output feedback controllers when state variables are unavailable for feedback. The document also details the procedure for obtaining control gains through Lyapunov stability analysis and Linear Matrix Inequalities (LMI) to ensure system stability.




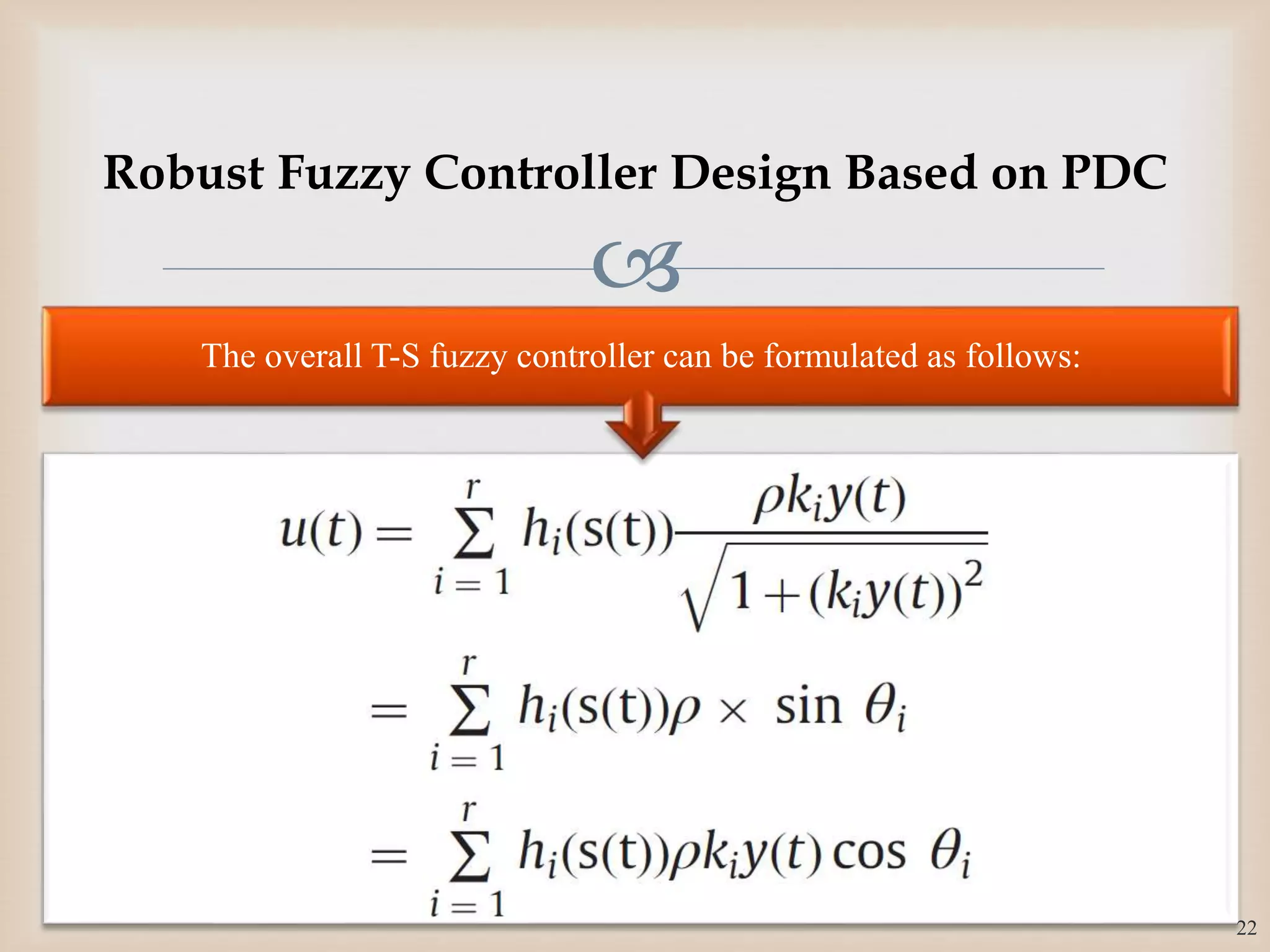
![
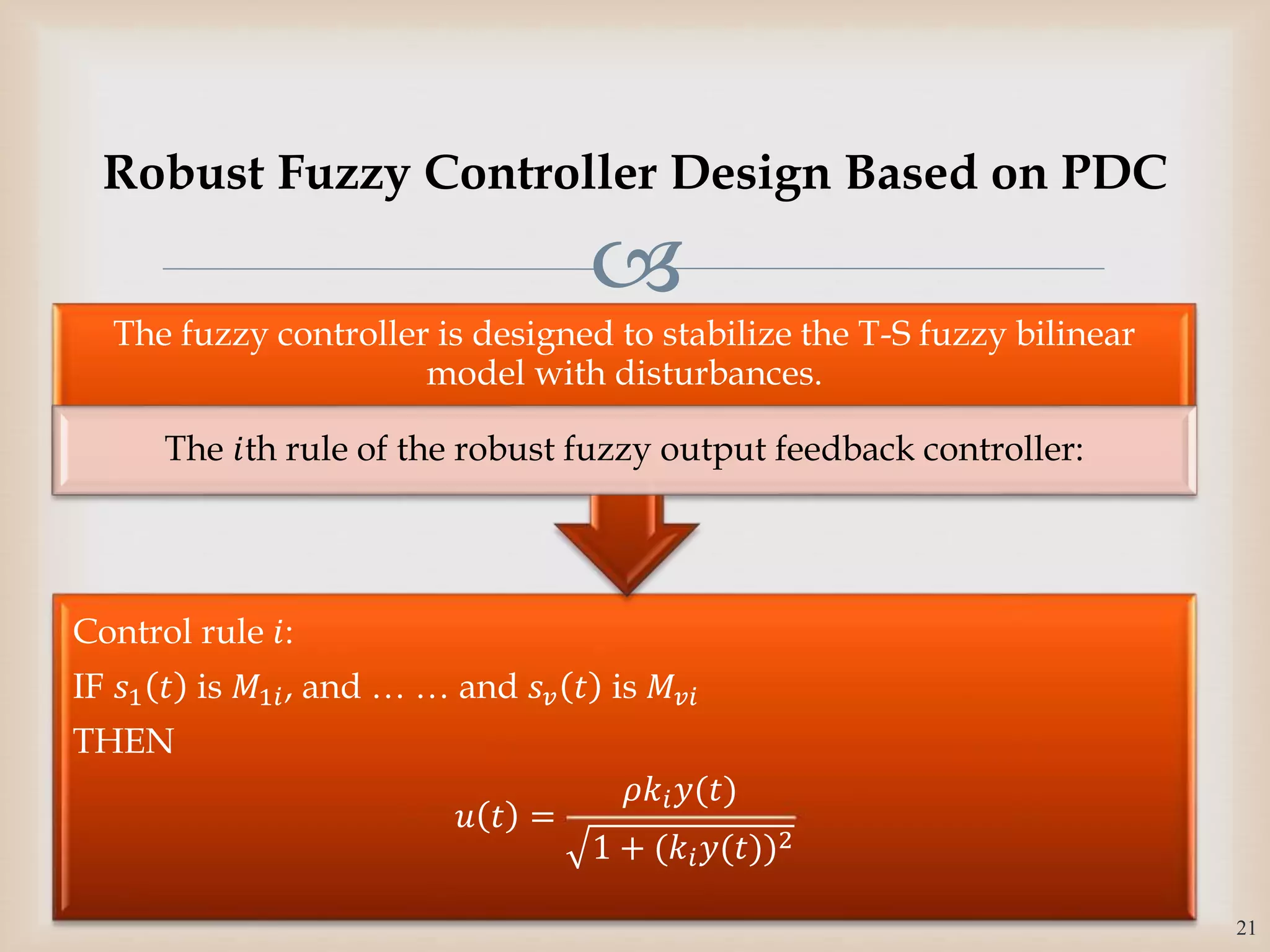
𝜃𝑖 ∈ [−
𝜋
2
,
𝜋
2
], 𝑘𝑖 ∈ 𝑅 is a scalar to be determined by LMI
conditions and 𝜌 > 0 is an arbitrary designed scalar, 𝑖
= 1,2, … , 𝑟.
where
23
Robust Fuzzy Controller Design Based on PDC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/robustfuzzyoutputfeedbackcontrollerforaffinenonlinearsystemsviatsfuzzybilinearmodel-cstrbenchmark-150716172604-lva1-app6891/75/Robust-Fuzzy-Output-Feedback-Controller-for-Affine-Nonlinear-Systems-via-T-S-Fuzzy-Bilinear-Model-CSTR-Benchmark-23-2048.jpg)
![
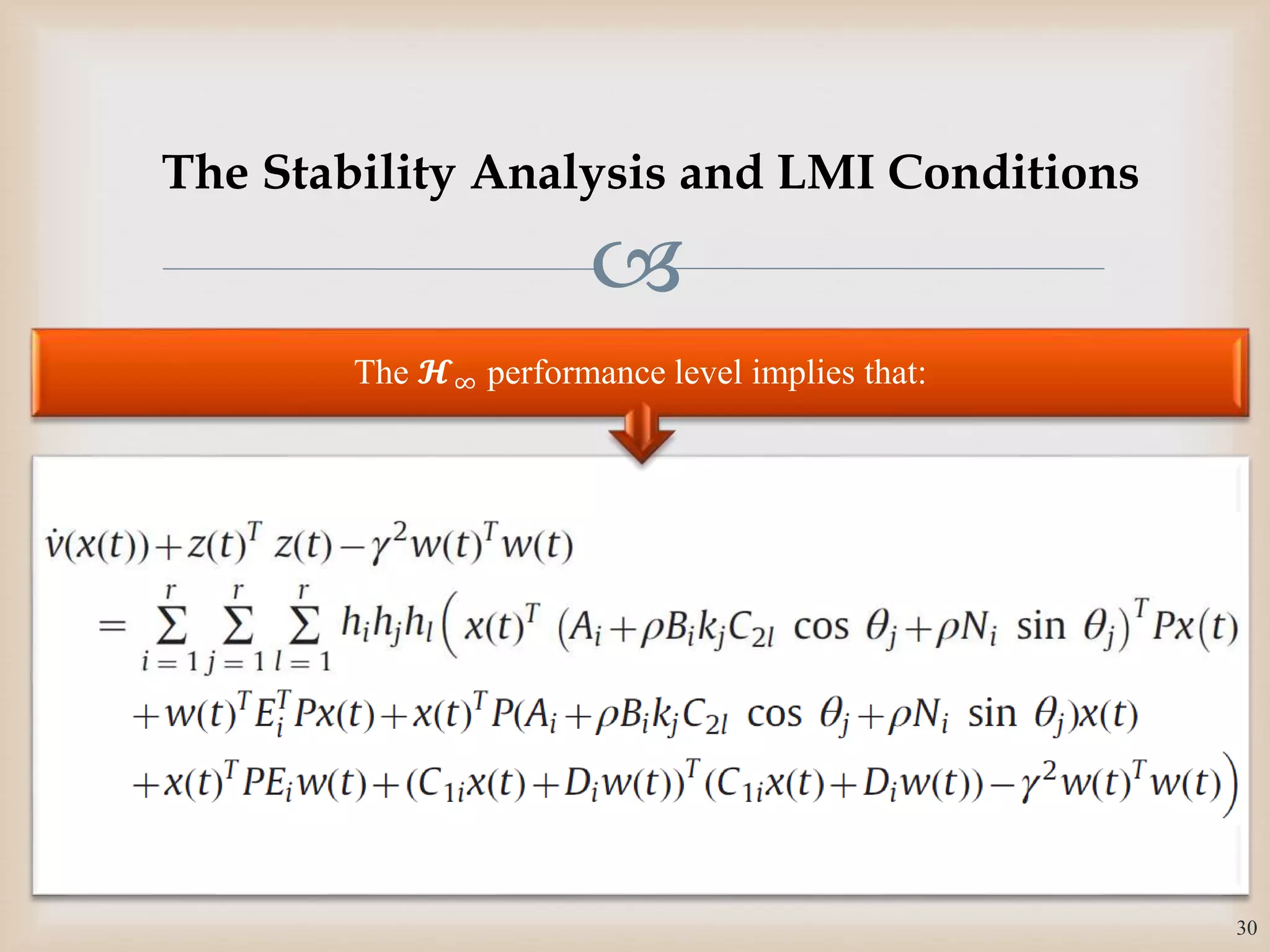
We introduce the following performance criterion with its
control objectives:
𝐽 = 0
∞
𝑧(𝑡) 𝑇
𝑧 𝑡 − 𝛾2
𝑤(𝑡) 𝑇
𝑤(𝑡) 𝑑𝑡
When 𝑤 𝑡 = 0, the resulting of the closed-loop system
is asymptotically stable.
For 𝛾 > 0, and 𝑥 0 = 0, the controlled output 𝑧 𝑡 of the
closed-loop system satisfies 𝑧(𝑡) 2 < 𝛾 𝑤(𝑡) 2 for all non-
zero 𝑤 𝑡 ∈ 𝐿2[0, ∞].
i
25
Robust 𝓗∞ Fuzzy Output Feedback Controller
ii](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/robustfuzzyoutputfeedbackcontrollerforaffinenonlinearsystemsviatsfuzzybilinearmodel-cstrbenchmark-150716172604-lva1-app6891/75/Robust-Fuzzy-Output-Feedback-Controller-for-Affine-Nonlinear-Systems-via-T-S-Fuzzy-Bilinear-Model-CSTR-Benchmark-25-2048.jpg)