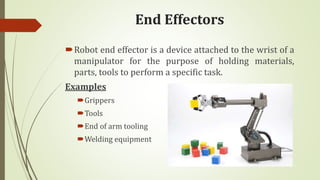
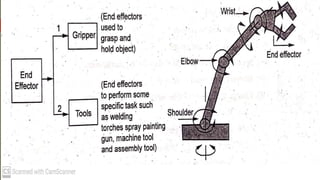
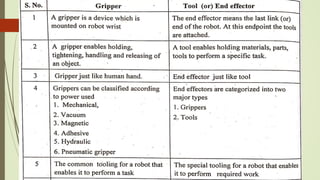
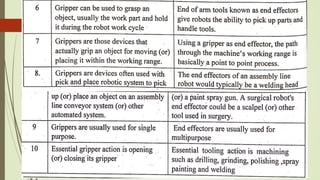
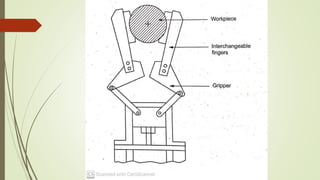
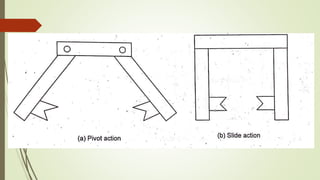
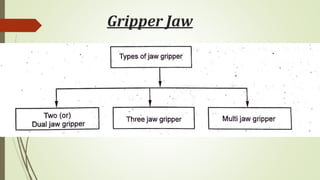
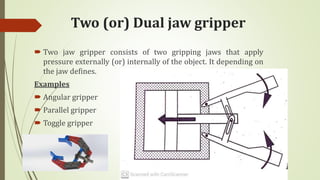
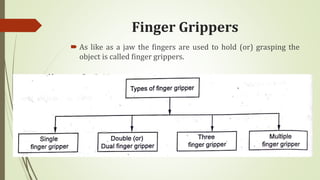
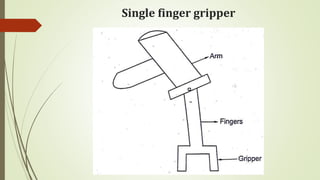
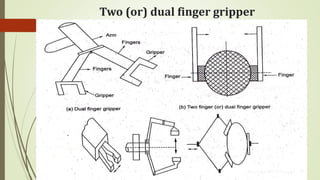
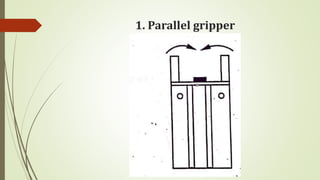
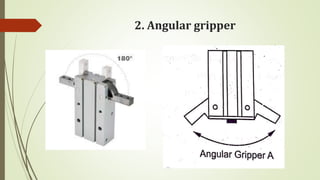
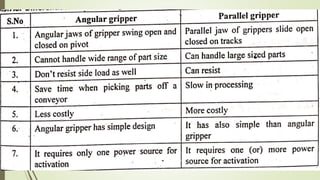
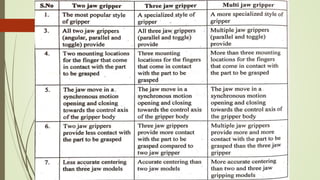
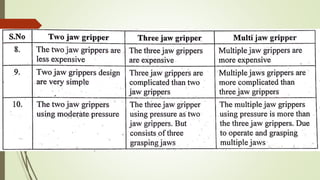
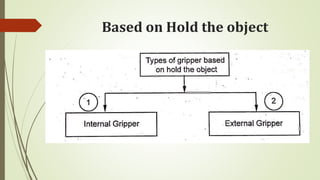
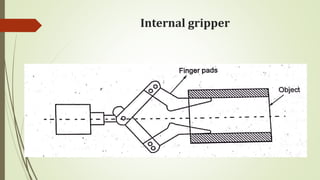
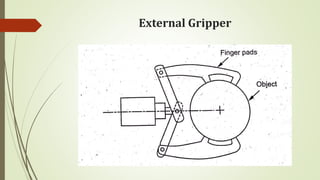
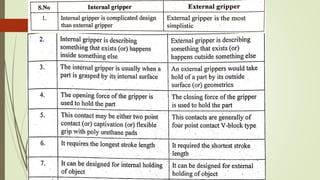
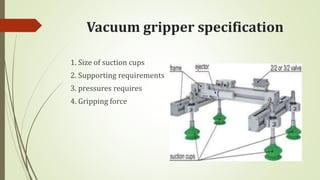
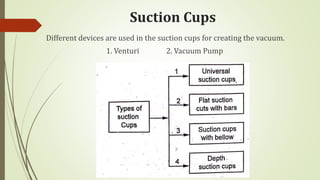
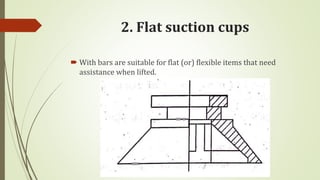
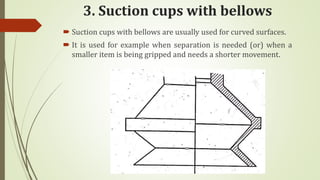
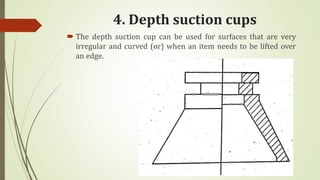
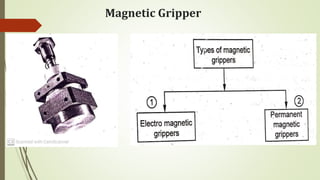
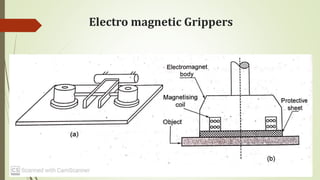
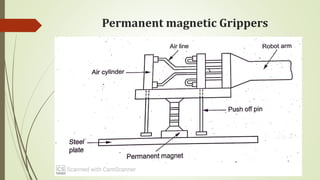
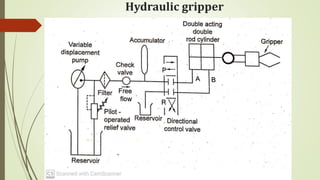
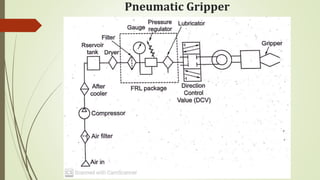
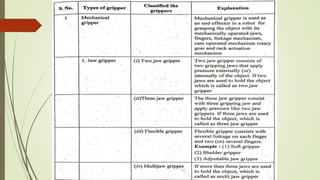
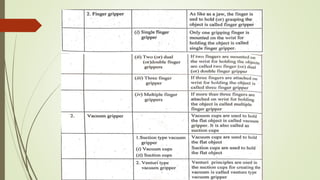
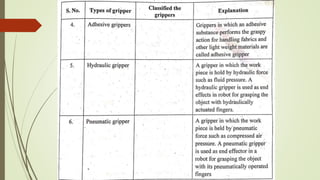
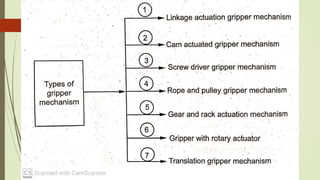
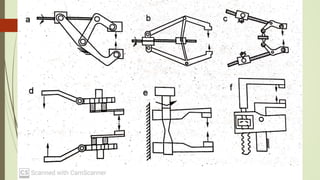
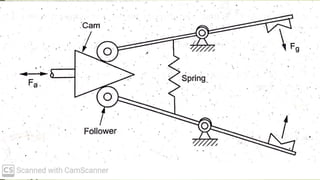
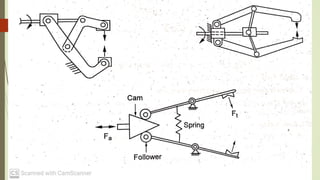
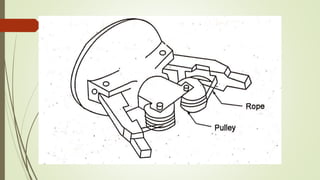
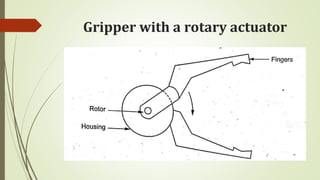
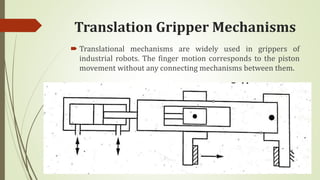
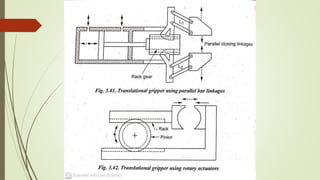
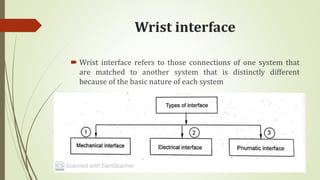
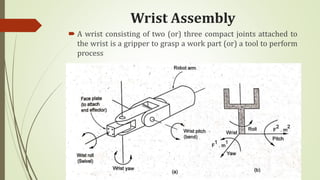
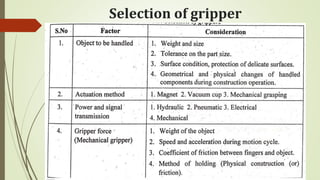
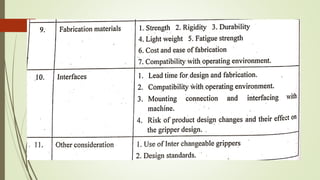
The document discusses different types of robot end effectors and grippers. It describes grippers classified based on their holding method (mechanical, vacuum, magnetic), number of fingers/jaws, and whether they grip internally or externally. Common grippers include mechanical, vacuum, magnetic, and pneumatic/hydraulic. Their mechanisms can involve linkages, cams, screws, or translation. Design considerations for grippers include gripping force, weight, and environmental capabilities.