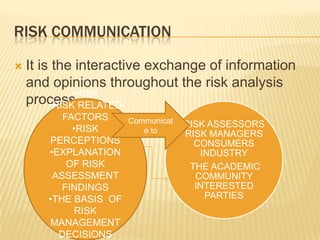
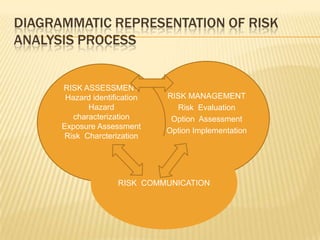
This document provides an overview of risk analysis as it relates to food safety. It defines risk as a function of hazard probability and severity. Risk analysis includes risk assessment, management, and communication. Risk assessment involves hazard identification, characterization, exposure assessment, and risk characterization. The document outlines the steps of a risk assessment and notes that risk management involves weighing policy alternatives based on risk assessment results. It also provides details on Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), a food safety system that identifies, evaluates, and controls hazards through establishment of critical control points and limits.