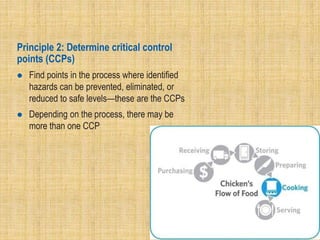
This document discusses food safety management systems. It defines food safety and hazards, and compares good manufacturing practices (GMP), good hygiene practices (GHP), and good agricultural practices (GAP). Common food safety requirements include prerequisite programs, HACCP, and ISO 22000. An effective food safety management system actively controls risks through procedures, training, monitoring, and corrective actions. The seven principles of HACCP provide a framework for identifying and managing food safety hazards. Record keeping is essential for verifying that food safety controls are implemented properly.