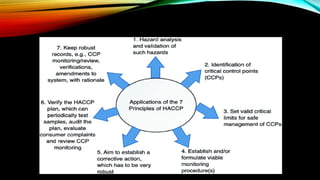
The document provides an overview of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), a system designed to identify and control food safety hazards from production to consumption. It details the history, principles, benefits, and procedures involved in implementing HACCP, emphasizing its importance in ensuring food safety for consumers and industries. Additionally, it discusses the challenges faced in adopting HACCP and delineates its advantages for consumers, businesses, and governments.