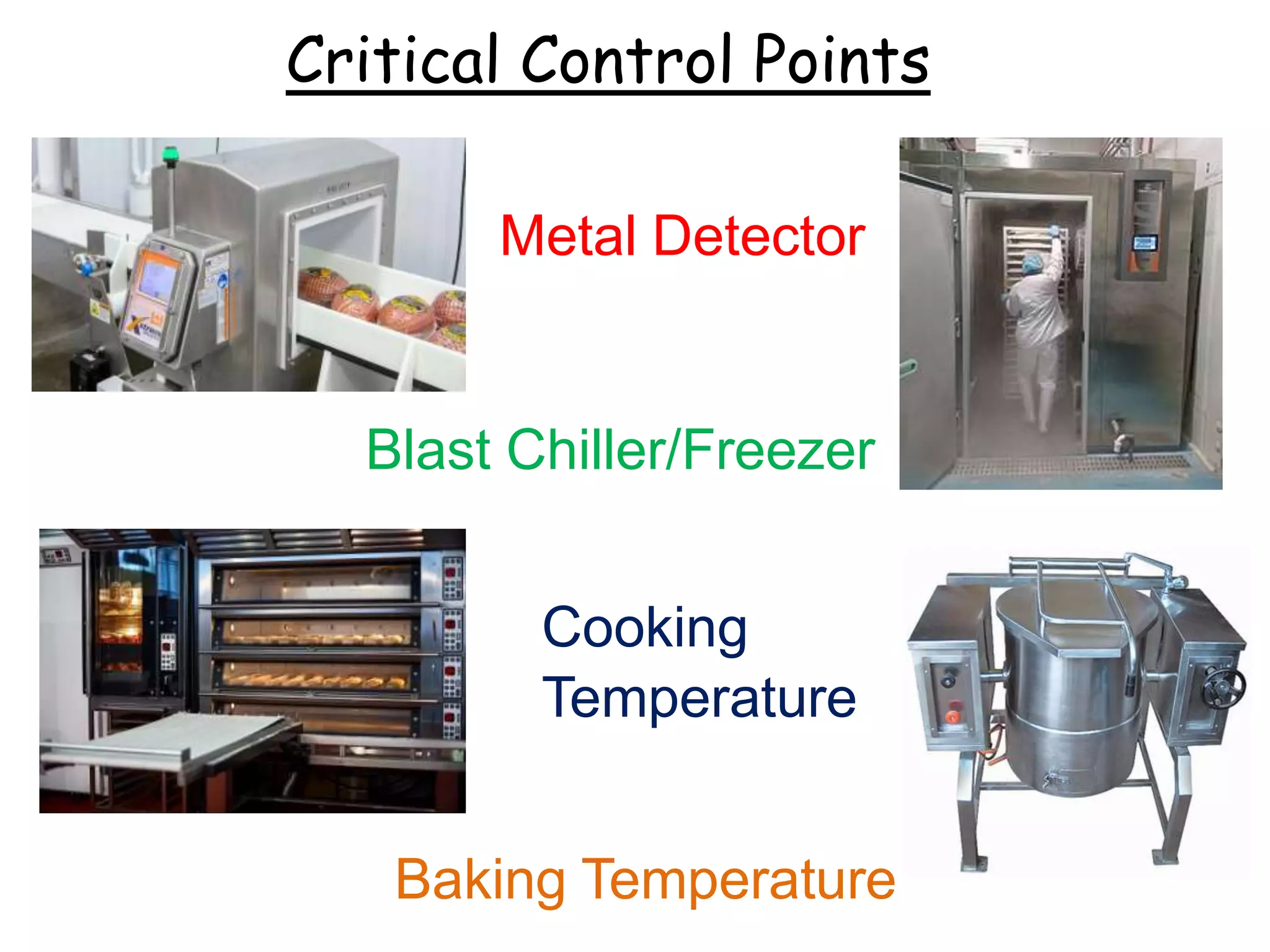
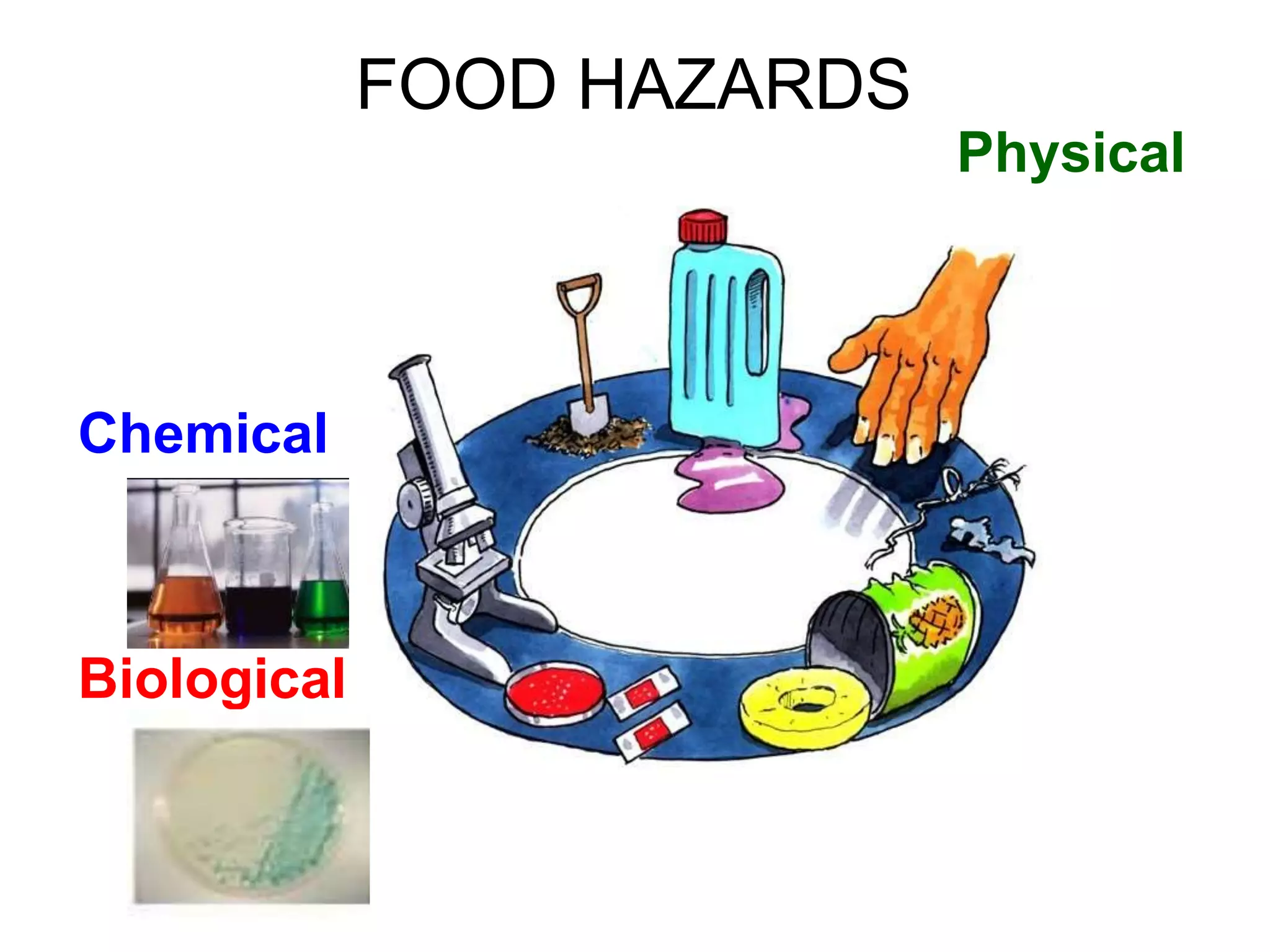
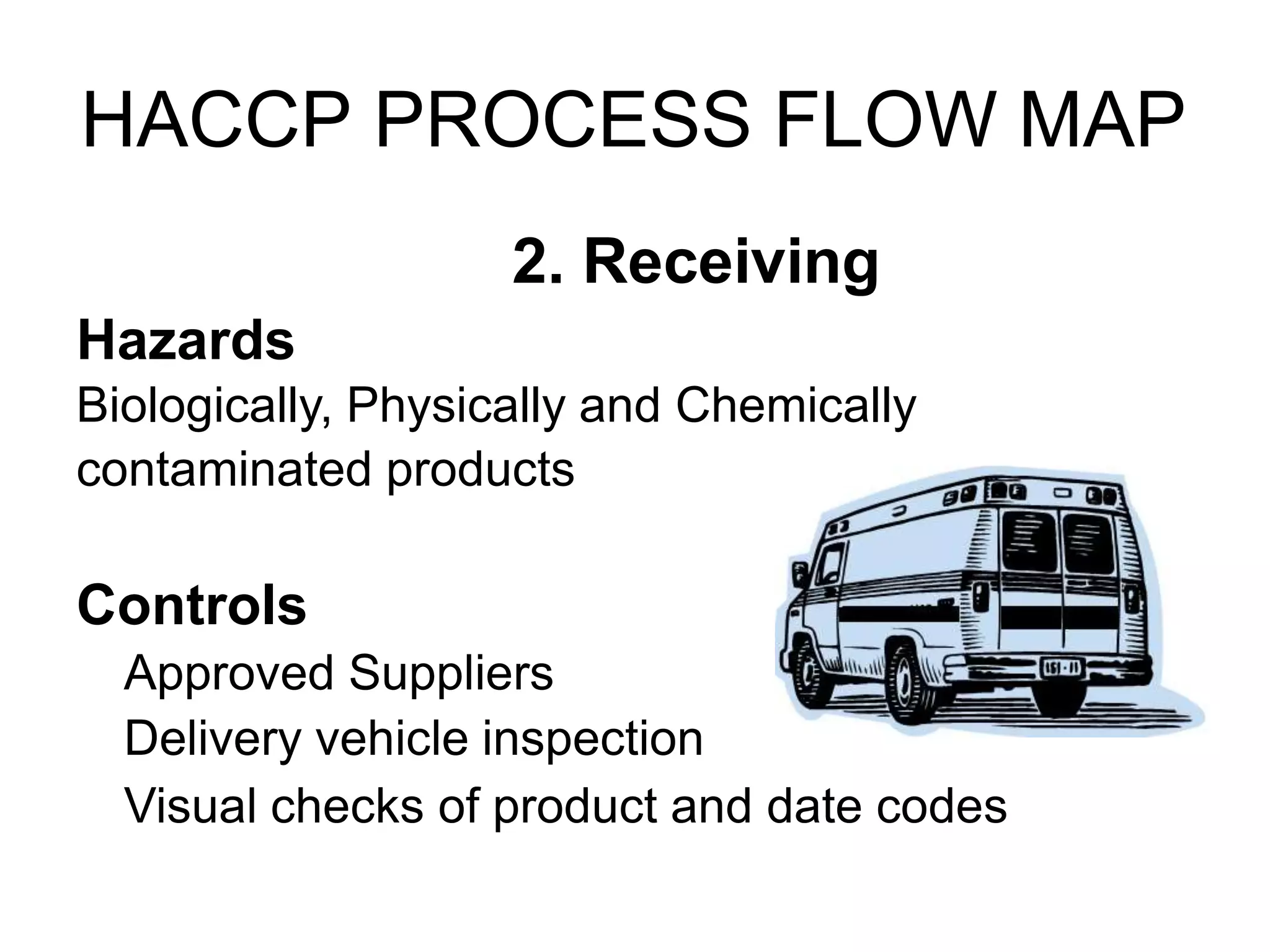
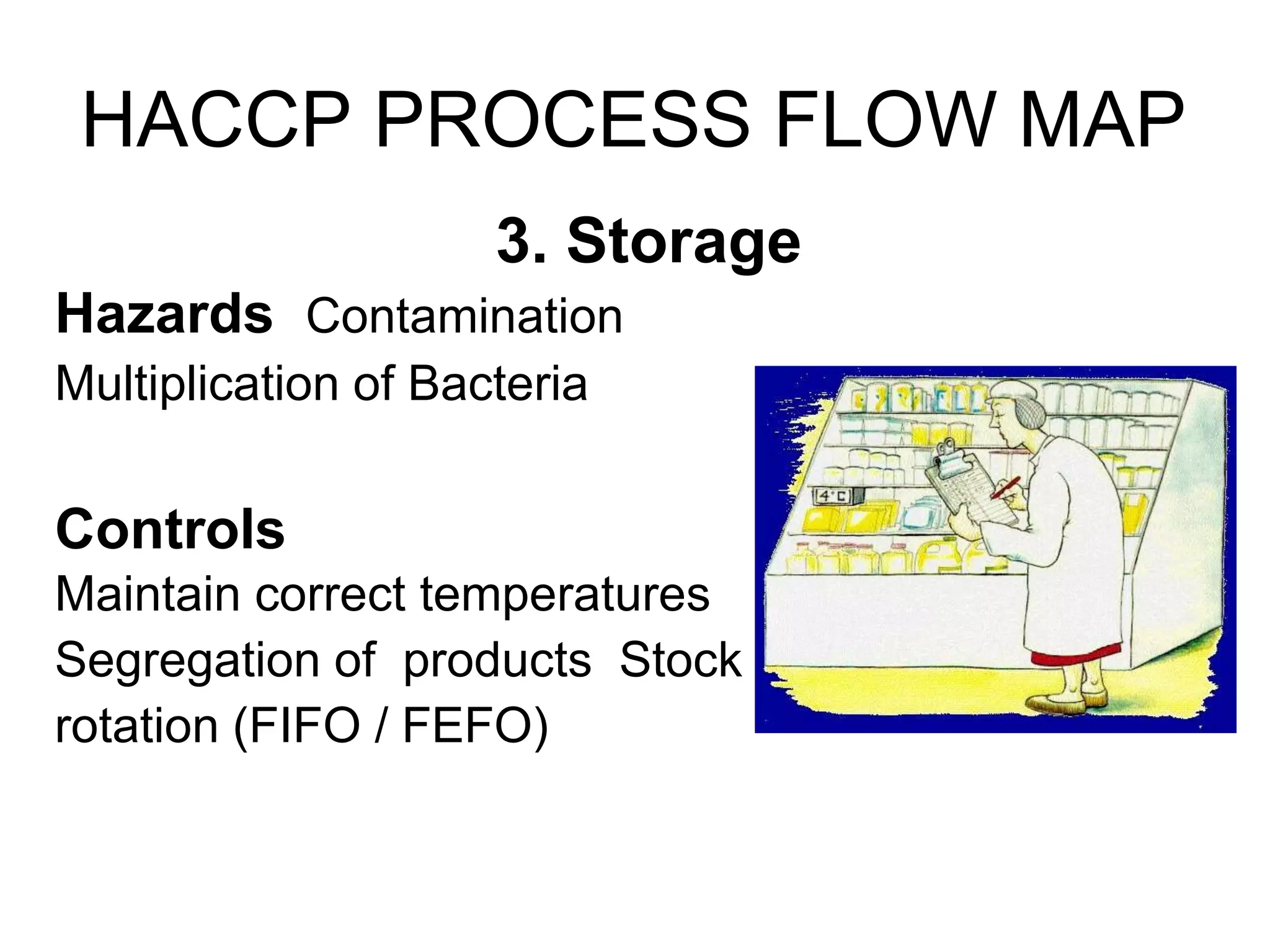
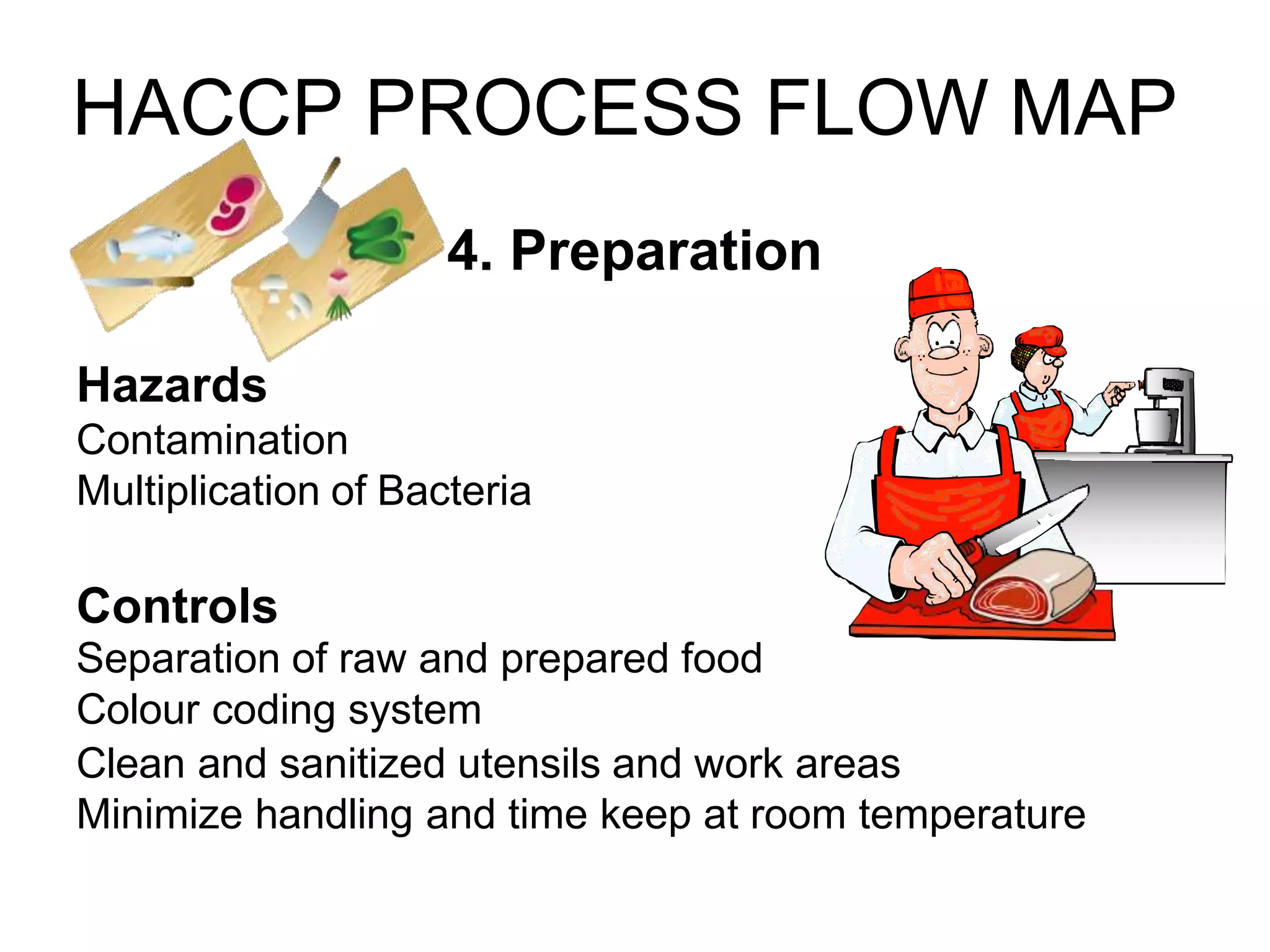
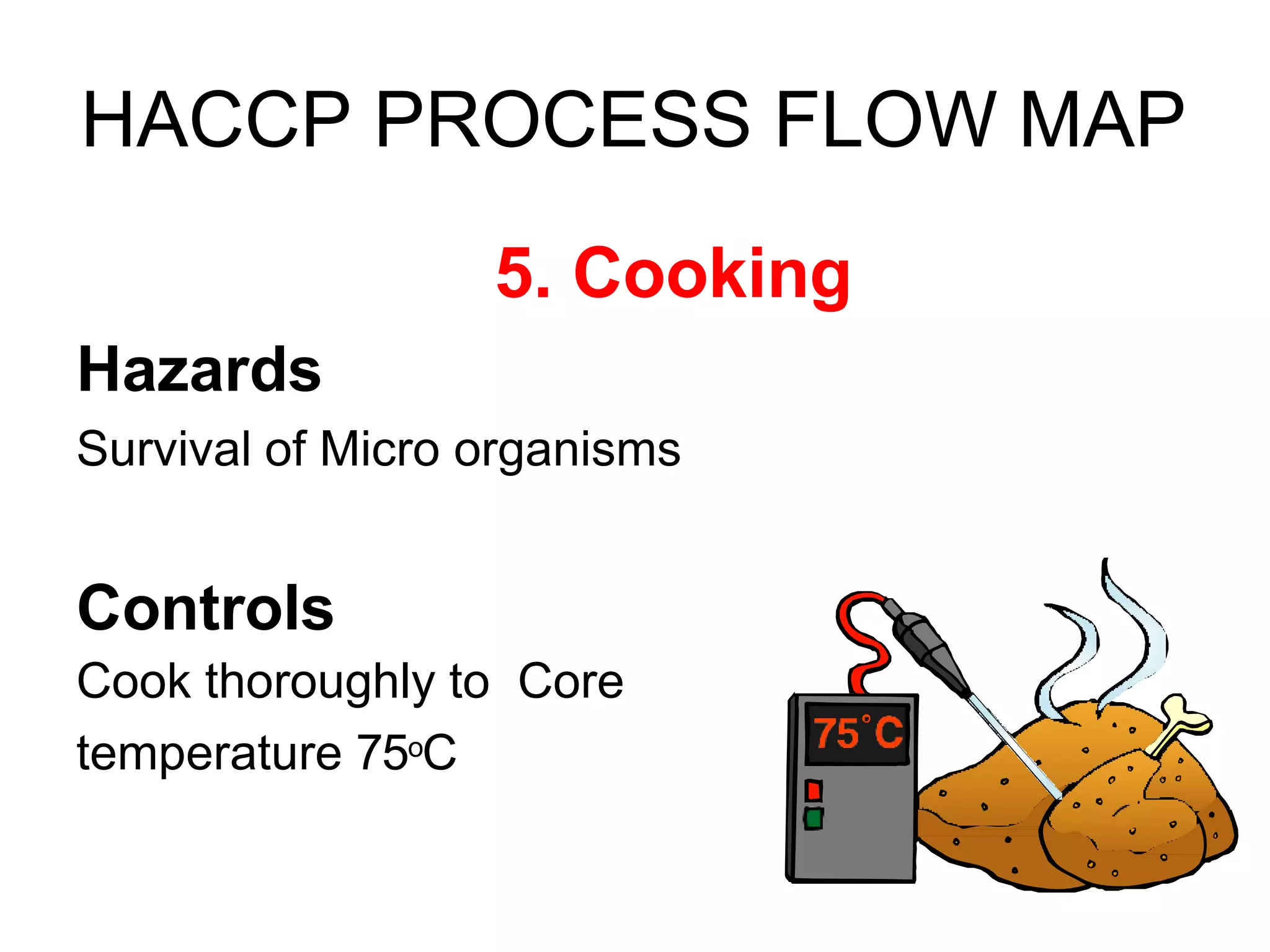
HACCP is a food safety management system that identifies, evaluates, and controls hazards that are significant for food safety. It involves conducting a hazard analysis to determine critical control points during food production. The seven principles of HACCP include identifying hazards, establishing critical limits, monitoring procedures, corrective actions, verification, and documentation. Key critical control points include cooking temperatures, storage temperatures, and using a metal detector. The HACCP process involves mapping the food flow from purchase to storage and identifying potential biological, chemical, and physical hazards and controls at each step.