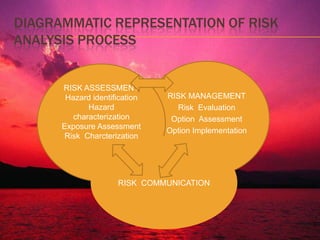
This document discusses risk analysis and HACCP systems. It defines risk as a function of the probability and severity of adverse health effects from hazards in food. It outlines the components of risk analysis: risk assessment, risk management, and risk communication. It then details the steps of risk assessment and describes how risk assessment should consider relevant practices throughout the food chain. It also discusses risk management, risk communication, and provides a diagram of the risk analysis process. Finally, it outlines the principles and benefits of implementing a HACCP system.