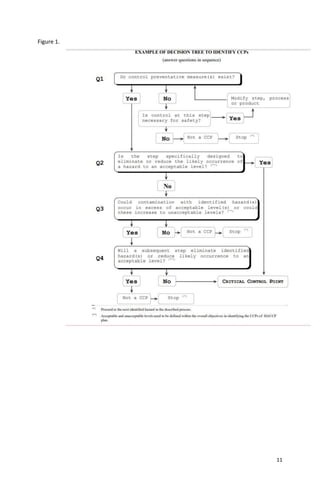
The document discusses Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP), a systematic preventative approach to food safety. It defines HACCP and explains its 7 principles: 1) conduct hazard analysis, 2) determine critical control points, 3) determine critical limits, 4) establish monitoring procedures, 5) establish corrective actions, 6) establish verification procedures, and 7) establish record keeping. It also discusses applying HACCP's process approach to retail and food service establishments by categorizing foods into 3 preparation processes based on the number of times they pass through the temperature danger zone. Critical control points are identified as steps that must be done to prevent, reduce, or eliminate food safety hazards.