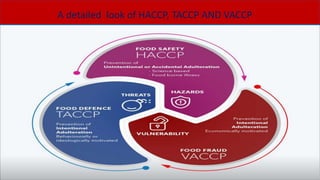
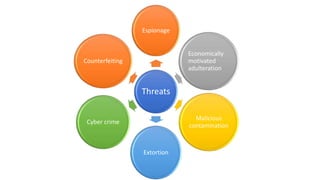
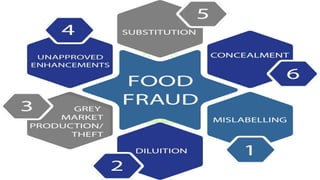
This document discusses food safety systems HACCP, TACCP, and VACCP. HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) is a logical approach to food safety that identifies hazards and prevents foodborne illness. TACCP (Threat Assessment Critical Control Point) and VACCP (Vulnerability Assessment Critical Control Point) were developed to address threats of deliberate attacks and vulnerabilities in the supply chain. TACCP focuses on food defense from threats like tampering, while VACCP addresses food fraud risks from economic adulteration. Both use risk assessments to determine critical control points to monitor and protect the supply chain. Implementing all three systems helps ensure food safety from both intentional and unintentional contamination