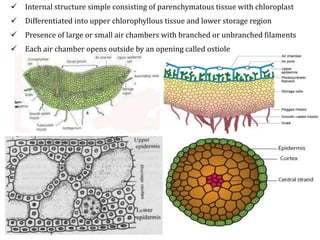
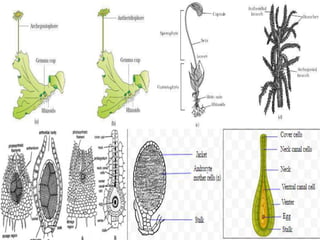
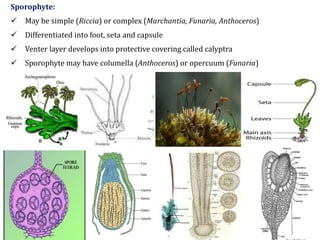
The document discusses the general characteristics, structural features, and reproductive methods of bryophytes, highlighting their role as amphibians of the plant kingdom. It details their habitat, nutritional modes, life cycle, and the alternation of generations, along with their economic and ecological importance. Key points include their use in soil formation, packing materials, seed beds, and as a potential fuel source.