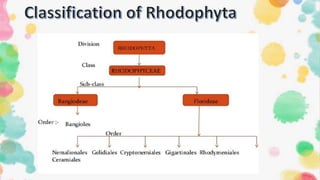
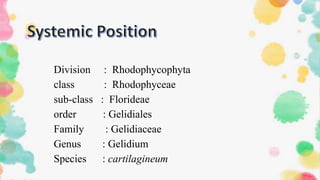
1. The document discusses the classification, characteristics, and life cycle of the red algae Gelidium. It belongs to the division Rhodophycophyta, class Rhodophyceae, sub-class Florideae, and order Gelidiales.
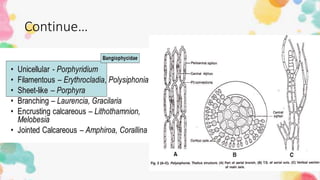
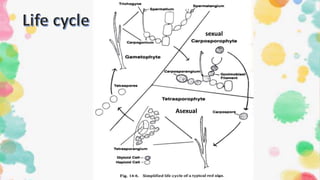
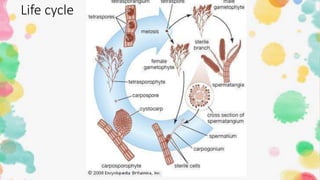
2. Gelidium has a stiff, cartilaginous thallus that is often pinnately branched. It reproduces both sexually, through non-motile gametes, and asexually, through fragmentation and non-motile spores.
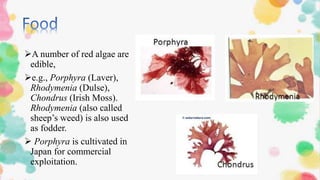
3. Red algae like Gelidium are used for medicines, food, and industrial products like agar and carrageenan. Some can also cause harmful algal blo