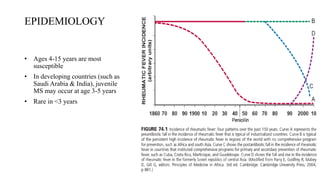
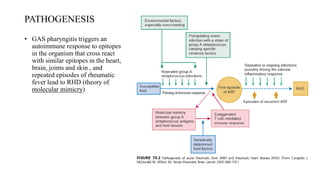
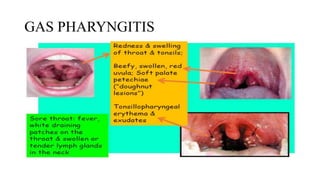
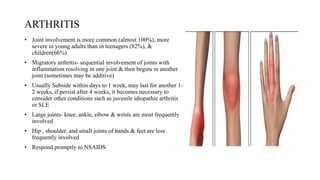
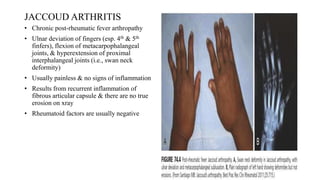
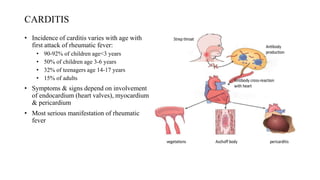
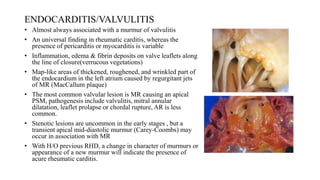
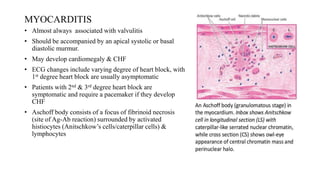
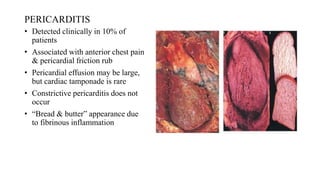
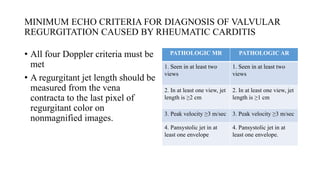
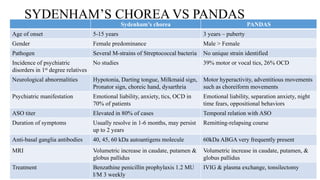
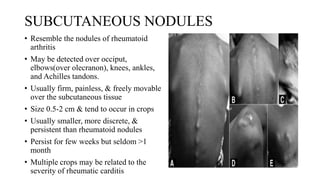
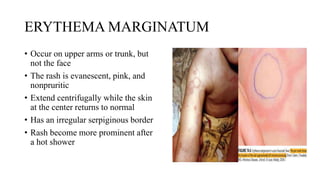
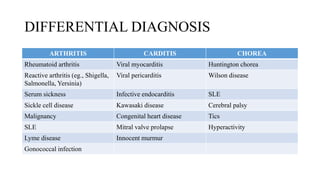
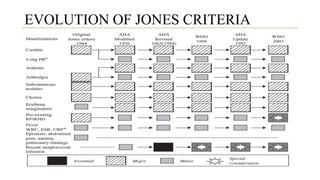
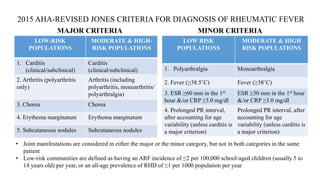
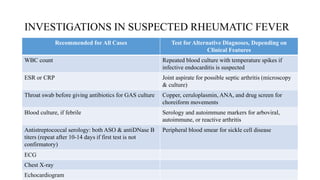
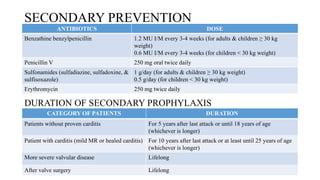
Rheumatic fever is a multifactorial disease following GAS pharyngitis, primarily affecting individuals aged 4-15 in developing countries, characterized by inflammation of the heart, joints, and other tissues. The condition can lead to serious complications such as rheumatic heart disease, heart failure, and stroke through various manifestations including arthritis, carditis, and chorea. Diagnosis relies on the Jones criteria, and treatment includes antibiotics and anti-inflammatory agents, with secondary prevention through regular antibiotic prophylaxis.