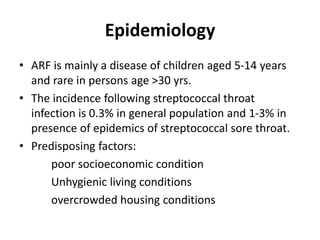
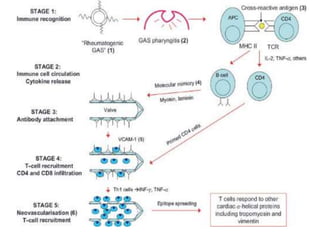
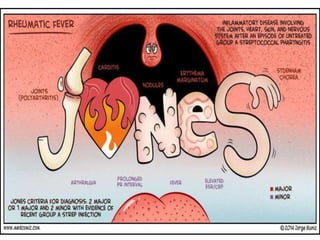
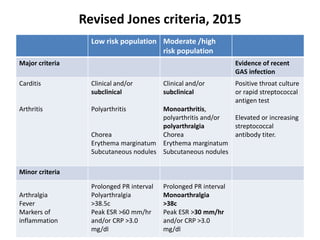
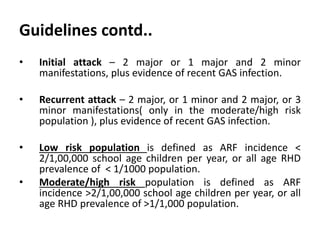
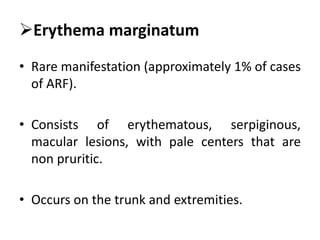
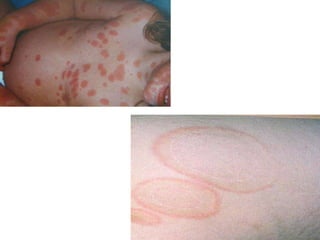
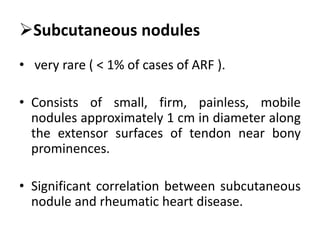
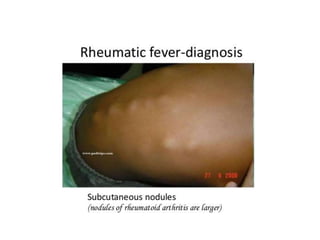
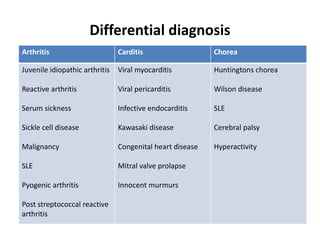
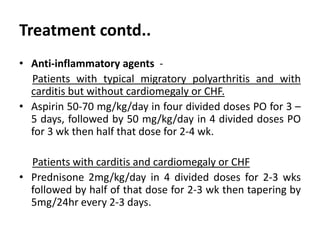
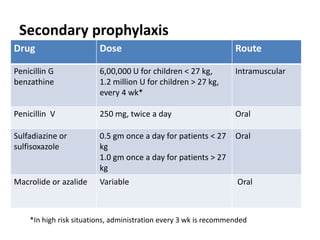
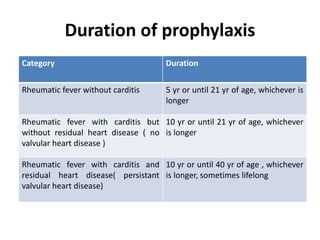
Rheumatic fever is an autoimmune disease that can occur as a result of a streptococcal throat infection. It affects multiple body systems but commonly involves the heart, joints, and brain. Symptoms may include heart inflammation (carditis), painful and migratory swollen joints (arthritis), jerky involuntary movements (chorea), and others. The disease is caused by an abnormal immune response that causes antibodies produced against streptococcal bacteria to also attack human tissues. Treatment involves bed rest, antibiotics to treat the initial infection, and anti-inflammatory drugs. Recurrences of the disease can be prevented with long-term antibiotic prophylaxis but cardiac damage may persist long-term in the form of rheumatic heart disease.