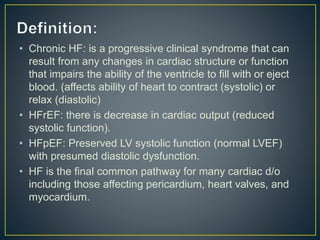
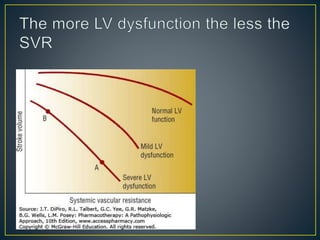
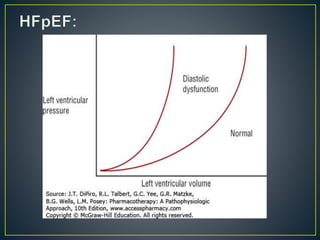
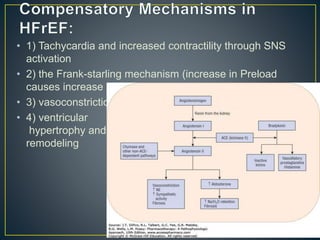
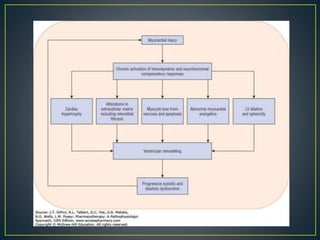
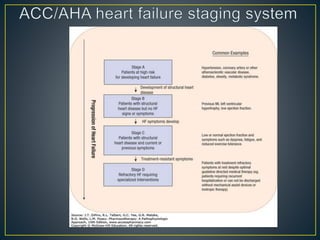
1) Chronic HF is a progressive syndrome that impairs the heart's ability to pump blood effectively. It can be caused by structural or functional changes to the heart and has two main types: HFrEF with reduced ejection fraction and HFpEF with preserved ejection fraction.
2) Risk factors include age, with risk doubling each decade, and prior conditions like hypertension, diabetes and myocardial infarction. Five-year mortality is around 50% and sudden cardiac death causes 40% of HF deaths.
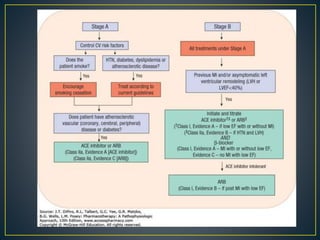
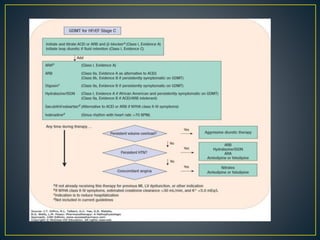
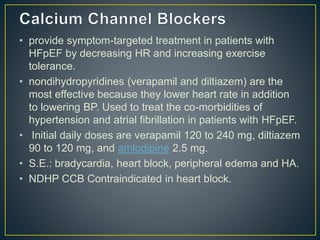
3) Treatment involves managing symptoms, slowing disease progression, and preventing hospitalizations through lifestyle changes, medications, and devices. Diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and aldosterone antagon