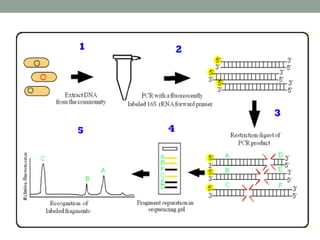
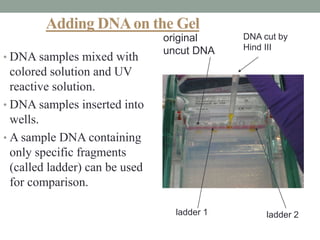
RFLP analysis involves using restriction enzymes to cut DNA into fragments of different lengths at specific nucleotide sequences. These fragments are then separated by gel electrophoresis based on their size and can be used to identify differences between DNA samples. DNA is extracted from samples, digested with restriction enzymes, and the fragments are run on a gel and either detected directly or transferred to a membrane through Southern blotting for detection using DNA probes. This allows analysis of genetic variation and has applications in forensics, disease detection, and genetic mapping.