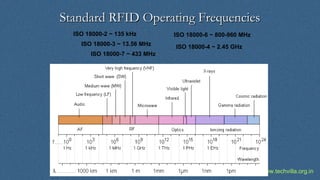
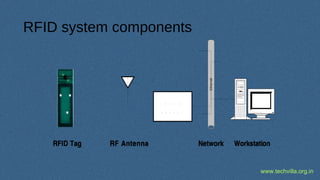
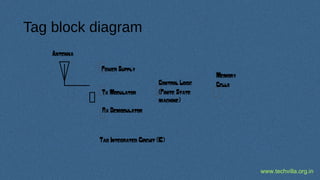
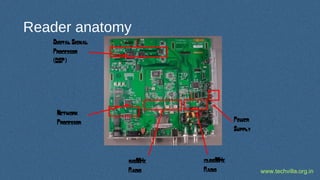
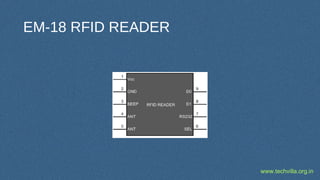
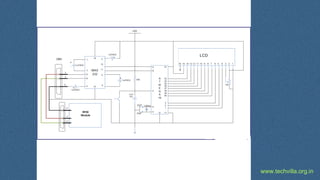
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology for uniquely identifying objects using electromagnetic signals, initially developed during WWII, and is now widely used in various industries. It involves transceivers, antennas, and transponders, operating in different frequencies and can function in passive or active modes, allowing applications such as inventory tracking, access control, and animal tracking. Furthermore, RFID standards exist to regulate the technology, and components like tags and readers play crucial roles in its functionality.