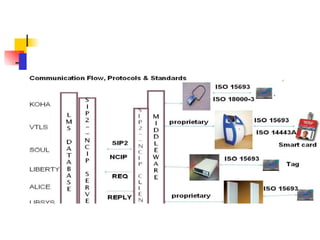
The document provides an overview of implementing RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology in modern libraries. It discusses what RFID is, the history and components of an RFID system including tags, readers, middleware and security gates. The benefits of RFID for libraries are automated check-in/check-out, inventory management and theft detection. Implementation requires an initial investment but provides long term benefits like reducing staff time and improving customer services. Key users of RFID in libraries are students, faculty and library staff.