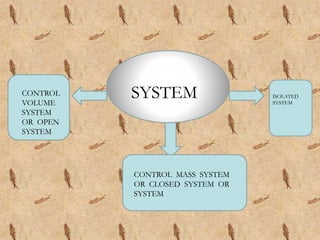
This document discusses Reynolds transport theorem and its application to conservation of mass in fluid flow using a control volume approach. It defines key terms like system, control mass system, control volume system, and isolated system. It also presents the continuity equation in differential and integral form for a control volume. The Reynolds transport theorem relates how the rate of change of an extensive property within a system equals the rate of change within a control volume plus the net rate of efflux from the control volume. As an example, it shows how the conservation of mass statement for a system and control volume are related using the Reynolds transport theorem.