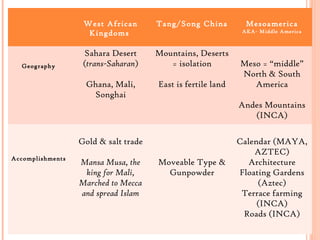
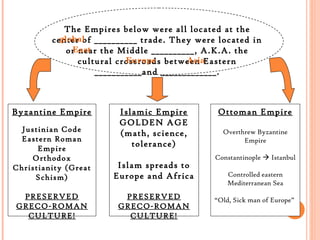
The document provides an overview of several global civilizations during the time period of the final exam, including their geography, accomplishments, and empires. West African kingdoms like Ghana, Mali, and Songhai dominated gold and salt trade across the Sahara Desert. The Tang and Song Dynasties in China saw developments like moveable type and gunpowder. Mesoamerican civilizations like the Maya and Aztec built advanced calendars, floating gardens, and terrace farming in mountainous regions between North and South America. The Byzantine, Islamic, and Ottoman Empires preserved Greco-Roman culture and dominated trade in the eastern Mediterranean.