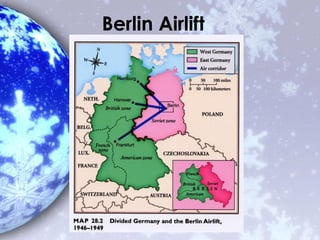
The Cold War was a state of geopolitical tension between the Soviet Union and the United States and their respective allies from 1945 to 1991. This period saw an arms race, proxy wars, and the establishment of military alliances like NATO and the Warsaw Pact. In the late 1980s, reforms under Gorbachev led to openness and democracy in the Soviet Union, eventually causing its collapse and the end of the Cold War.