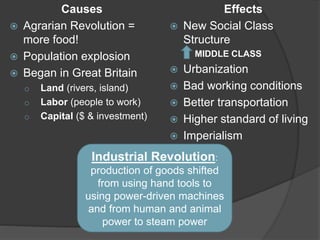
The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain because it had all the necessary factors of production: land, labor, and capital. The revolution led to major social changes like the rise of a middle class and urbanization. It also contributed to the rise of imperialism in the 1800s-early 1900s as nations sought new markets and resources. Imperialism had both economic and political causes and effects like domination of other regions, conflict, and forced changes.