The document discusses several key aspects of an increasingly globalized world:
1) It describes an interdependent global economy where developments in one region can impact others, and highlights differences between developed and developing economies.
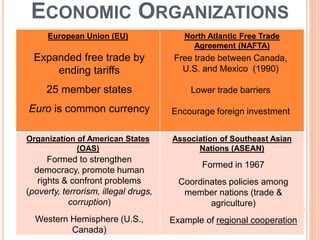
2) It provides examples of major economic organizations that promote regional cooperation and trade such as the EU, NAFTA, OAS, and ASEAN.
3) It outlines several major global problems including environmental issues like pollution and global warming, terrorism, poverty, and health challenges exacerbated by growing populations and uneven access to resources.
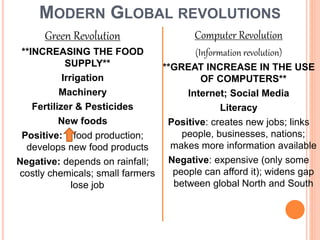
4) It discusses modern global revolutions in agriculture and technology and their mixed impacts, as well as challenges currently facing regions like Africa and Latin America.