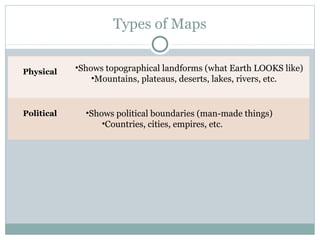
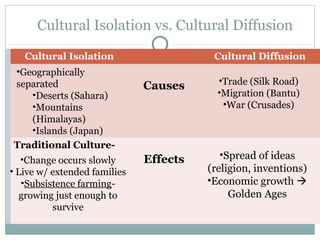
This document provides an introduction to global history. It discusses primary and secondary sources that historians use to understand the past. It also outlines different social scientists like economists, geographers, archaeologists, and anthropologists and how they study and interpret history. The document defines different types of maps, what culture is, and the differences between cultural isolation and cultural diffusion. A major turning point in history discussed is the Neolithic Revolution and domestication of plants and animals, which led to permanent settlements and early civilizations along river valleys like Mesopotamia, Indus Valley, Yellow River Valley, and Nile River Valley.