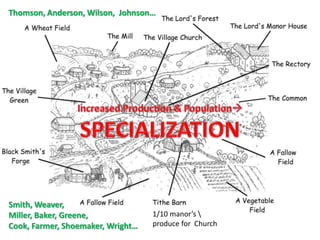
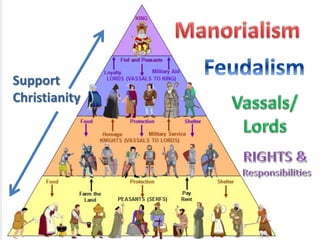
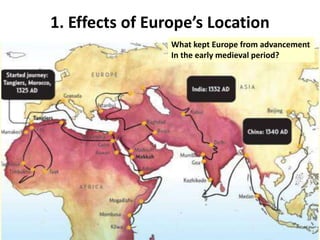
The document provides an overview of early medieval Europe following the fall of Rome from 500-1000 CE. It discusses several key developments:
1. The early Middle Ages was a period of instability as Germanic tribes expanded and powers like the Caliphate and Byzantines threatened Europe. Monasteries helped spread Christianity and revive learning.
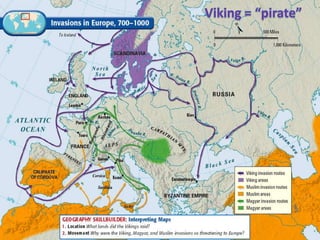
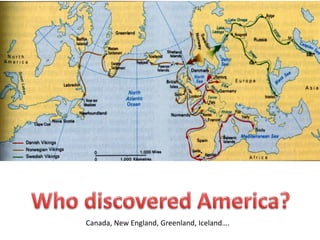
2. Vikings emerged as a formidable military power, using advanced longships to raid across Europe and beyond. They settled in places like Iceland and Greenland.
3. The Franks rose to power in Gaul/France under Clovis and the Carolingian dynasty. Charlemagne expanded the Frankish kingdom and was crowned Holy Roman Emperor in 800 CE.