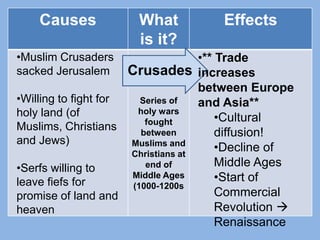
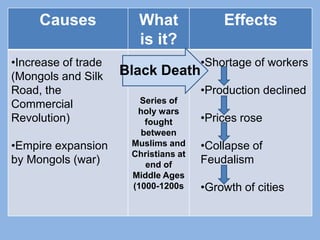
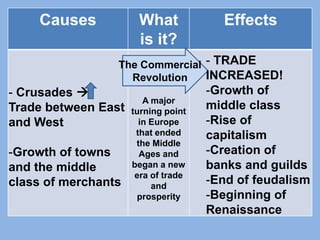
The document discusses several major global interactions throughout history that caused the spread of ideas and cultural diffusion. These include the rise of the Mongol Empire in the 13th century, which established stability and increased trade along the Silk Road, the Crusades from 1095-1200s which increased trade between Europe and Asia, the Black Death plague in the 1300s which reduced populations and labor forces in Europe and led to a decline in feudalism, and the Commercial Revolution in Europe which ended the Middle Ages and began an era of increased trade and prosperity. The Age of Exploration beginning in the 1400s then led to European dominance worldwide as countries like Spain and Portugal explored and established global trade networks and imperialized the Americas.