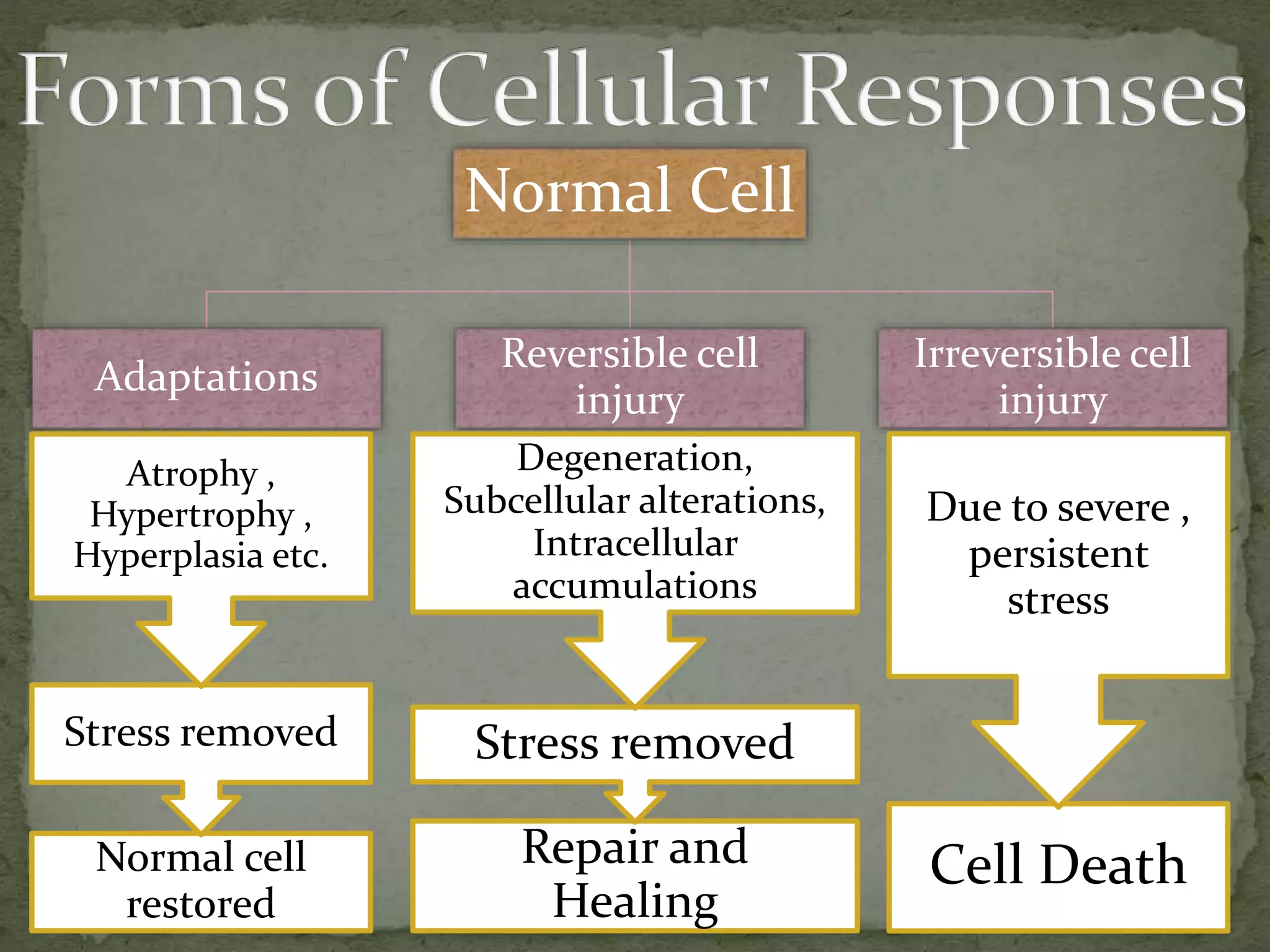
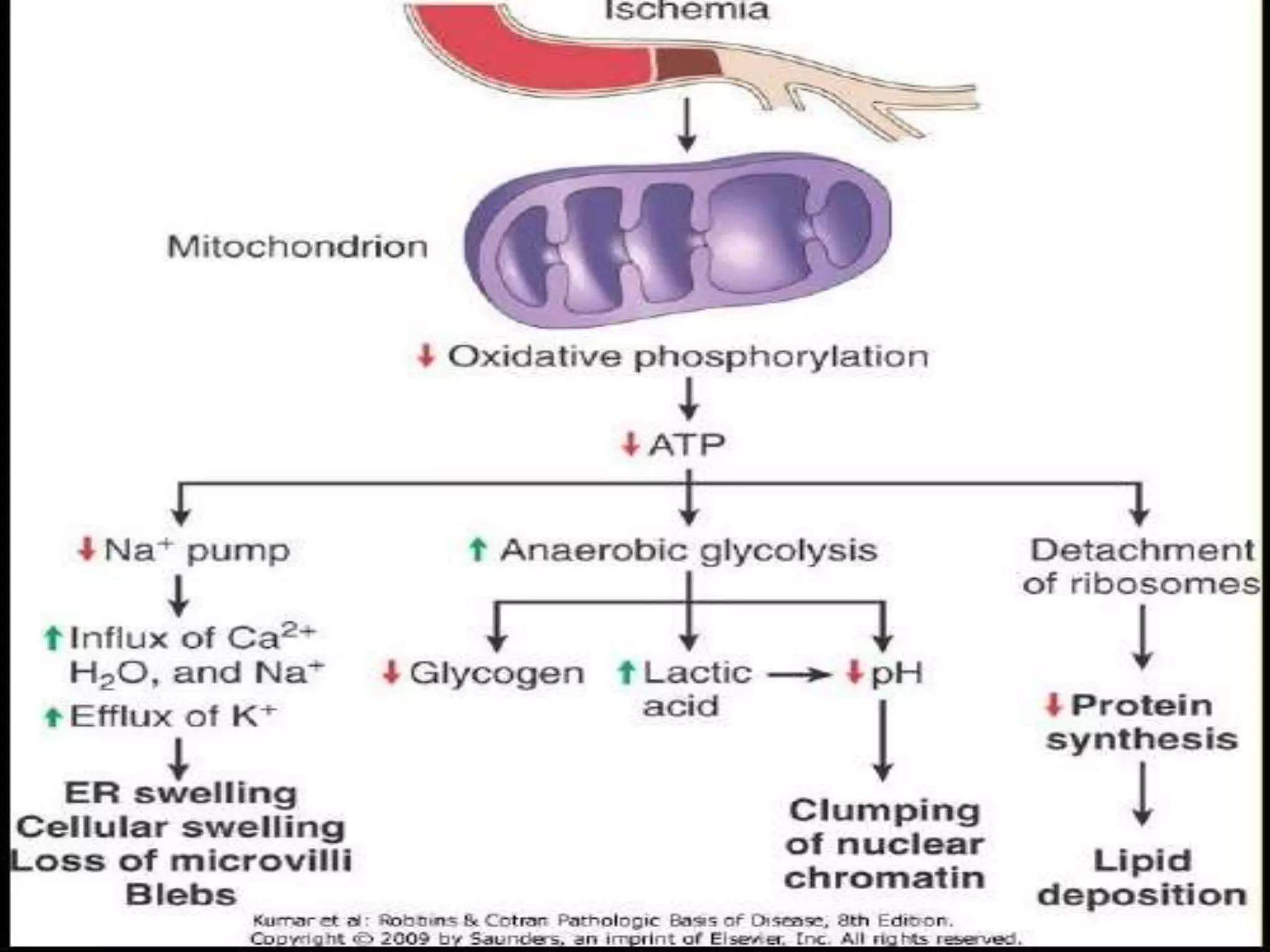
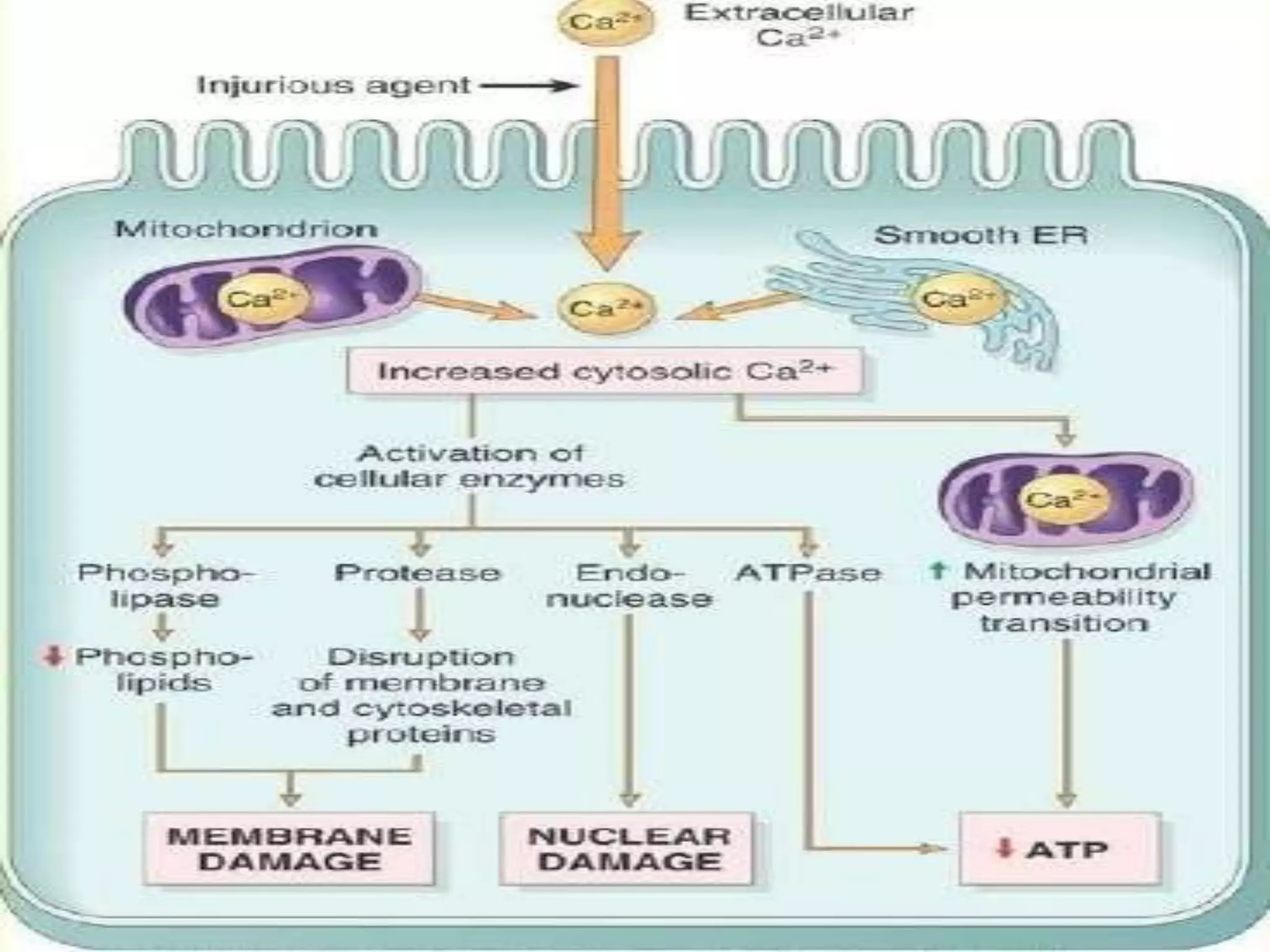
This document discusses etiology and pathogenesis of cell injury. It defines cell injury as changes in a cell's internal and external environment due to various stresses from etiological agents. The cellular response depends on host factors like cell type and extent of injury. Injury can result in reversible or irreversible cell injury depending on factors like agent type/duration and cell adaptability. Common causes of cell injury include hypoxia, ischemia, toxins, microbes, nutrition imbalances, and aging. Ischemia and hypoxia are the most frequent causes of cell injury in humans. Reversible injury involves ATP depletion and membrane changes, while irreversible injury brings further damage including to mitochondria and nuclei, leading to cell death.