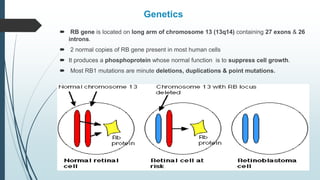
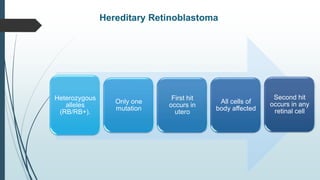
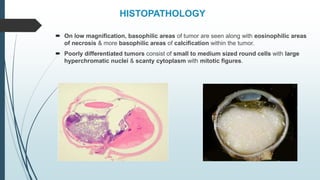
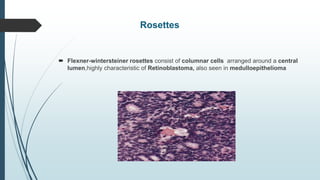
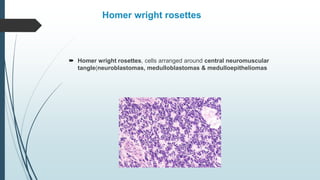
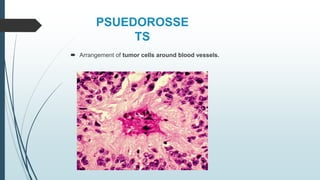
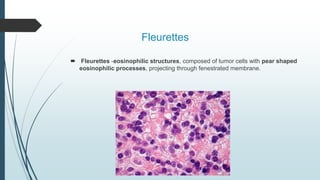
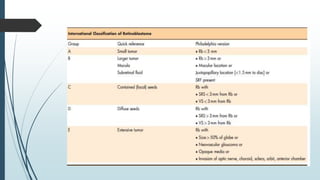
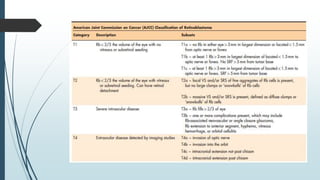
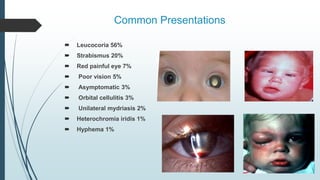
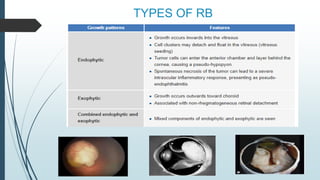
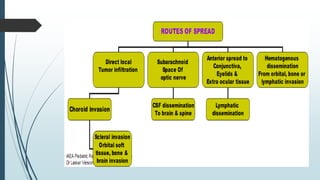
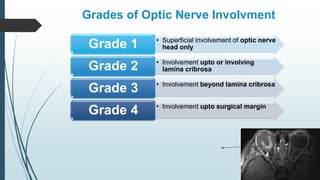
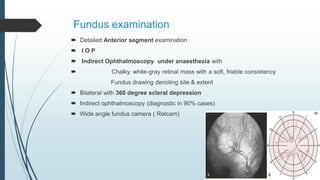
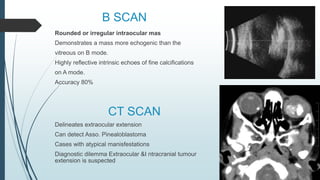
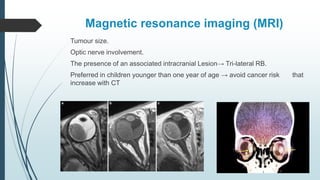
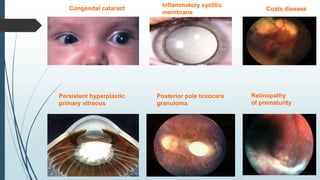
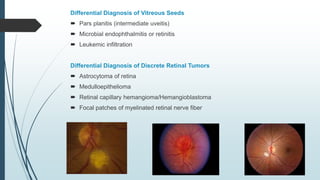
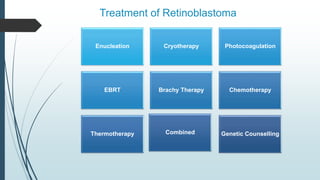
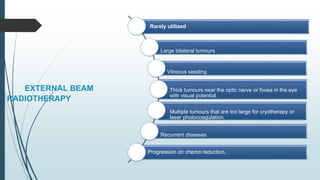
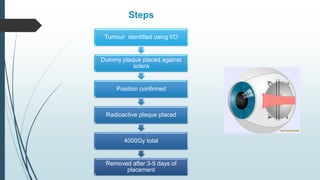
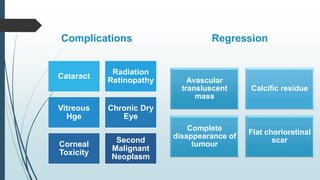
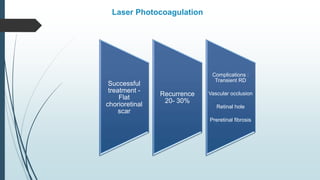
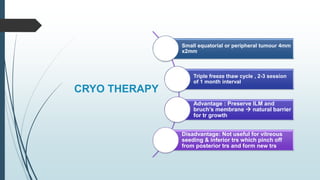
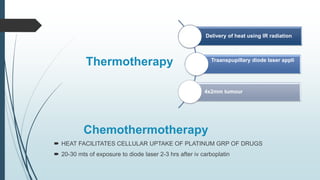
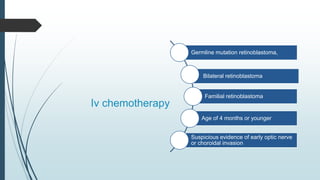
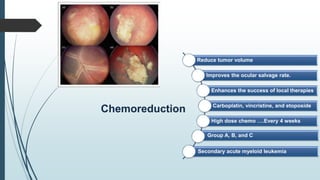
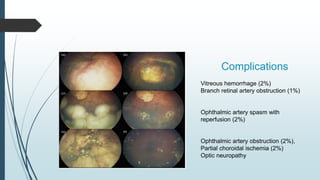
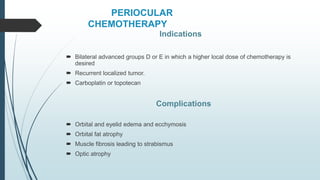
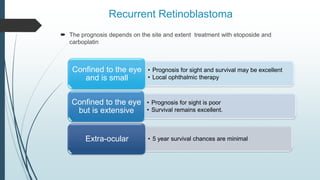
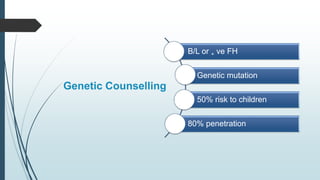
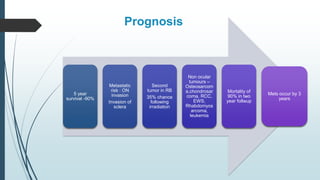
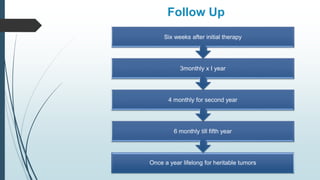
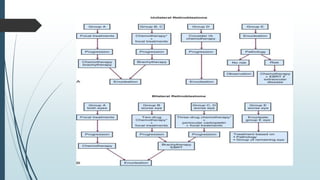
Retinoblastoma, first named in 1926, is the most common intraocular malignancy in children, with a diagnosis typically occurring around 18 months of age. The disease arises from retinoblasts and is associated with mutations in the RB gene located on chromosome 13, with familial cases constituting 6% of occurrences. Diagnosis involves family history, physical examination, and various imaging techniques, while treatment options range from enucleation and chemotherapy to laser therapies, with a 5-year survival rate of approximately 90% in non-metastatic cases.