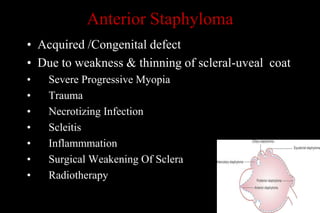
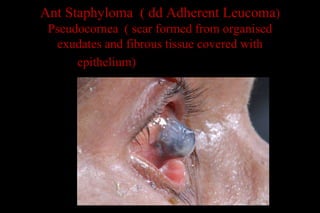
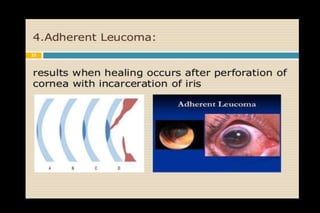
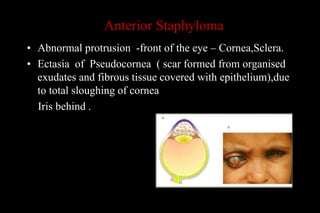
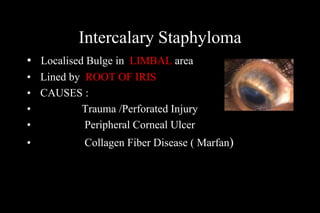
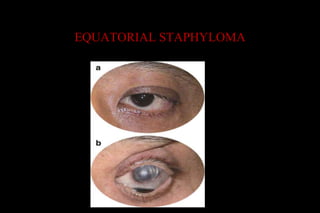
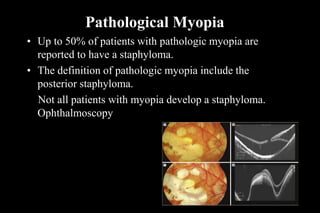
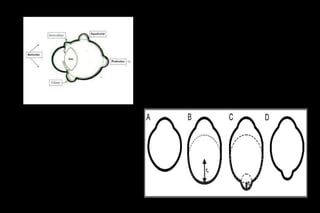
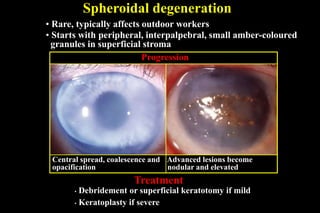
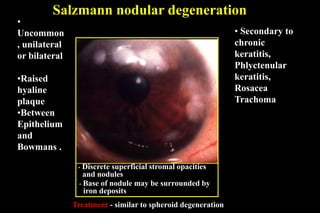
This document discusses different types of staphylomas, which are abnormal protrusions of the eyeball that can occur in various locations. Anterior staphylomas involve bulging of the cornea and sclera near the front of the eye. Posterior staphylomas occur behind the equator and involve bulging of the sclera lined by the choroid. Staphylomas can be caused by conditions like severe myopia, trauma, infection, inflammation, and certain collagen disorders. Complications may include glaucoma or reduced vision. Treatment depends on the type and severity but may involve surgery or steroids.