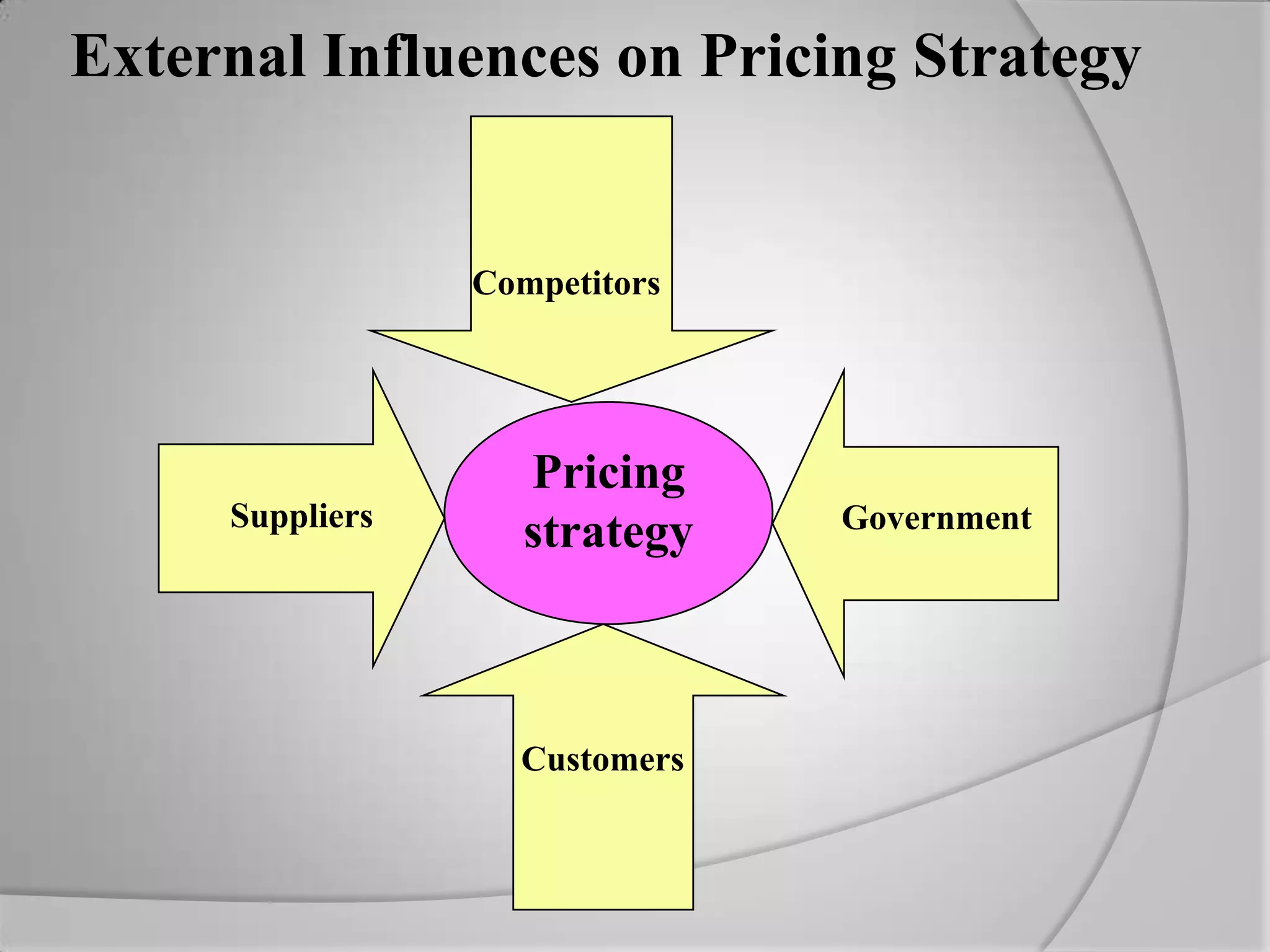
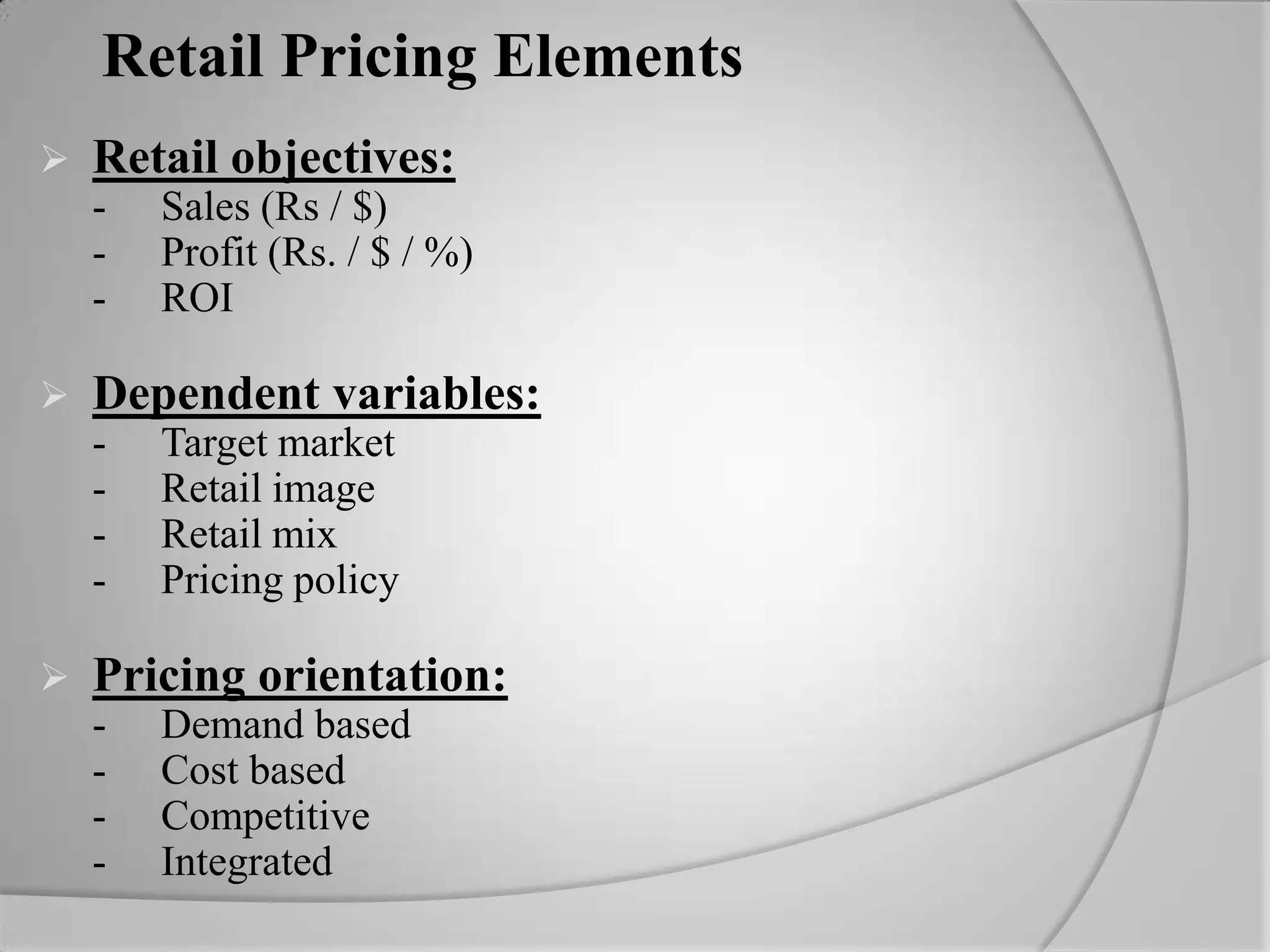
The document discusses retail pricing strategies. It begins by defining the goals of setting the right price that is acceptable to both consumers and retailers. It then outlines various external factors that influence pricing decisions. The document goes on to explain different pricing elements, objectives, and dependent variables that must be considered. It provides details on several specific pricing strategies retailers can employ, such as customary pricing, variable pricing, price lining, and leader pricing. It also discusses cost-oriented pricing approaches like markup pricing and markdown pricing. The overall document serves as a guide for retailers to understand how to establish prices for their merchandise.