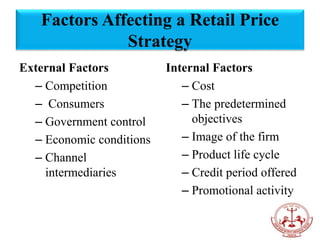
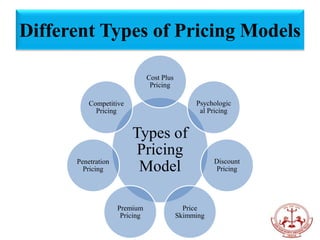
Retail pricing is a crucial aspect of the retail marketing mix, influencing revenue and brand image. It involves considering factors such as product demand, market competition, and economic conditions, while employing various pricing strategies like cost-plus, competitive, or psychological pricing. Additionally, both internal and external factors, including consumer behavior and government regulations, play significant roles in shaping a retailer's pricing approach.