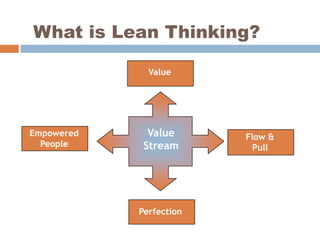
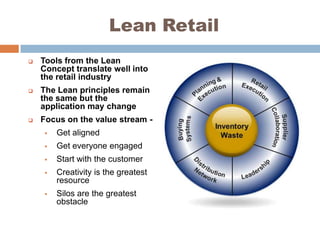
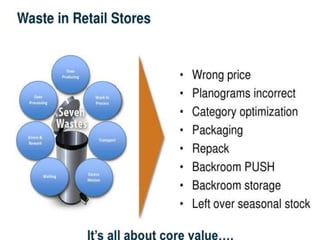
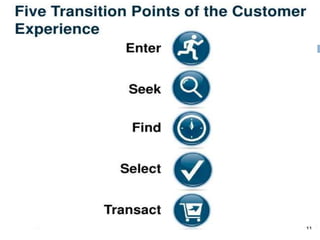
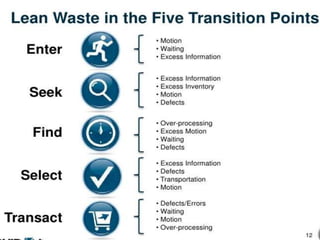
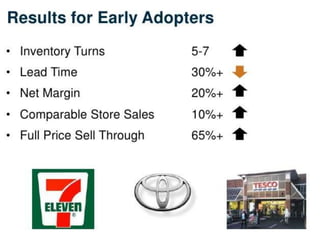
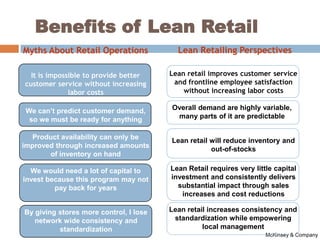
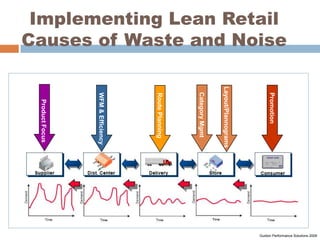
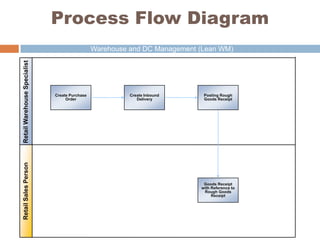
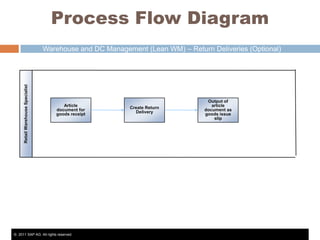
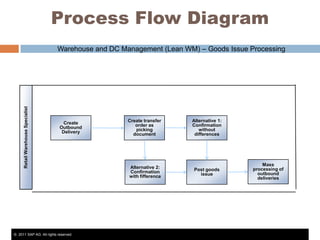
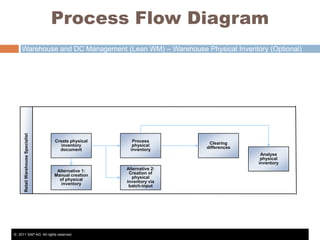
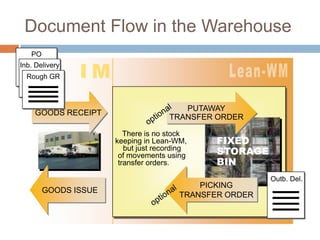
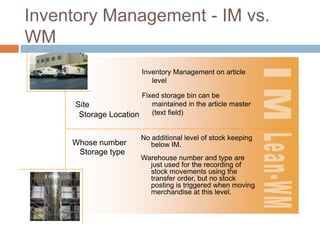
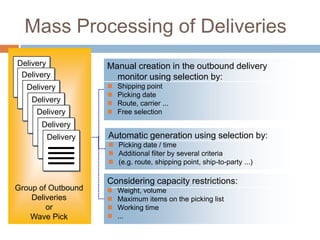
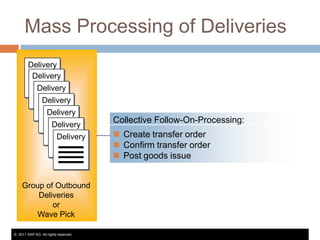
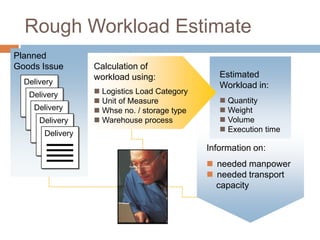
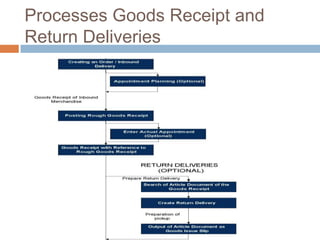
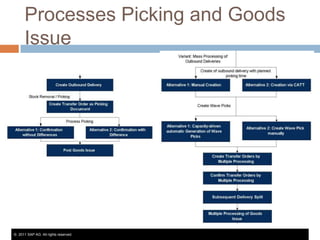
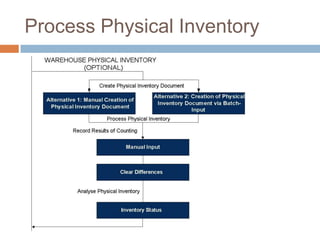
The document discusses the implementation of lean retail management, emphasizing the reduction of waste and enhancement of customer value through various lean techniques. It outlines the principles of lean retail execution and provides a scenario on lean warehouse management, highlighting key processes and benefits. Additionally, it addresses common misconceptions about lean retail and its ability to improve customer service without incurring additional costs.