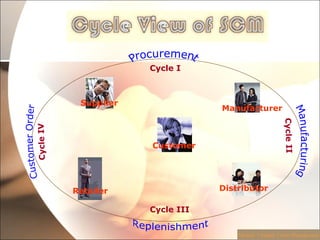
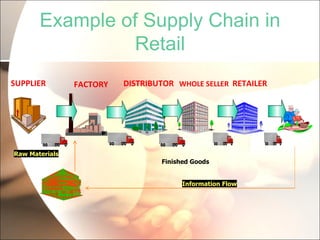
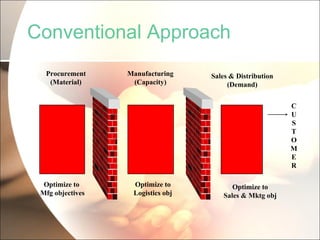
The document discusses supply chain management (SCM) in retail. It defines SCM as the flow of goods from raw materials to the end customer, involving manufacturers, suppliers, transporters, warehouses, retailers. The objectives of SCM in retail are to reduce costs, save time, increase customer satisfaction and profit margins. An integrated SCM coordinates activities across the supply chain from suppliers to customers. This improves delivery, reduces inventory and costs, and increases productivity and forecasting accuracy.
![Supply Chain Management in Retail Submitted By: Uday Mishra GSBA G. Noida [email_address] 9891683518](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scm-in-retail-1234766255422197-1/85/Scm-In-Retail-by-Uday-mishra-1-320.jpg)