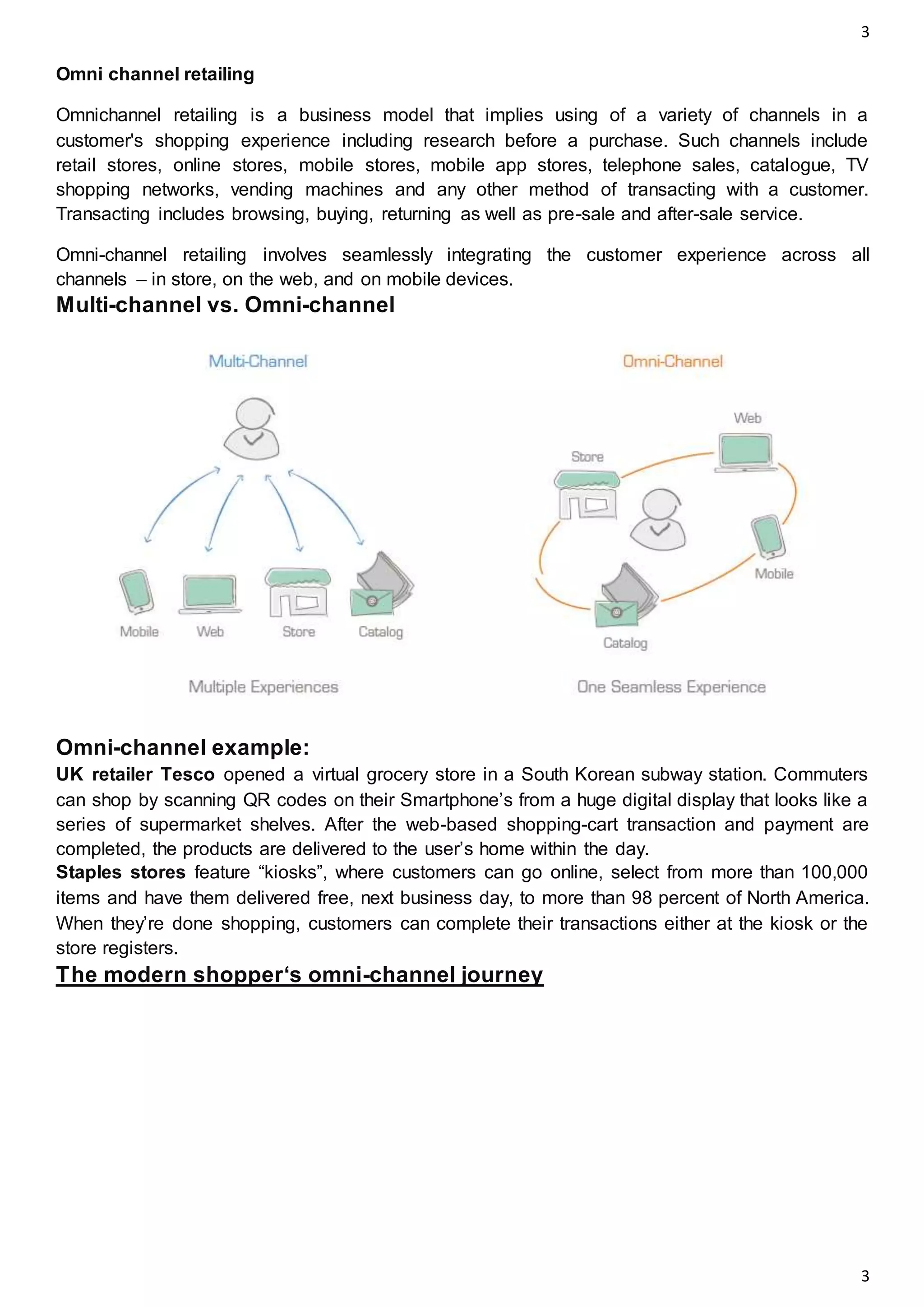
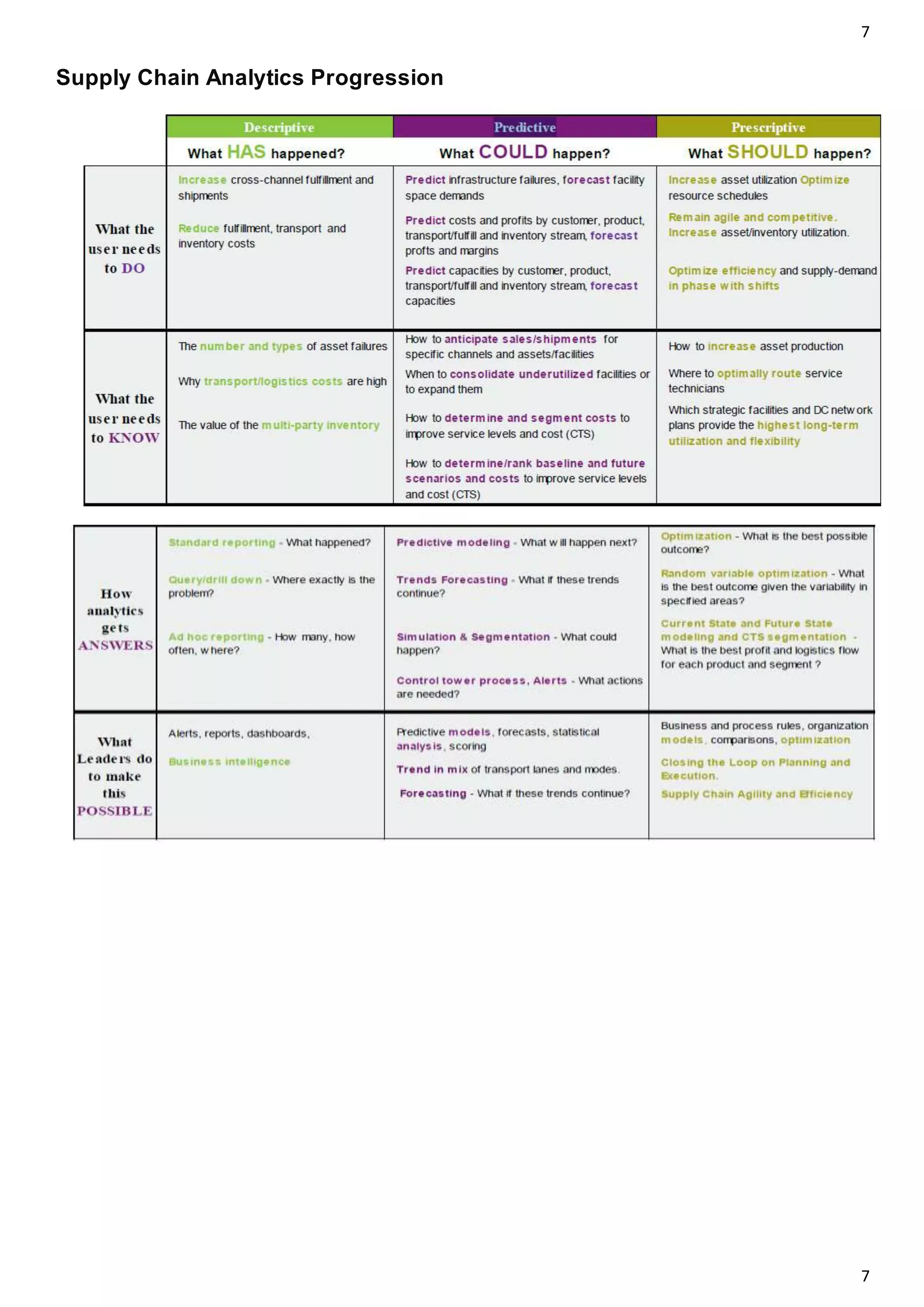
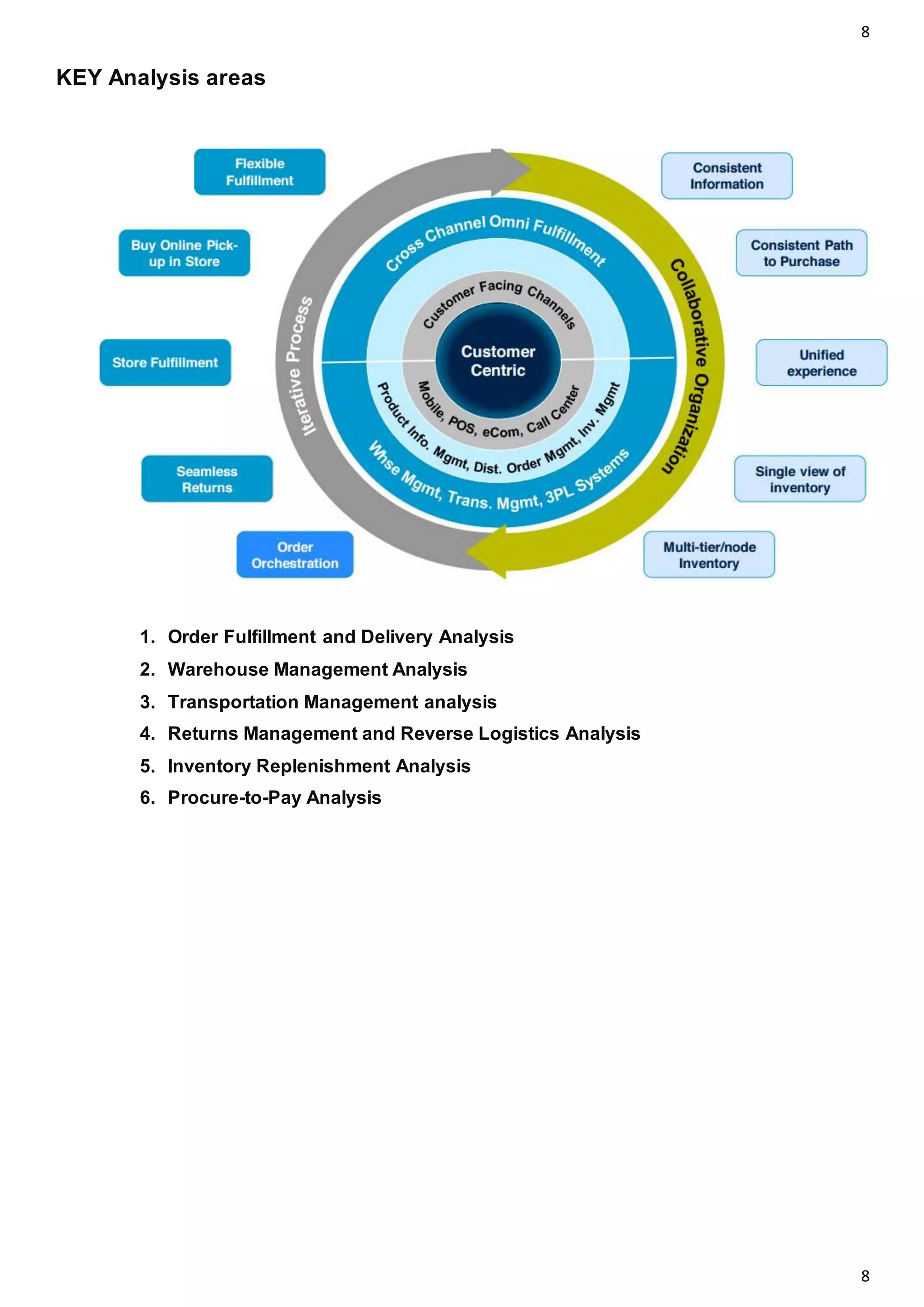
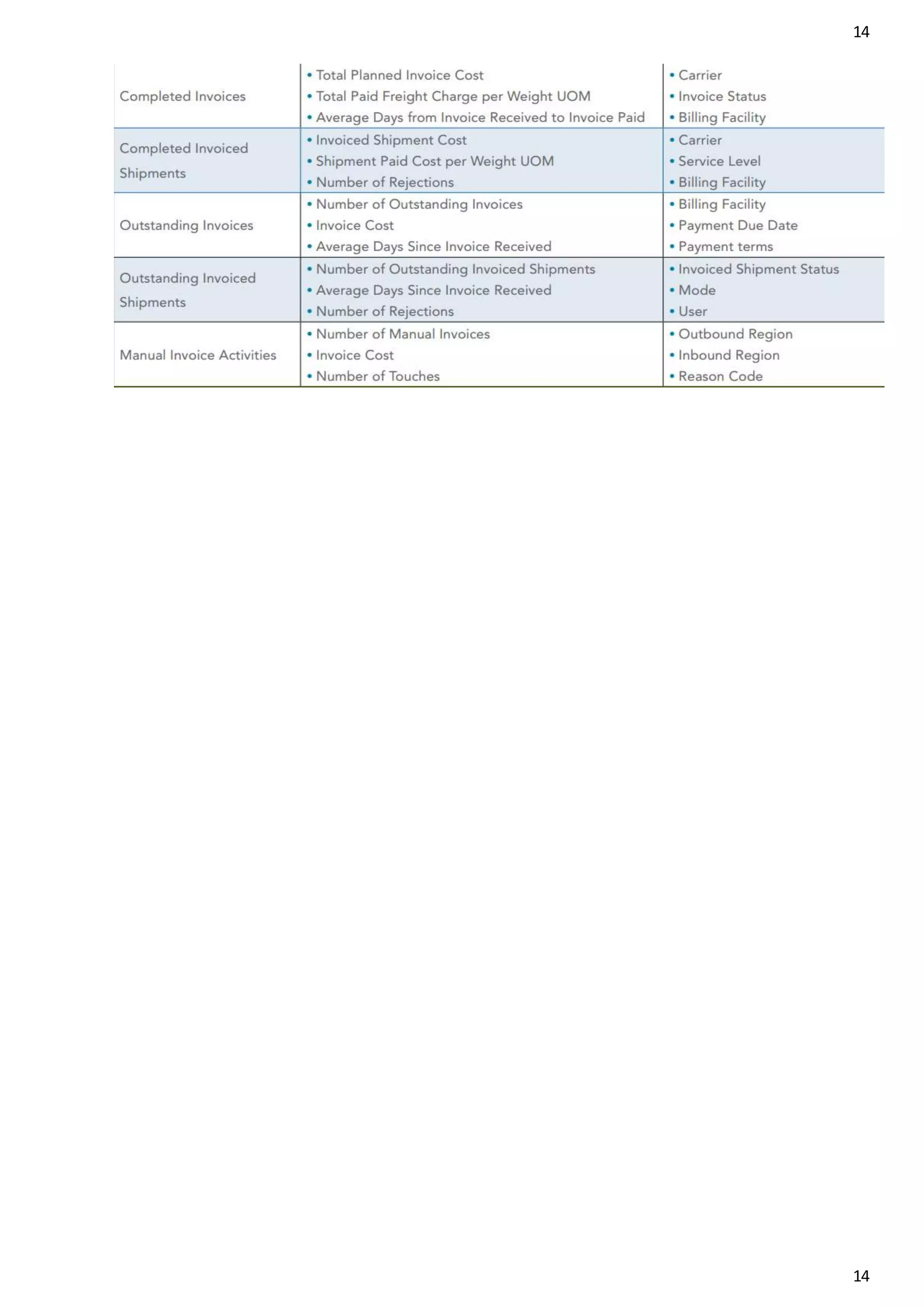
The document outlines the concept of omni-channel retailing, emphasizing the integration of various shopping channels to enhance customer experience. It identifies key stakeholders, challenges in supply chain management, and analytics necessary for effective order fulfillment, inventory management, and returns processing. The text also highlights the significance of responsive distribution networks and real-time tracking in optimizing omni-channel operations.