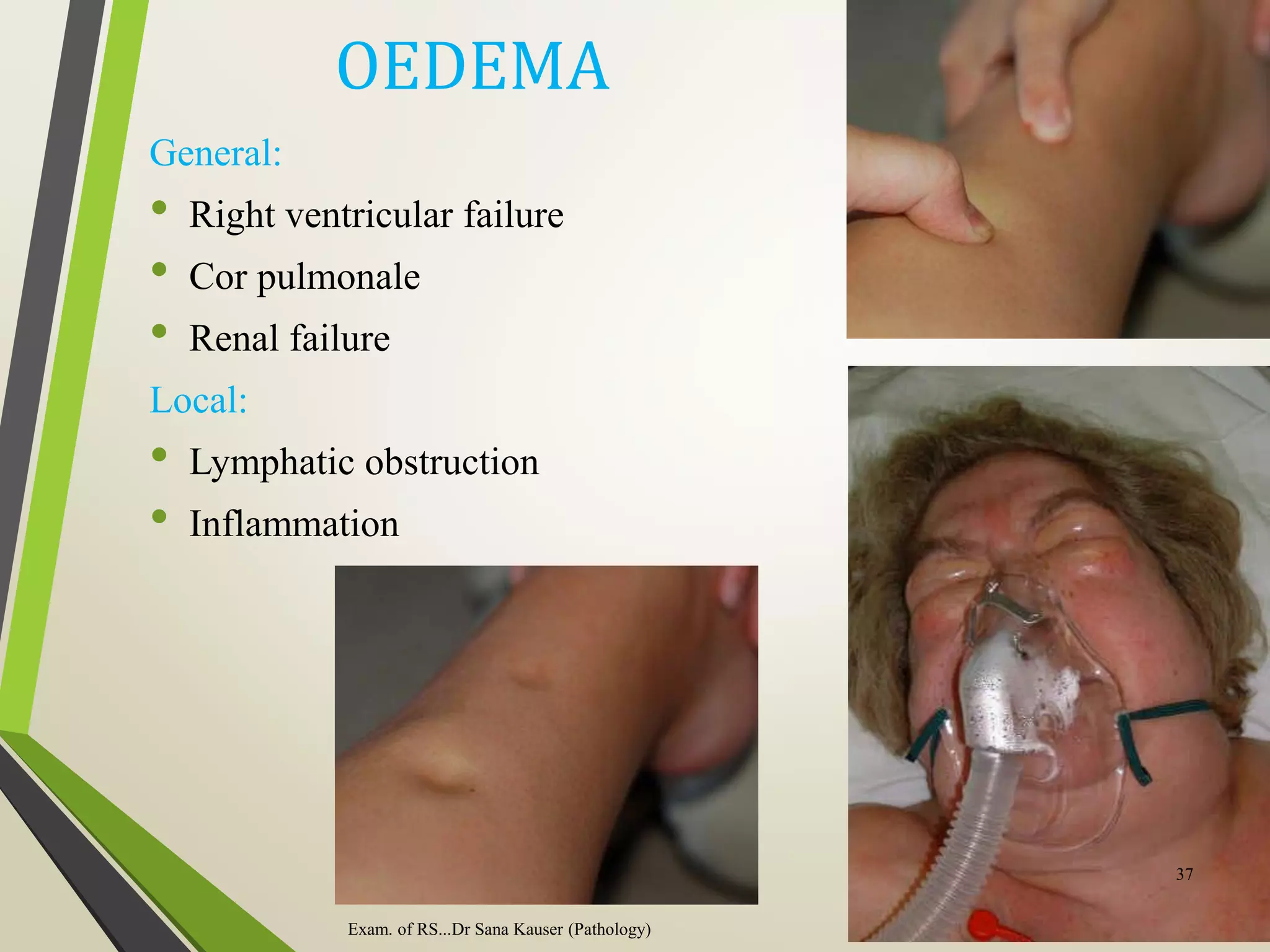
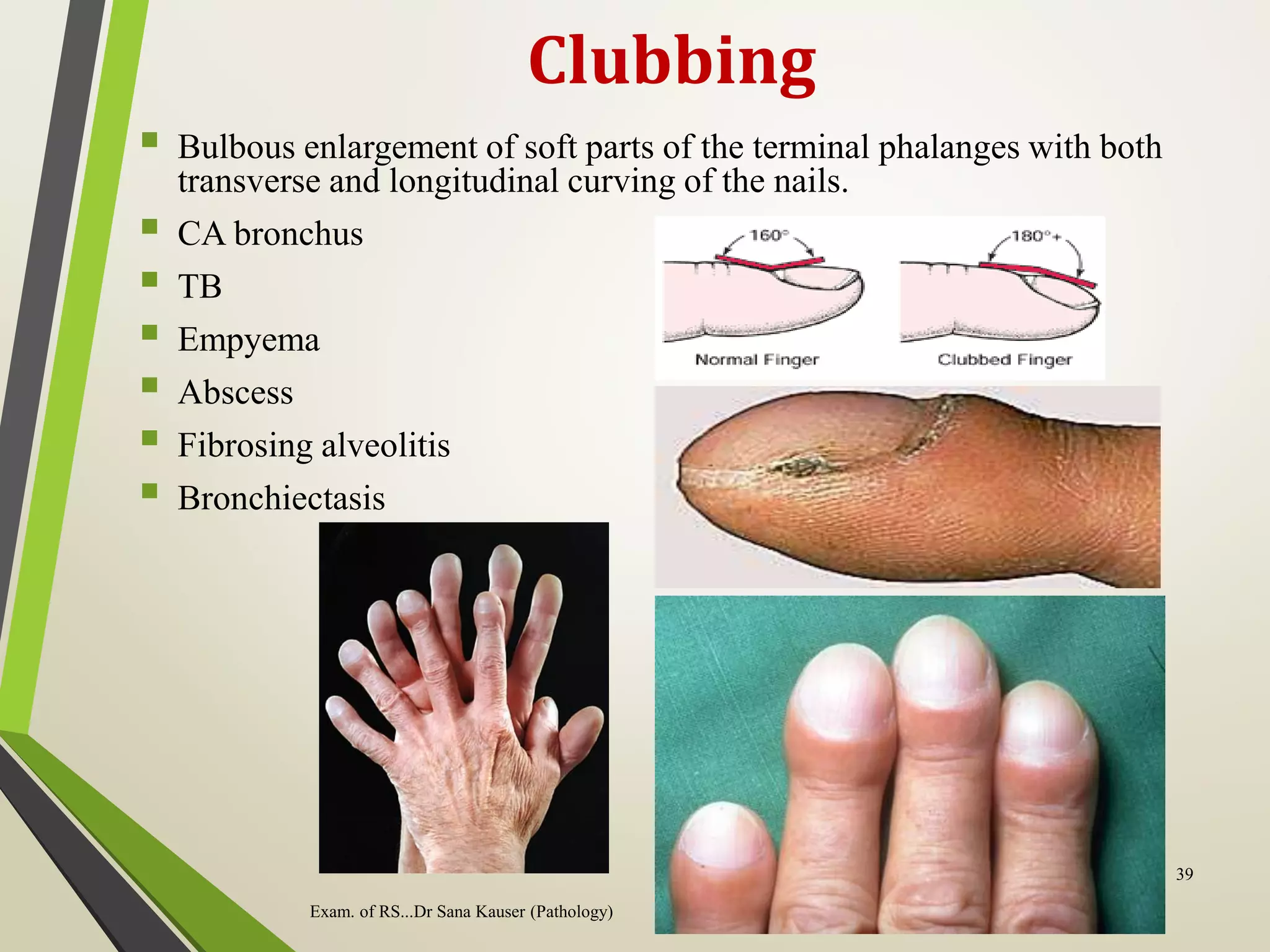
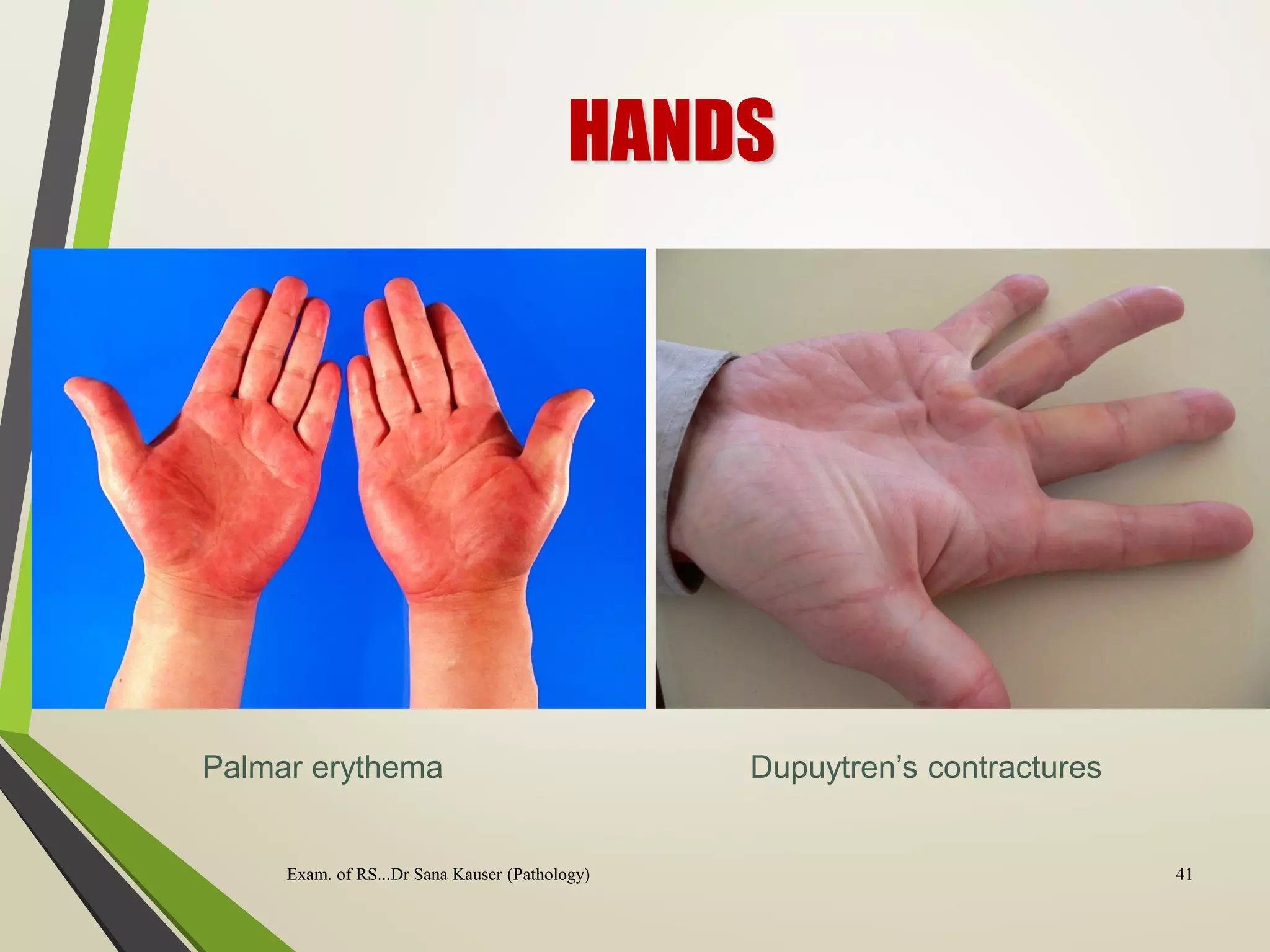
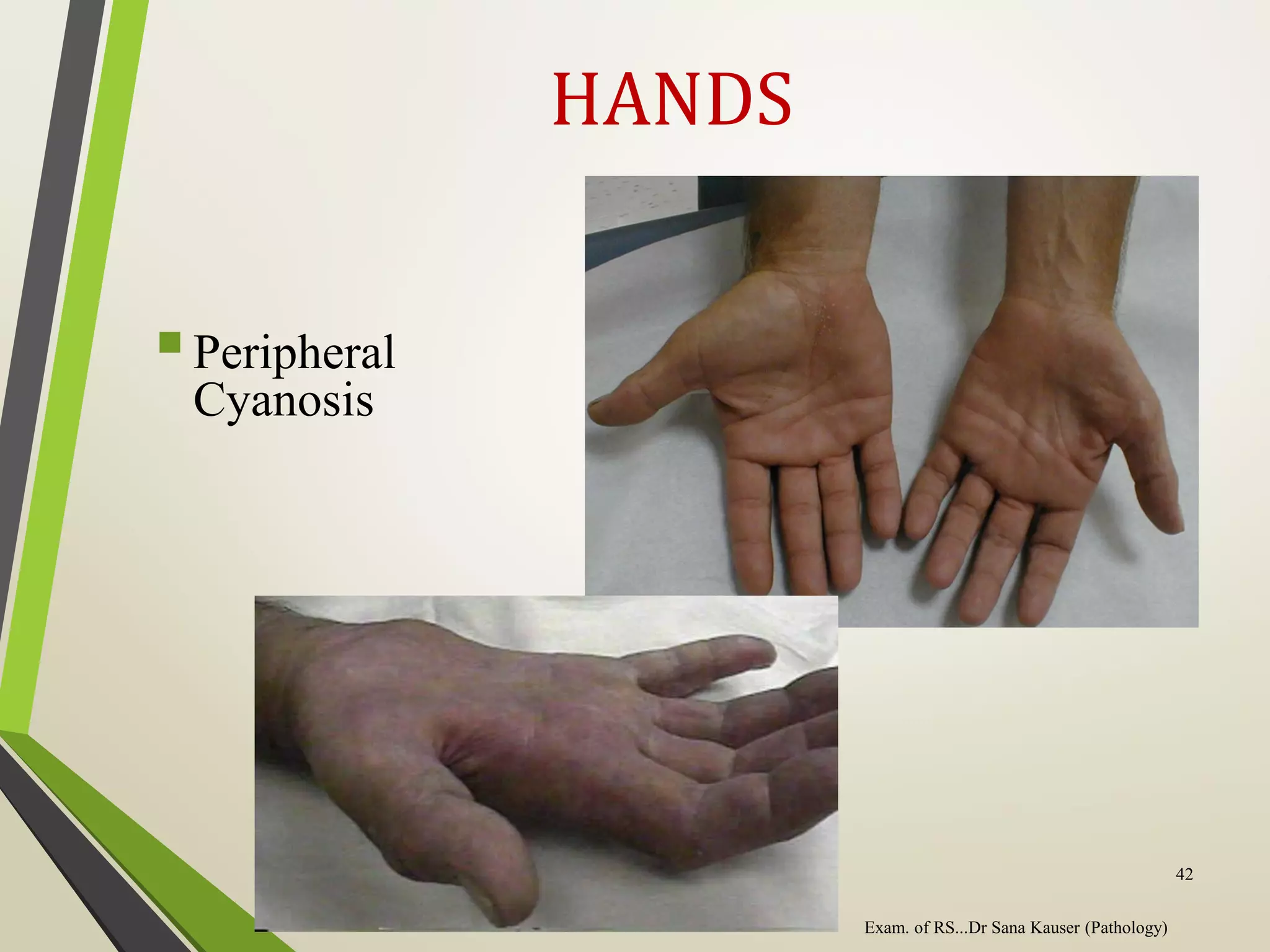
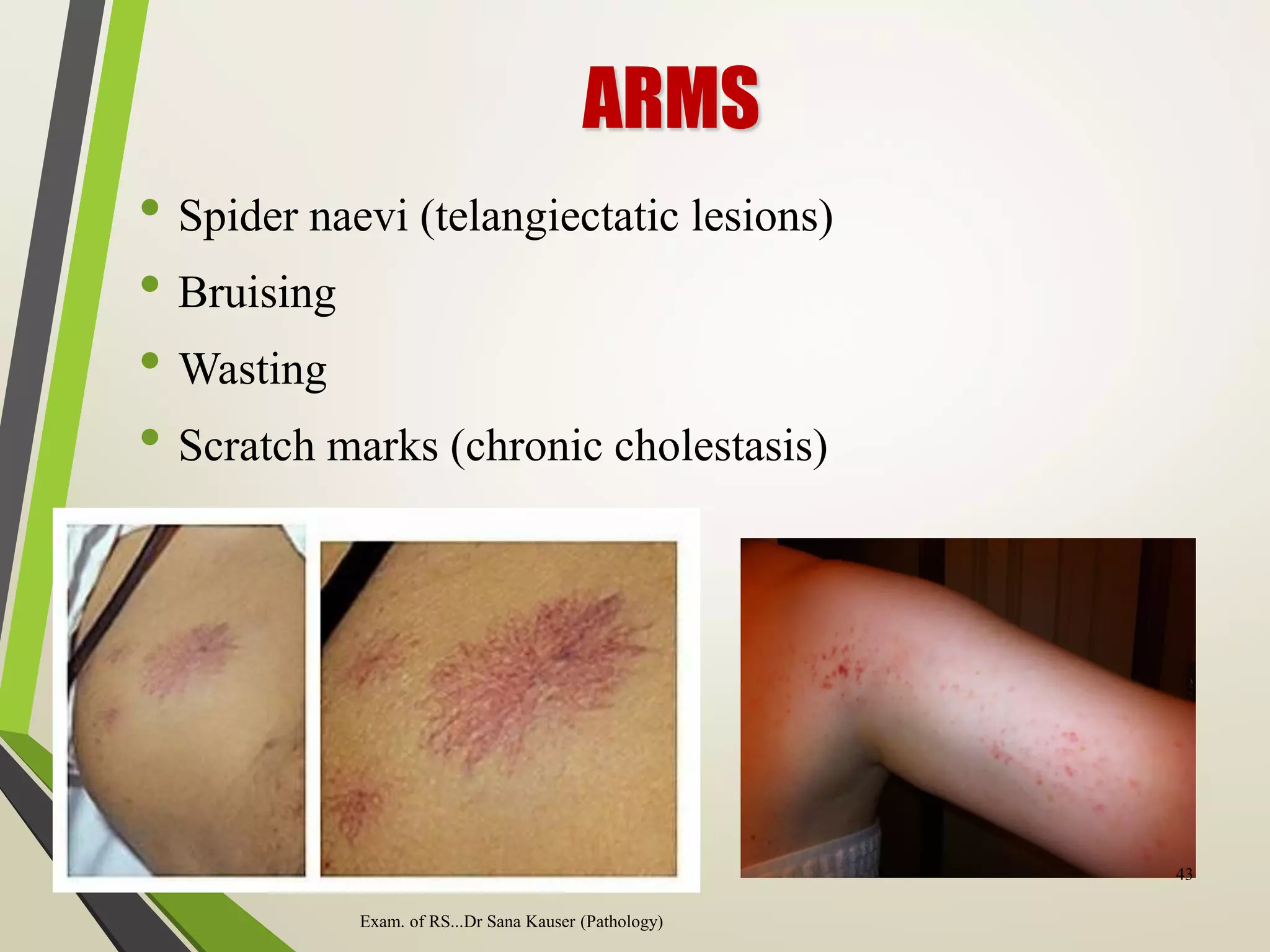
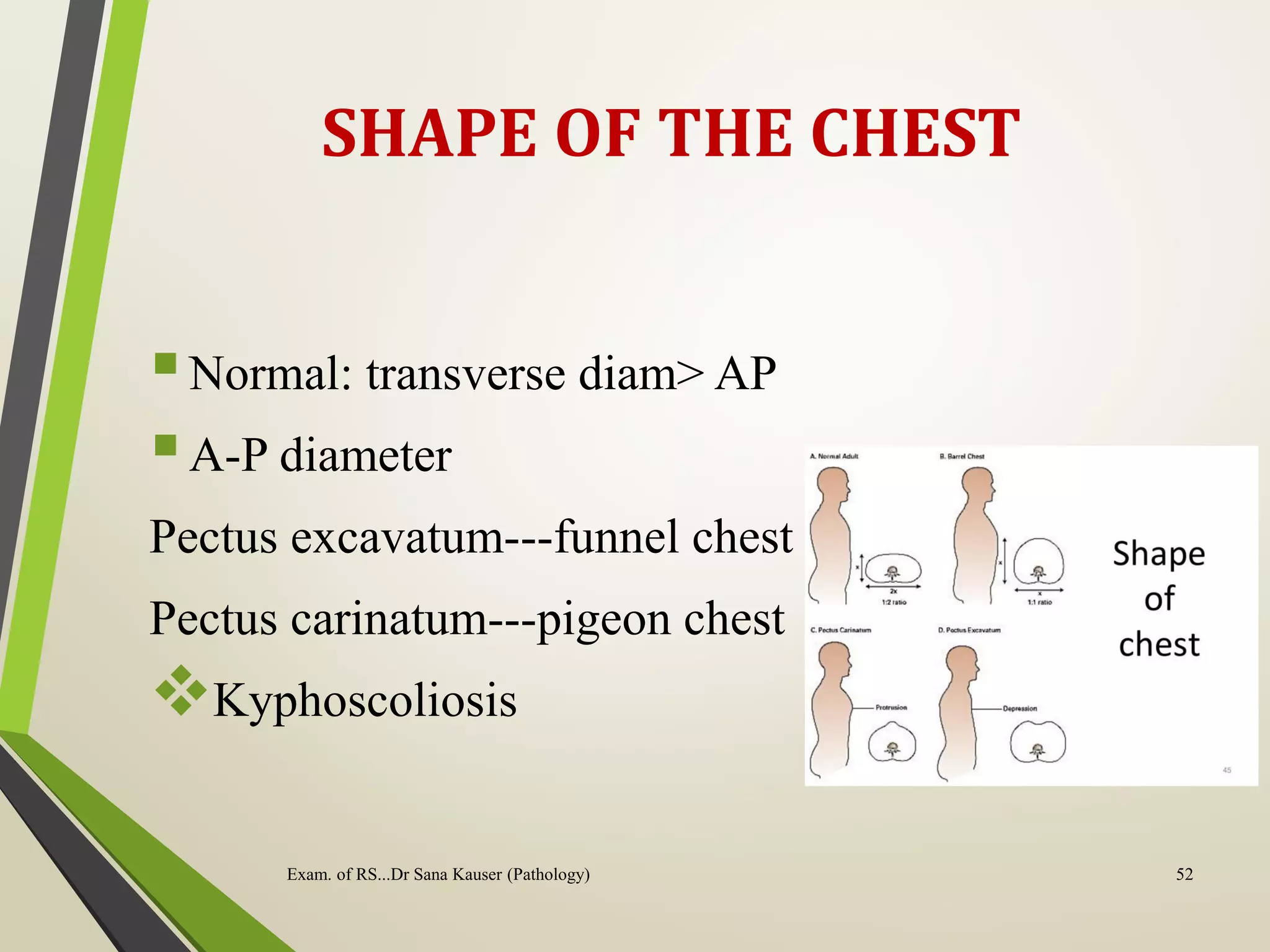
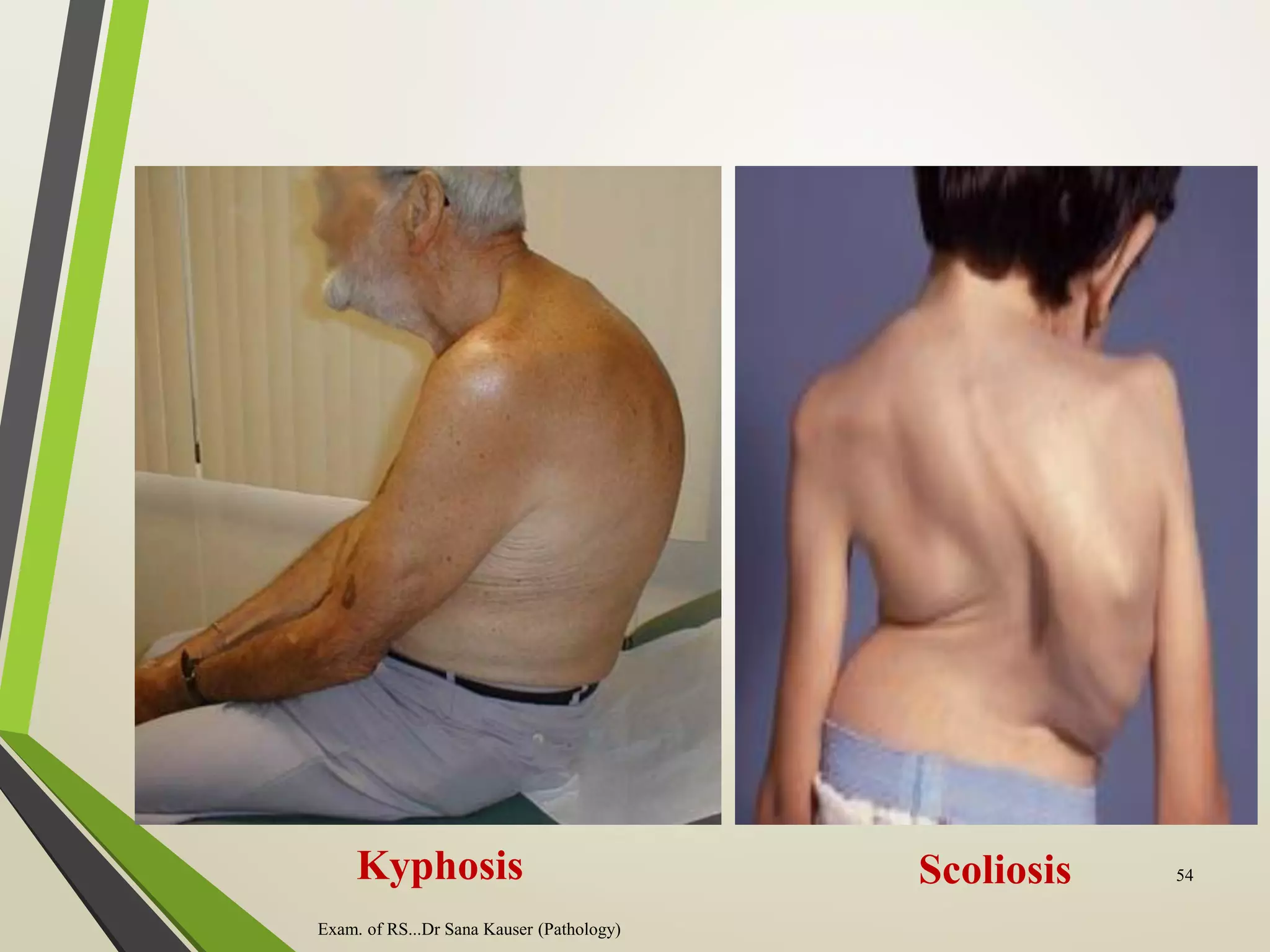
Regular or irregular
Exam. of RS...Dr Sana Kauser (Pathology) 55
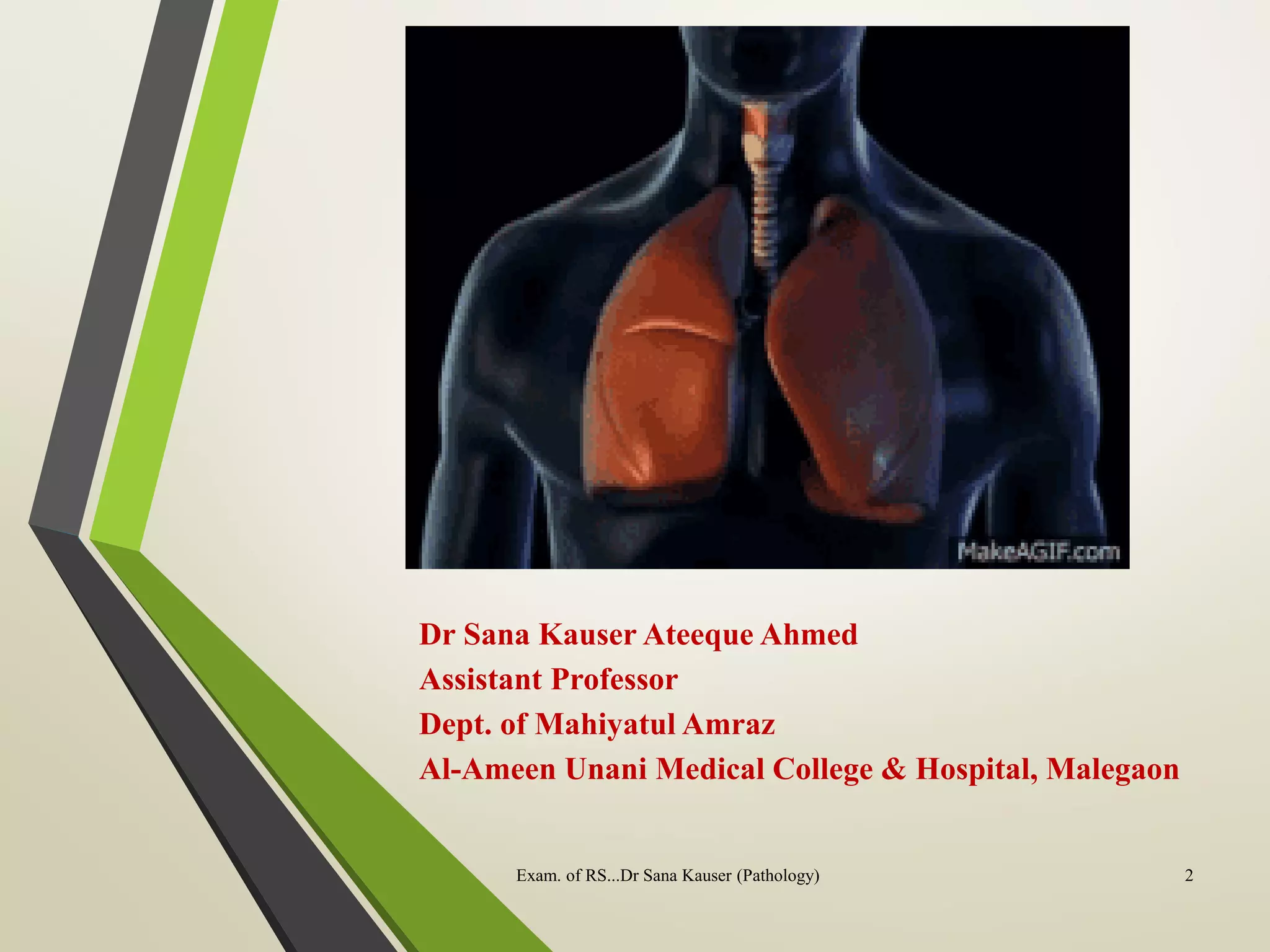
�INSPECTION
• Chest movements
- Symmetrical or asymmetrical
- Equal or unequal
- Paradoxical movement
- Use of accessory muscles
- Diaphragmatic movements
- Flail chest
Exam. of RS...Dr Sana Kauser (Pathology) 56
�Paradoxical movement
- Inward movement of chest wall during inspiration in conditions like
- Tension pneumothorax
- Flail chest segment
- Diaphragmatic hernia
Use of accessory muscles
- Supraclavicular, infraclavicular, intercostal retractions seen in















































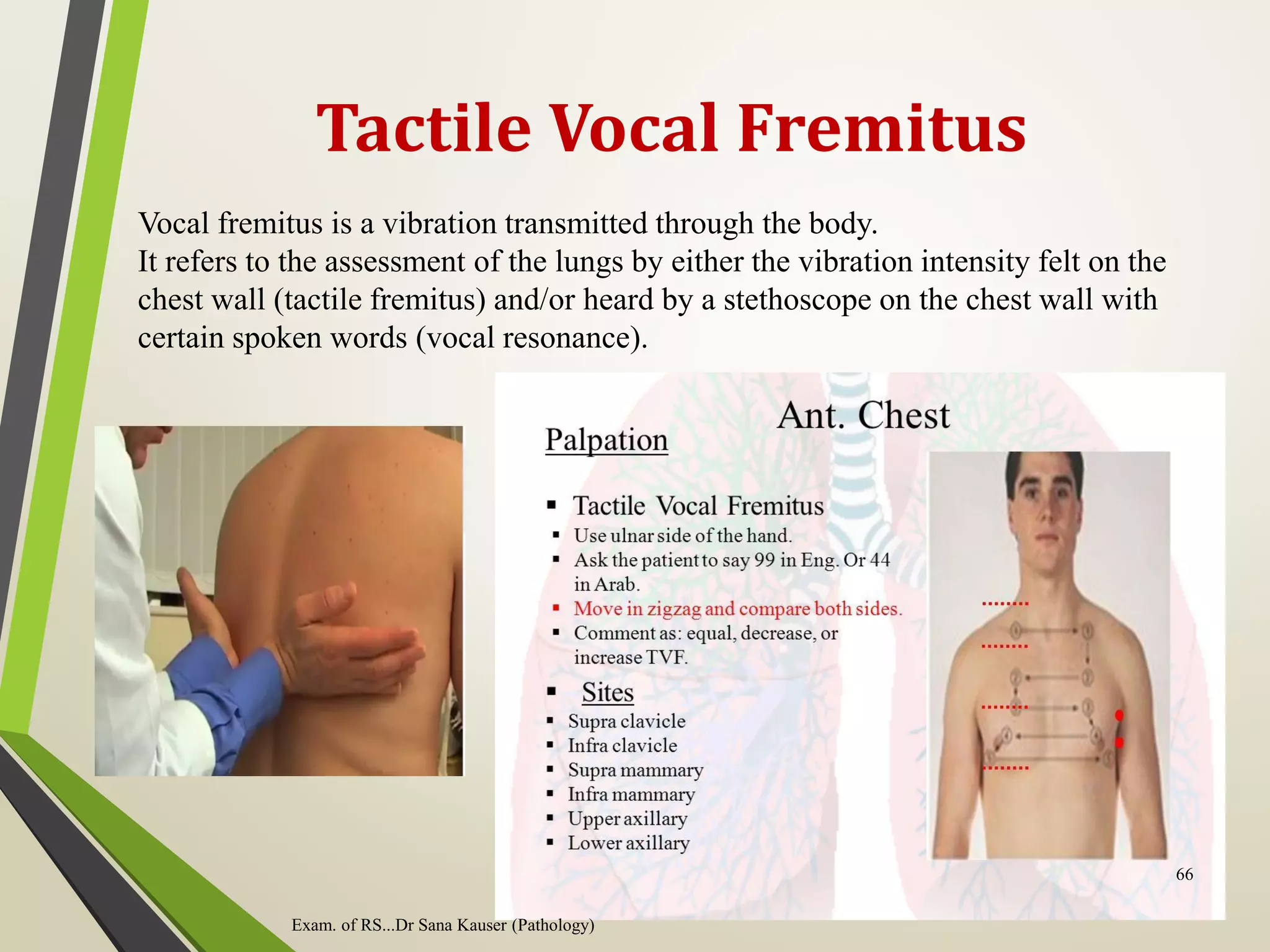
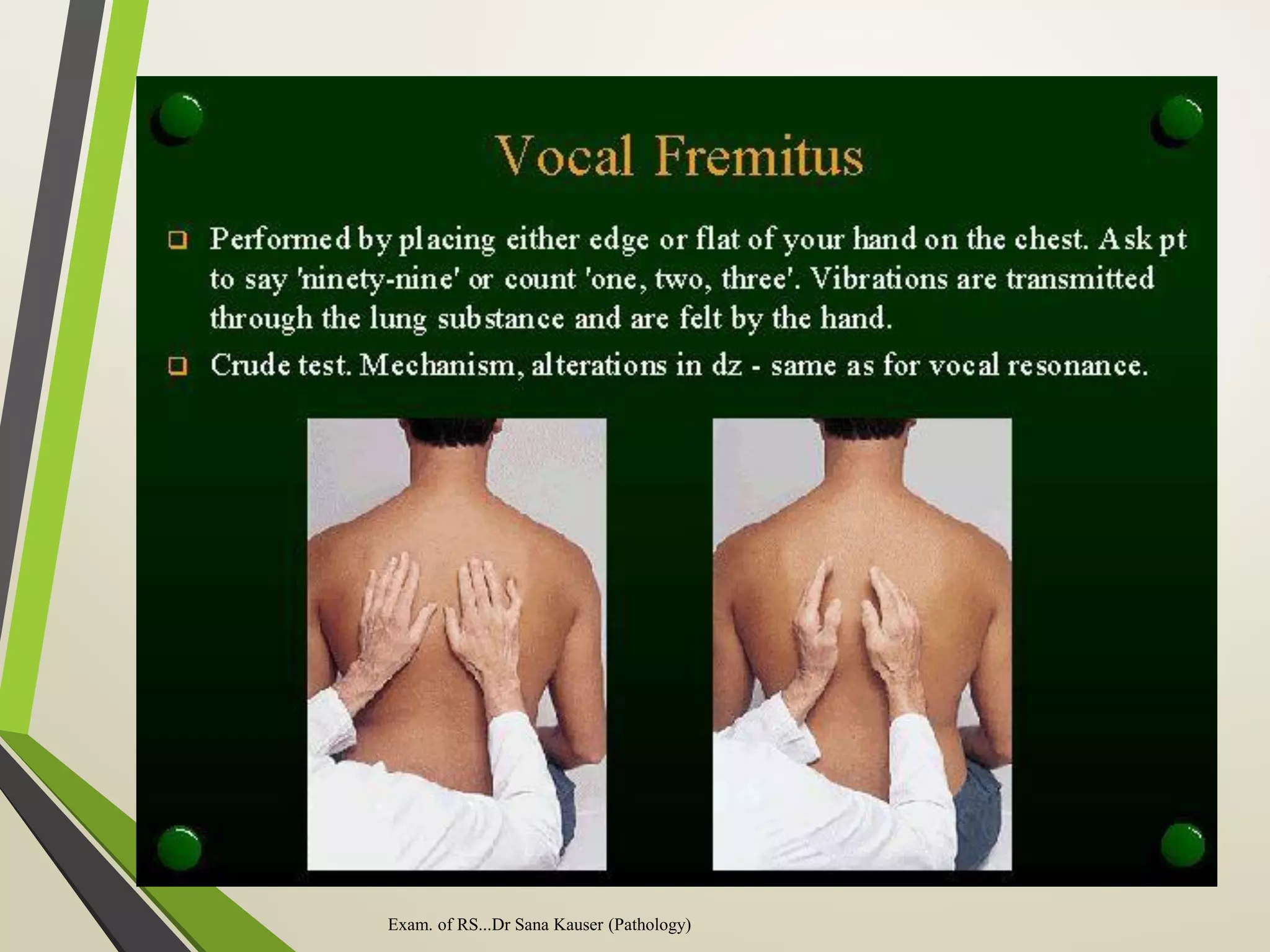


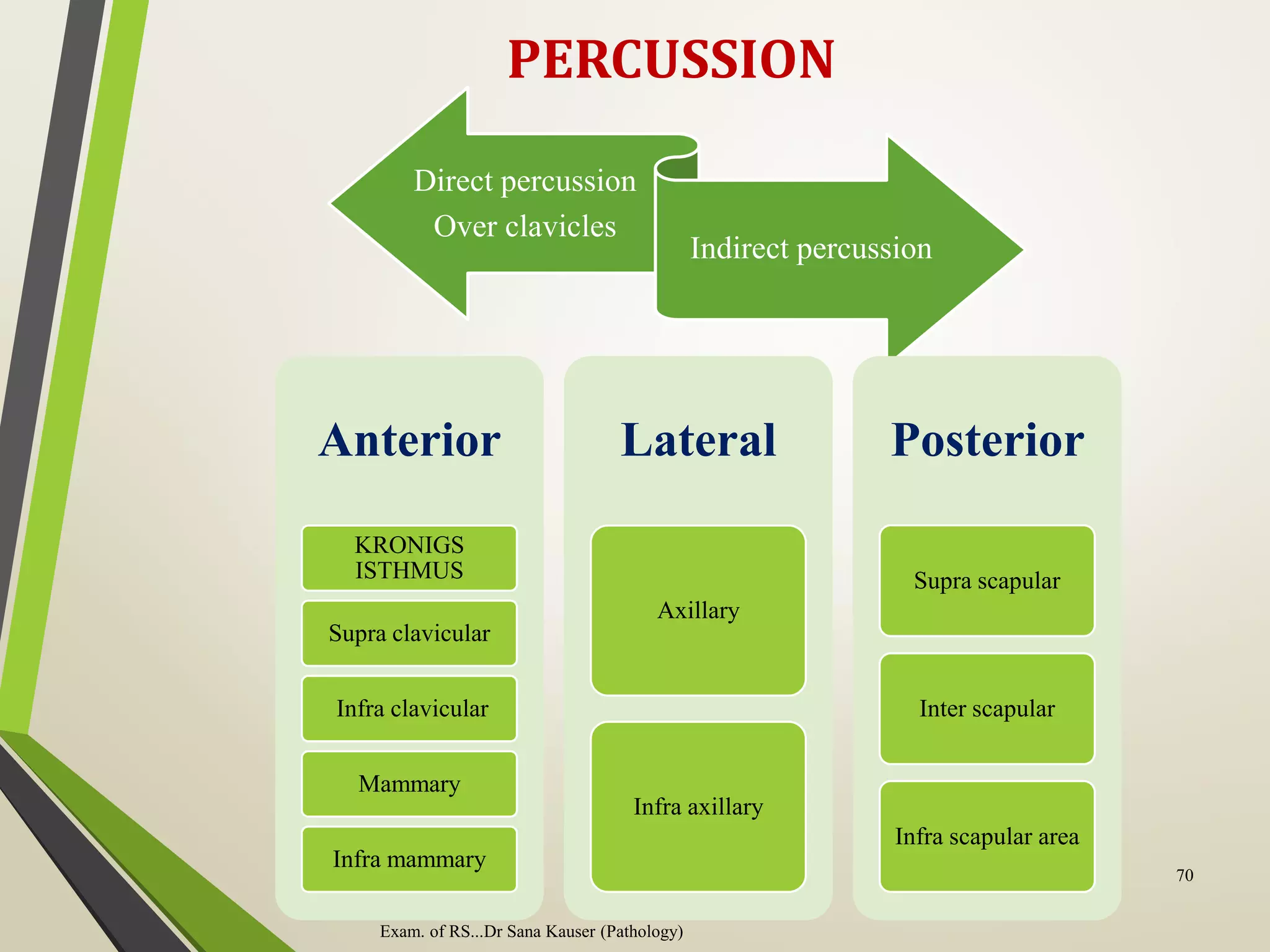



![Cont…
• Kronig isthmus is a band of resonance representing
the apex of lung,[1] also it's described as the narrow strap-
like portion of the resonant field that extends over
the shoulder, that connect the larger areas of resonance
over the pulmonary apex in front and behind.[2
• Skodaic resonance - a peculiar, high-pitched sound, less
musical than that obtained over a cavity, elicited by
percussion just above the level of a pleuritic effusion.
• Shifting dullness and fluid thrill (wave) are clinical signs
that confirm ascites. Free fluid will flow to the dependent
part of the abdominal cavity, while the gut filled with air
will float in the middle. If the child is supine, the fluid
collects posteriorly and in the flanks.
Exam. of RS...Dr Sana Kauser (Pathology)
74](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/respiratorysystemexam-230513050217-c6f2bb77/75/Respiratory-System-Exam-Dr-Sana-Kauser-Patho-pdf-72-2048.jpg)















