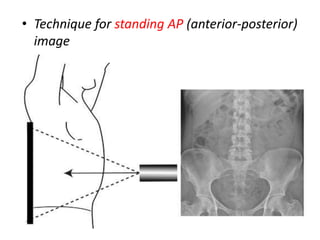
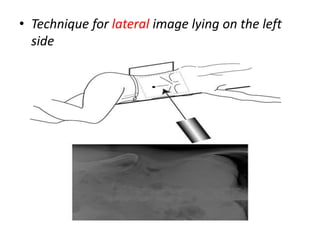
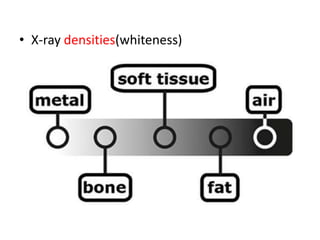
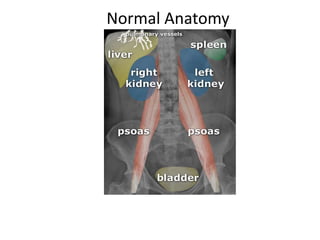
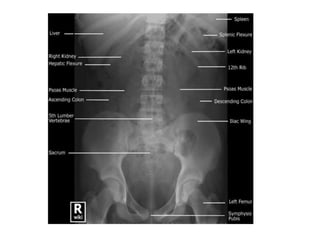
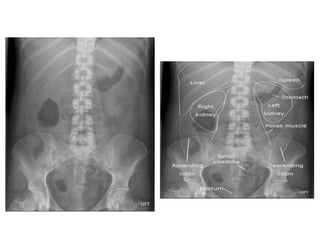
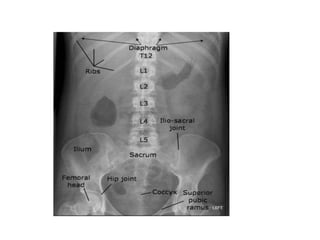
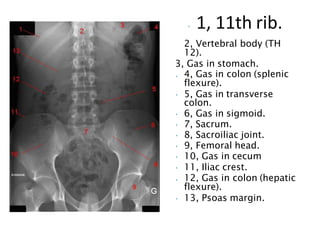
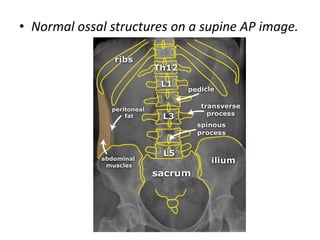
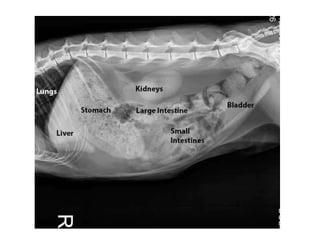
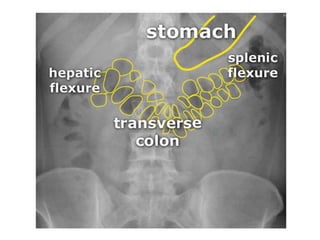
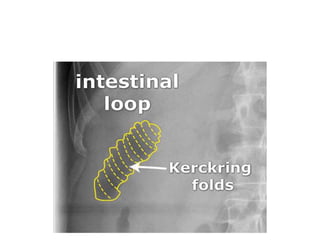
This document discusses abdominal x-rays (AXR), including their indications, techniques, normal anatomy, and checklist for assessment. AXRs can be used to detect bowel obstructions, perforations, renal pathology, foreign bodies, and more. They are performed in supine, standing, or lateral positions. Normally on AXR, gas appears black, fat is dark grey, soft tissue is light grey, bone/calcification is white, and metal is intense white. Key structures like ribs, vertebrae, stomach, intestines, and sacrum should be identifiable. The checklist recommends assessing technique, psoas muscle visibility, organ contours, calcifications, intestinal positioning and dilation, free air, skeletal changes, and