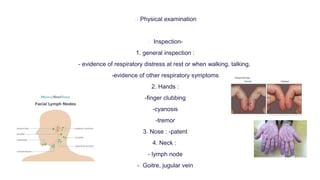
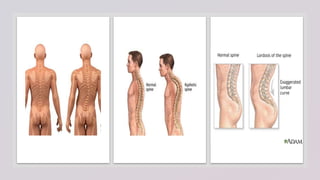
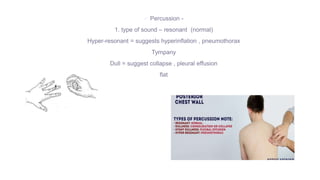
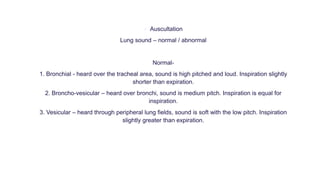
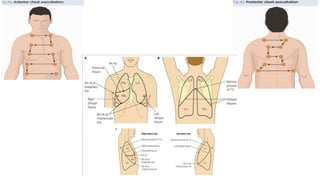
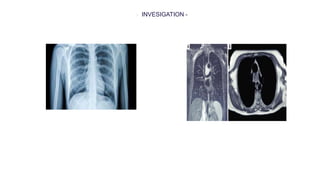
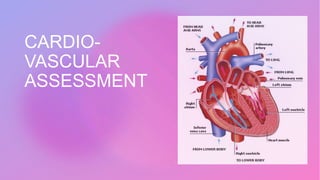
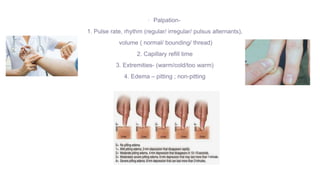
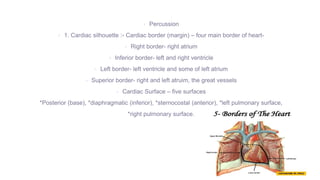
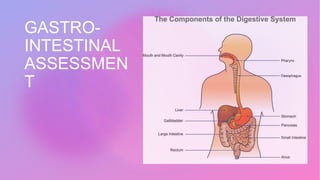
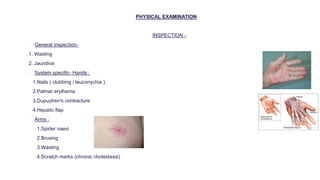
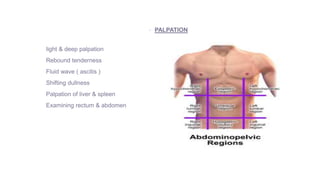
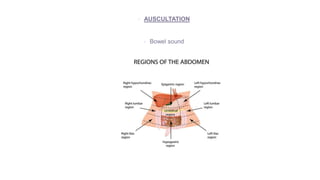
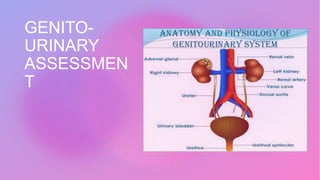
This document provides information on assessing different body systems including respiratory, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and genitourinary systems. It discusses collecting relevant history, performing a physical examination, and ordering appropriate diagnostic tests for each system. The history sections cover current health issues, past medical history, family history, and psycho-social factors. The physical examinations describe inspection techniques like auscultation of the lungs and palpation of the abdomen. Common complaints, exam findings, and potential diagnostic tests are also outlined for each assessment.