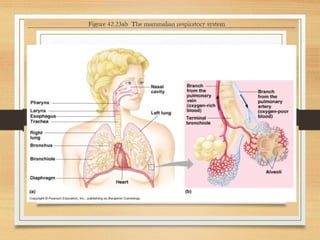
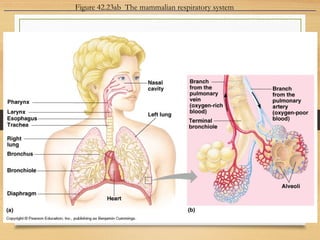
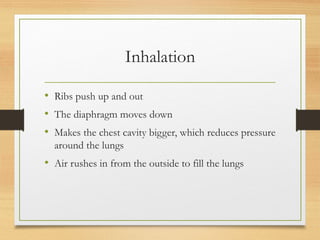
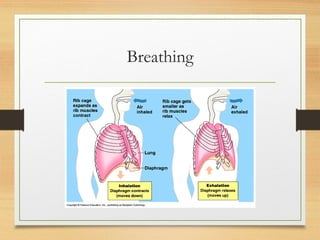
The document summarizes the key parts and functions of the human respiratory system including the nasal cavity, pharynx, epiglottis, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, and diaphragm. It also describes gas exchange that occurs in the lungs where oxygen diffuses into blood cells and carbon dioxide diffuses out. The process of breathing is explained including how inhalation and exhalation are controlled by the diaphragm and intercostal muscles to expand and contract the chest cavity.