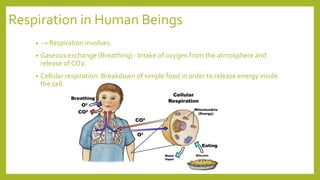
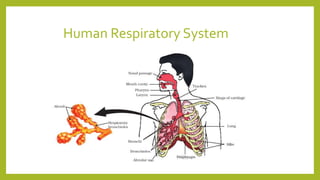
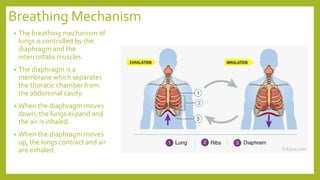
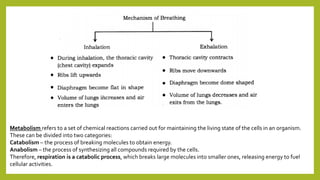
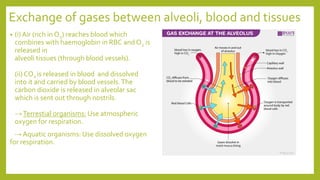
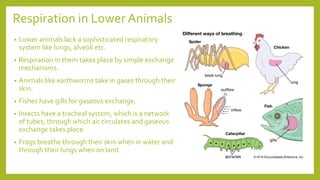
Respiration involves two processes - breathing, which is the exchange of gases between the atmosphere and cells, and cellular respiration, which breaks down food inside cells to release energy. In humans, respiration occurs through a respiratory system that filters and transports air through the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli and blood capillaries, facilitating gas exchange between inhaled air and blood. The diaphragm and intercostal muscles control breathing by expanding and contracting the lungs to inhale and exhale air.