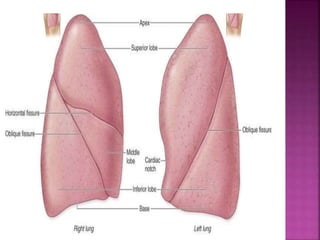
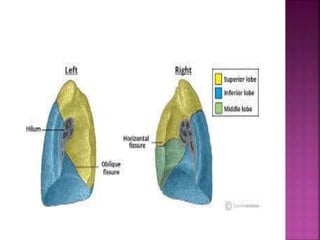
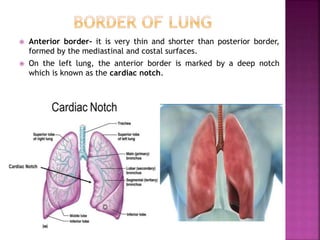
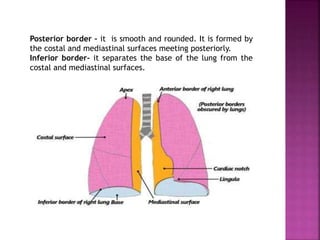
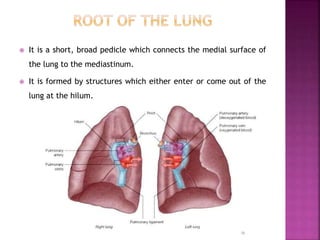
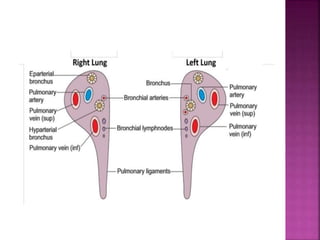
The document summarizes the anatomy and structure of the lungs. It describes the lungs as a pair of spongy, expandable respiratory organs located in the thoracic cavity. Each lung is divided into lobes by fissures and has two surfaces - a costal surface facing the chest wall and a medial surface facing the mediastinum. The lungs receive blood supply from both the bronchial circulation and pulmonary circulation and are innervated by the pulmonary plexus of nerves.