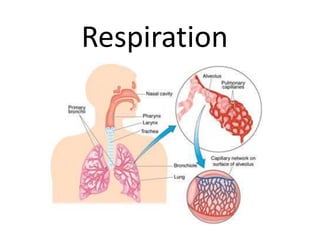
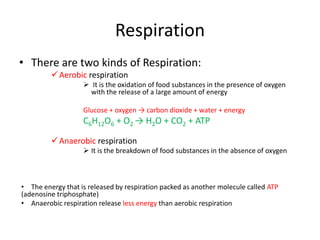
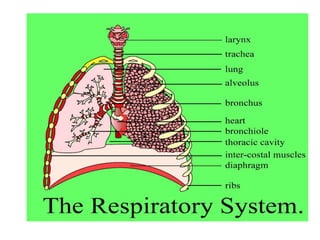
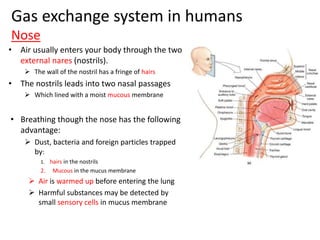
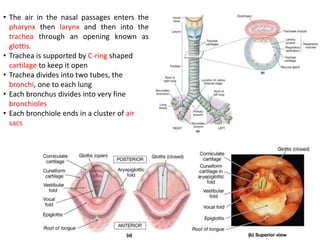
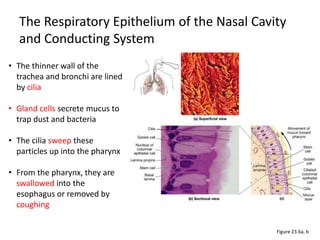
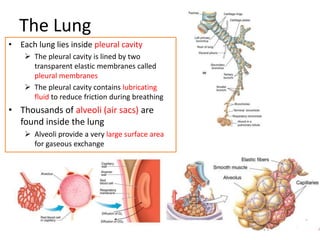
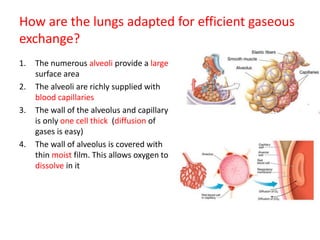
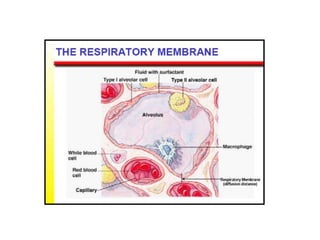
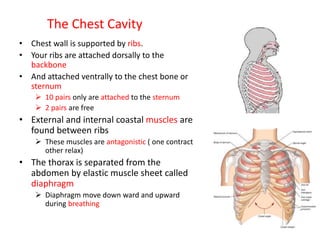
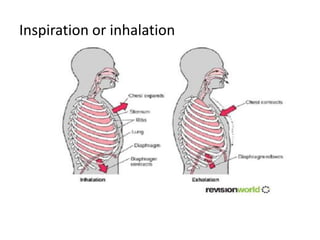
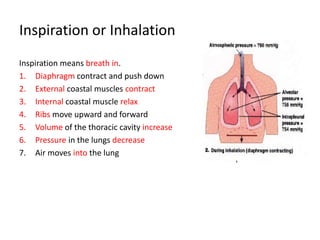
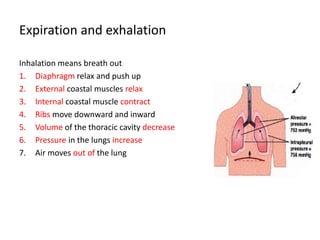
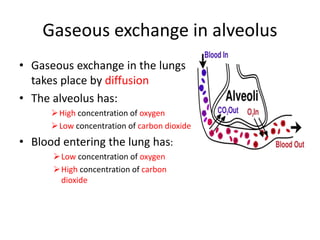
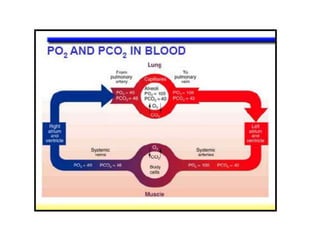
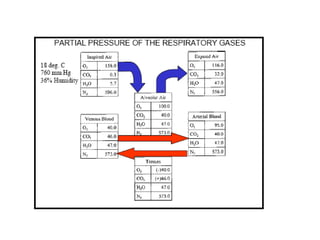
Living organisms respire to gain energy from food to power essential functions like movement, growth, and reproduction. Respiration involves the breakdown of food molecules through oxidation, releasing energy that is captured in ATP. There are two types of respiration: aerobic respiration uses oxygen to fully break down glucose, producing much more energy, while anaerobic respiration occurs without oxygen, generating lactic acid and less energy. Respiration takes place in cells across living things to fuel their various energy-requiring processes.