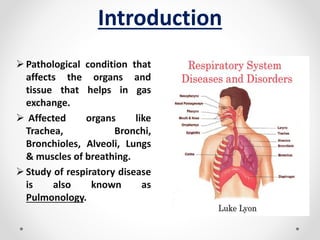
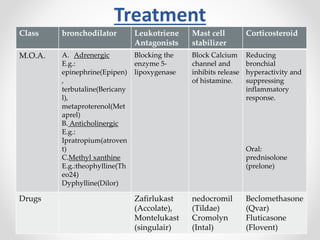
The document discusses respiratory diseases, outlining their classification into infectious diseases, obstructive lung diseases, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It presents the prevalence of various respiratory conditions, their etiologies, diagnostic tools, and treatment options, including medications for conditions like asthma, tuberculosis, and lung cancer. The document also highlights symptoms, types of cough, and common viral infections such as the common cold and swine flu.