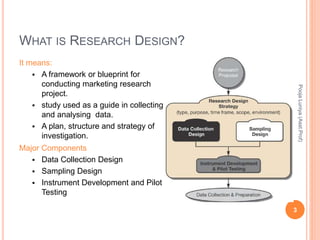
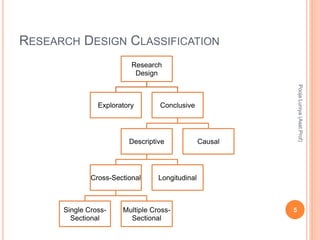
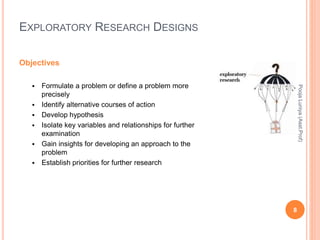
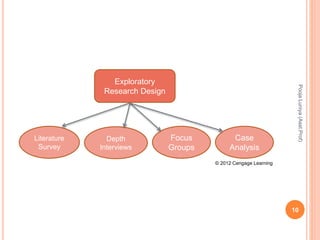
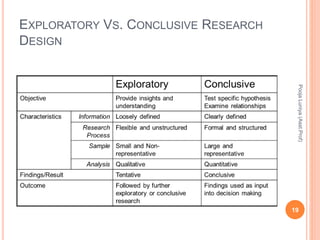
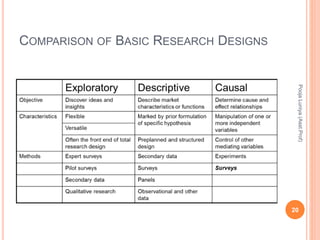
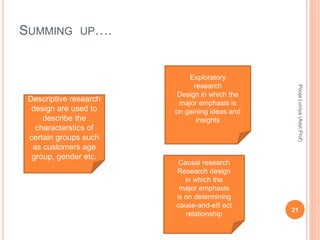
The document discusses different types of research designs used in marketing research. It describes exploratory research design which aims to formulate problems or develop hypotheses through literature reviews, experience surveys, and case studies. Descriptive research design aims to describe characteristics of populations through cross-sectional or longitudinal studies using structured data collection and probability sampling. Causal research design aims to determine cause-and-effect relationships through experiments and controlled data collection and analysis to establish evidence of relationships between variables. The document compares exploratory, descriptive, and causal research designs and their objectives, characteristics, and methods.