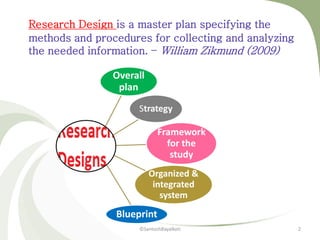
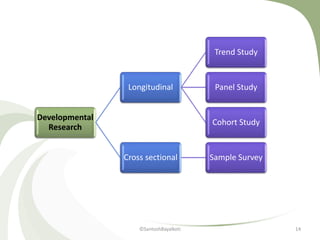
The document discusses various types of research designs. It describes exploratory research design as research undertaken when little is known about a problem to gain background information and develop hypotheses. Descriptive research design aims to describe and measure phenomena at a point in time. Qualitative research design uses informal techniques to gather and analyze non-numerical data to understand perceptions and opinions. Interventional research design controls variables to test hypotheses and determine causal relationships.