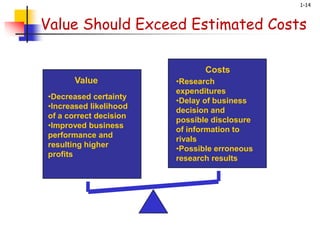
The document provides an introduction to business research. It defines business research as the systematic and objective process of generating information to aid business decisions [1-2]. The scope of business research helps decision-makers investigate problems objectively across different functional areas like finance, operations and marketing using similar research methods [1-3]. Research is classified based on its purpose, intended use, time dimension, and techniques [1-4]. Basic research expands knowledge while applied research solves real problems [1-5, 1-6, 1-7]. Research techniques include quantitative and qualitative methods [1-9]. Business research supports the managerial decision process and evaluation [1-11, 1-12]. Determining when