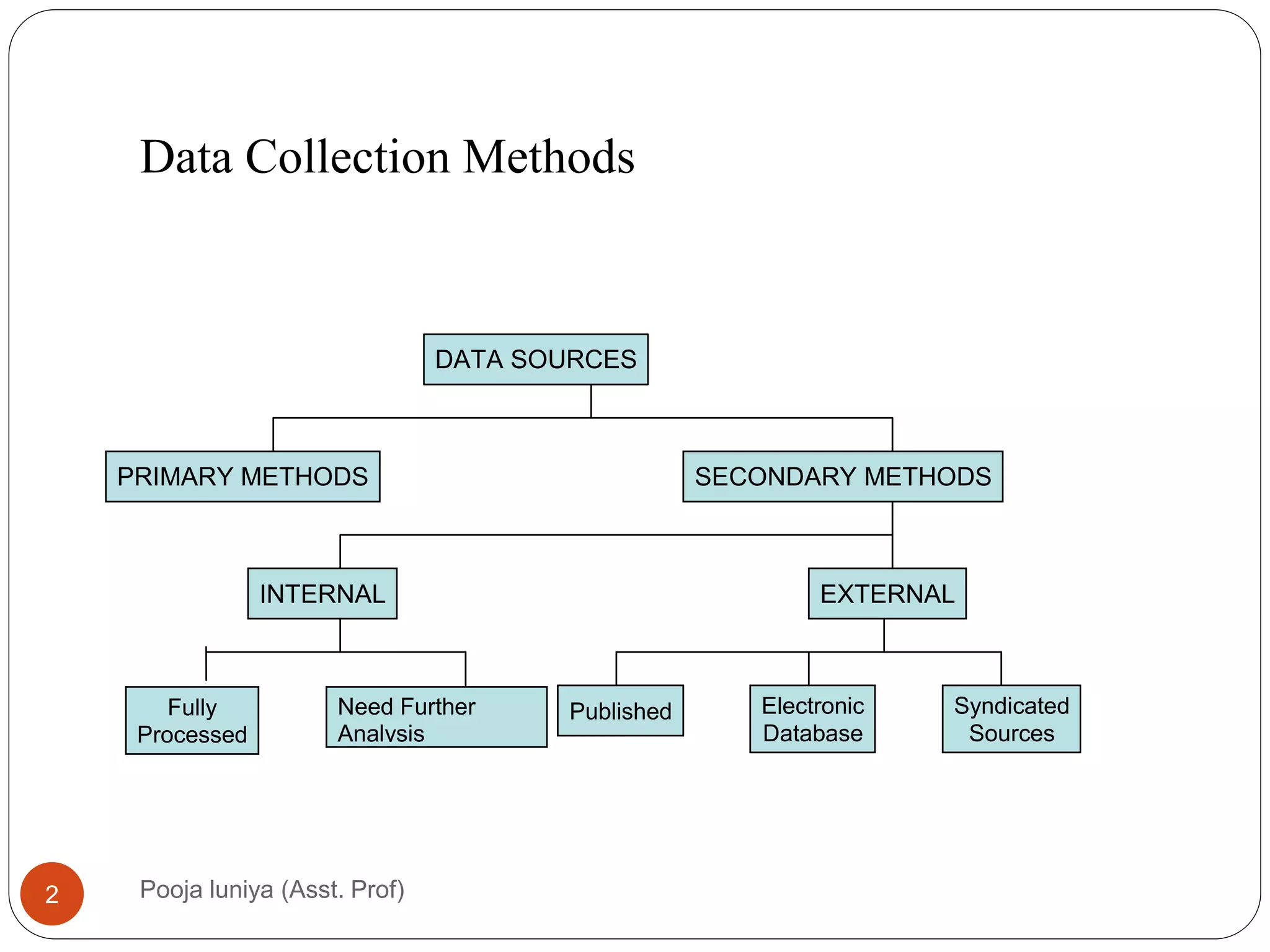
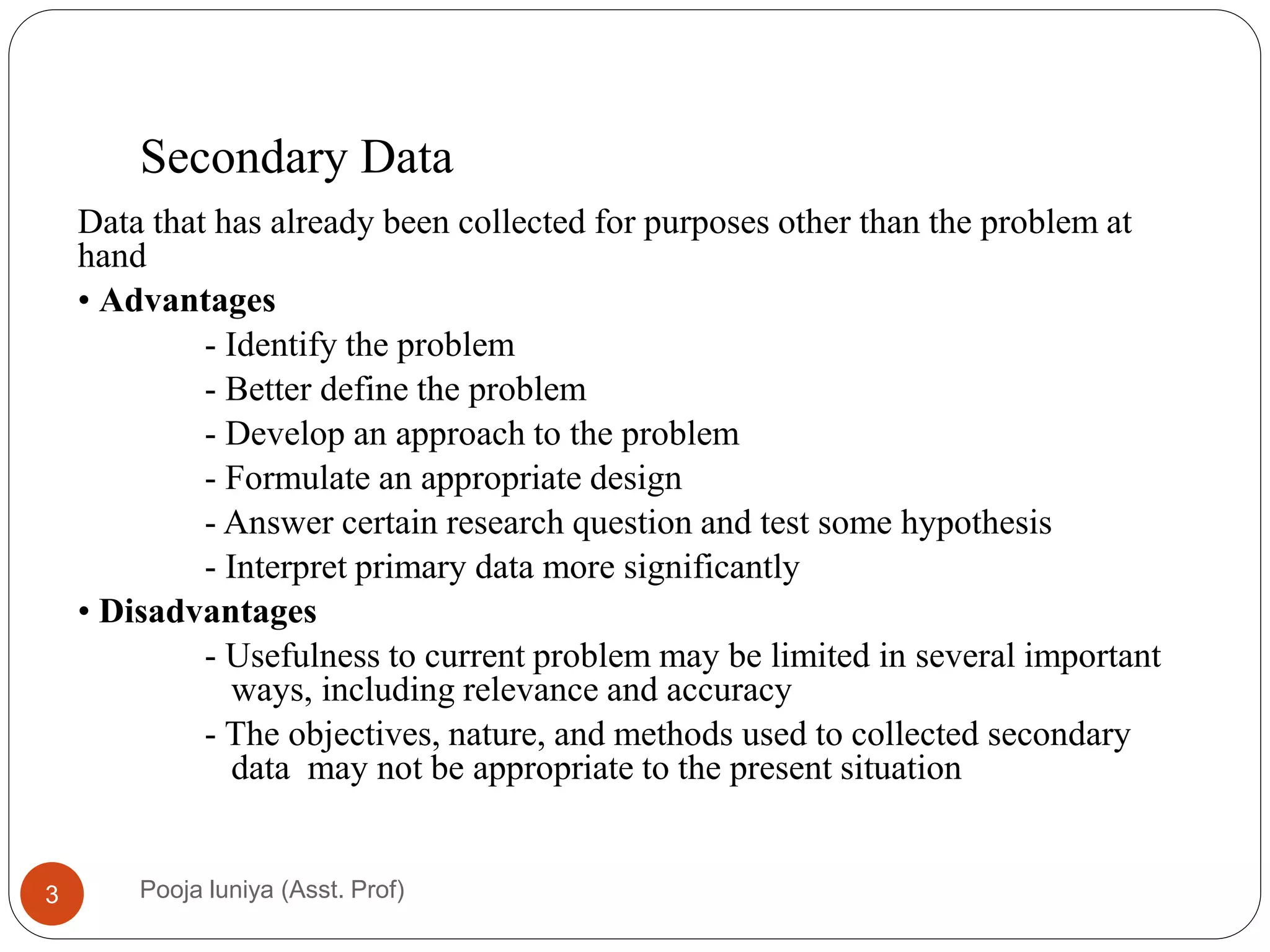
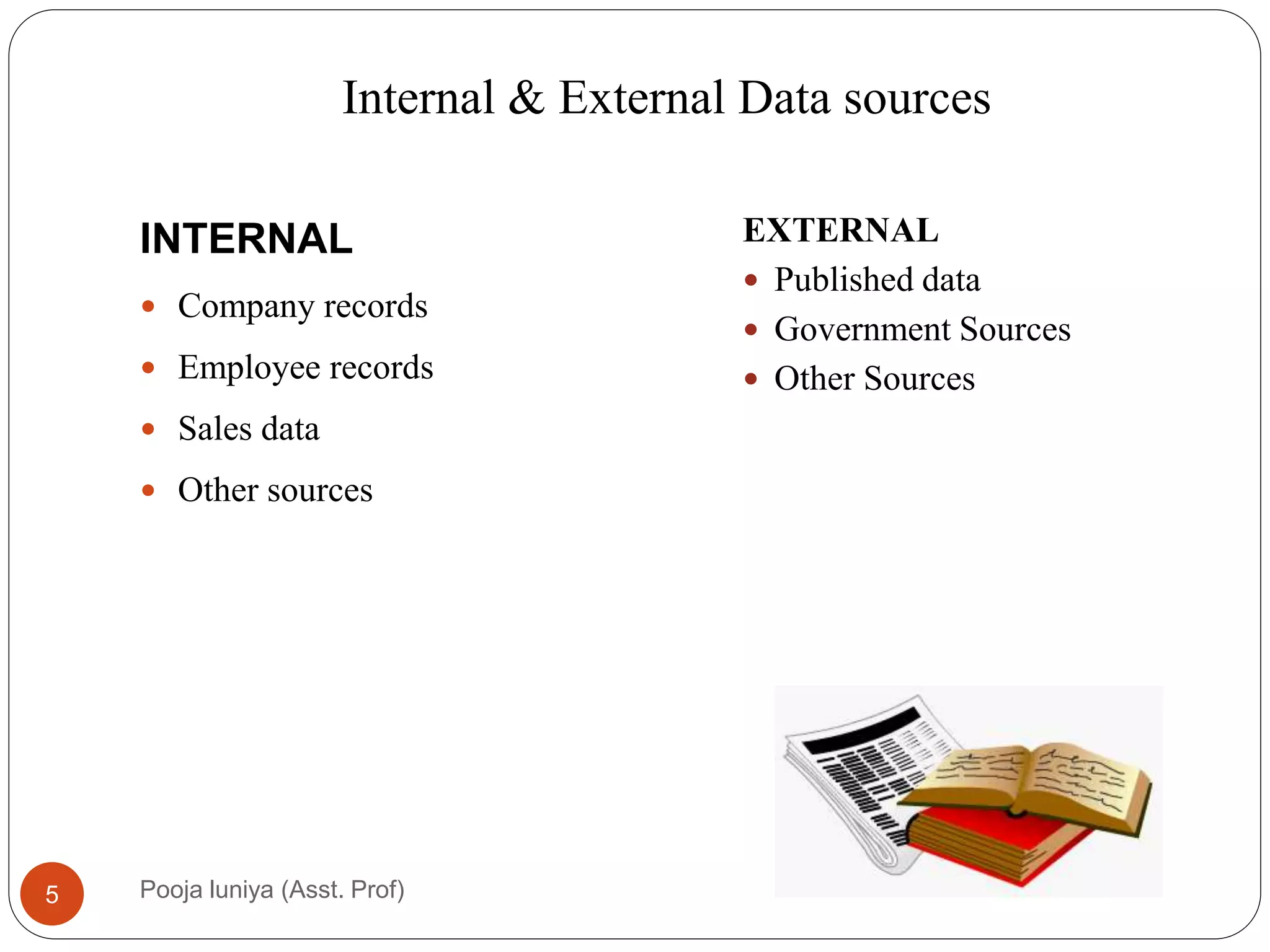
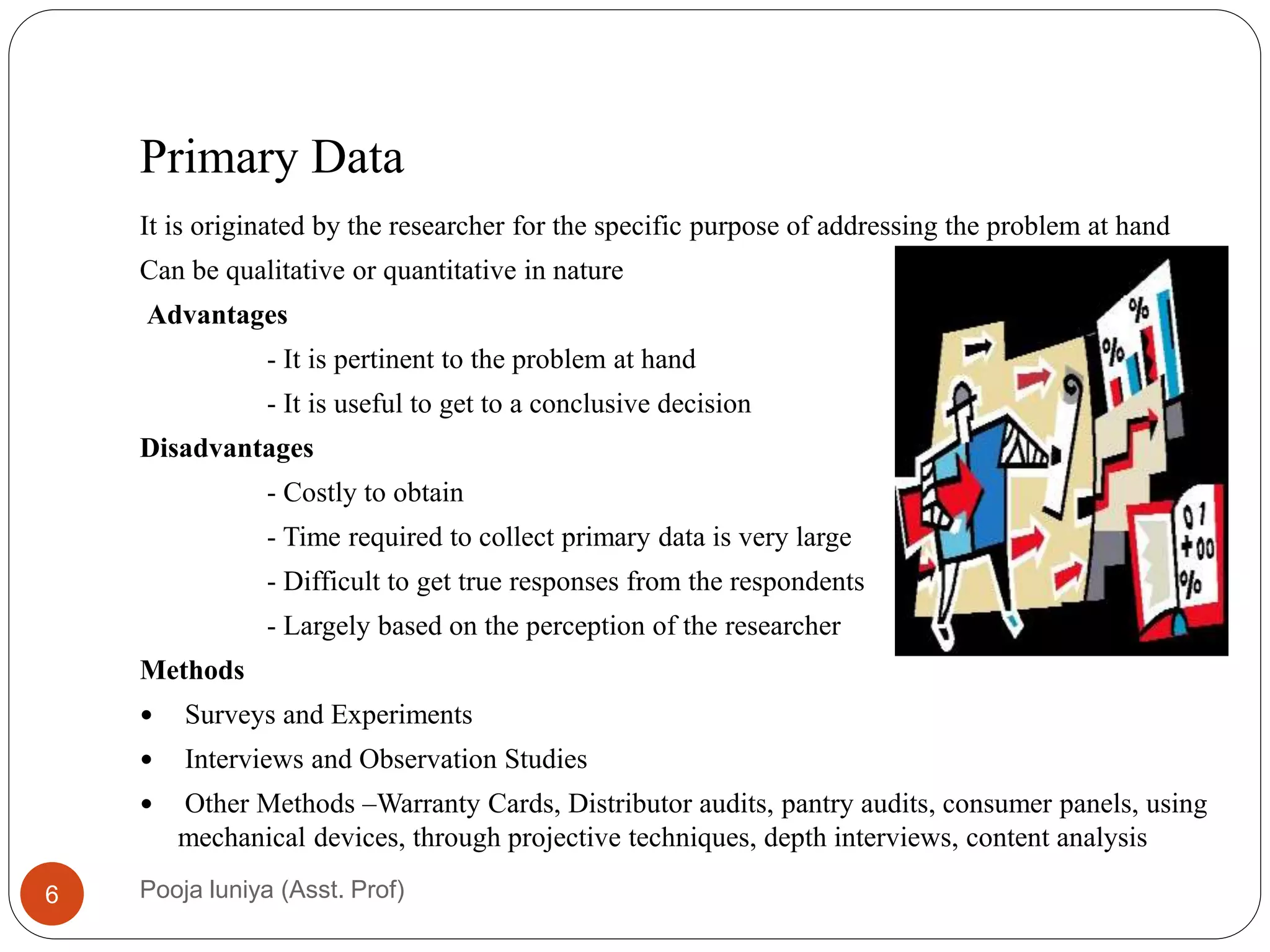
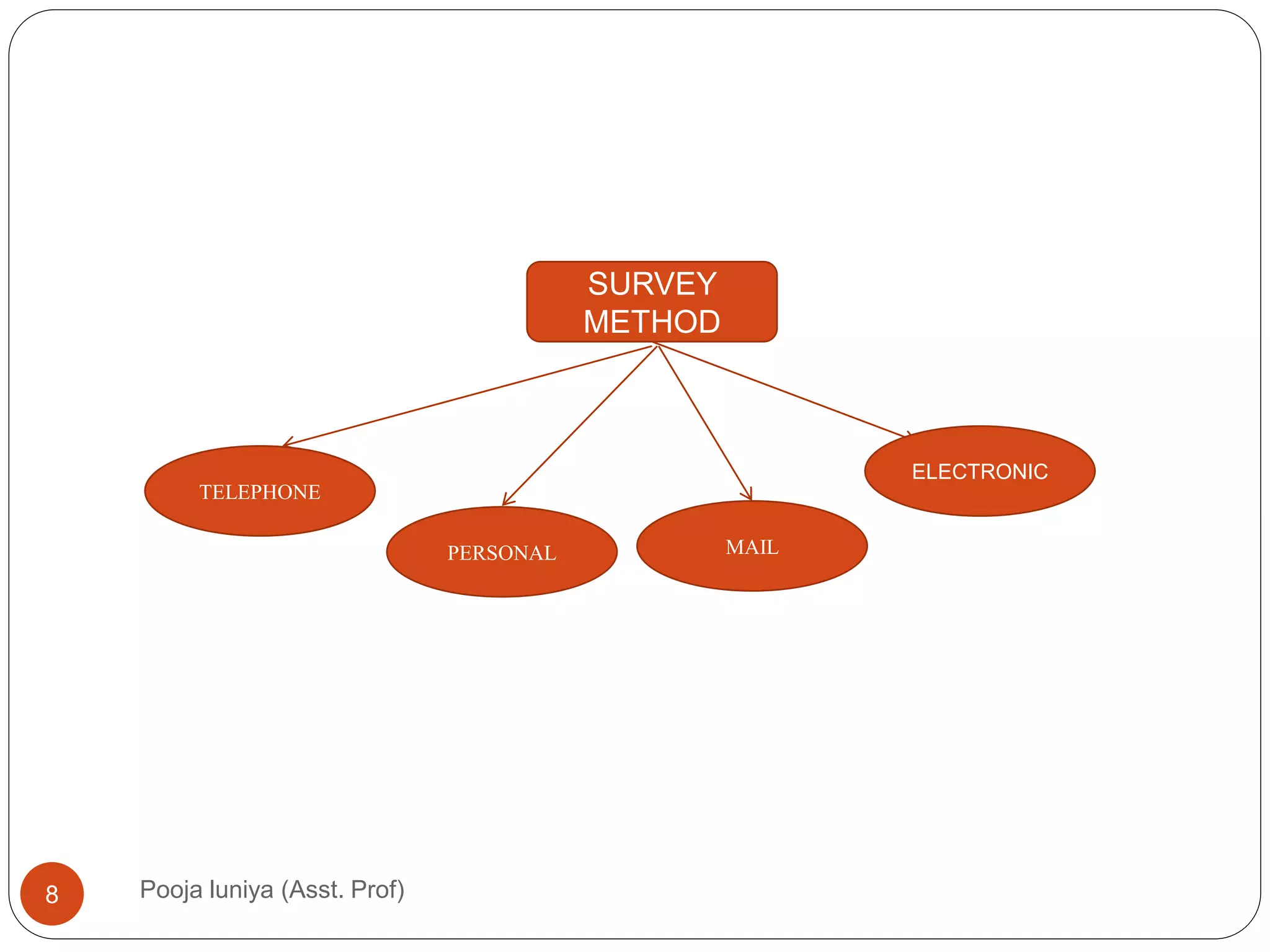
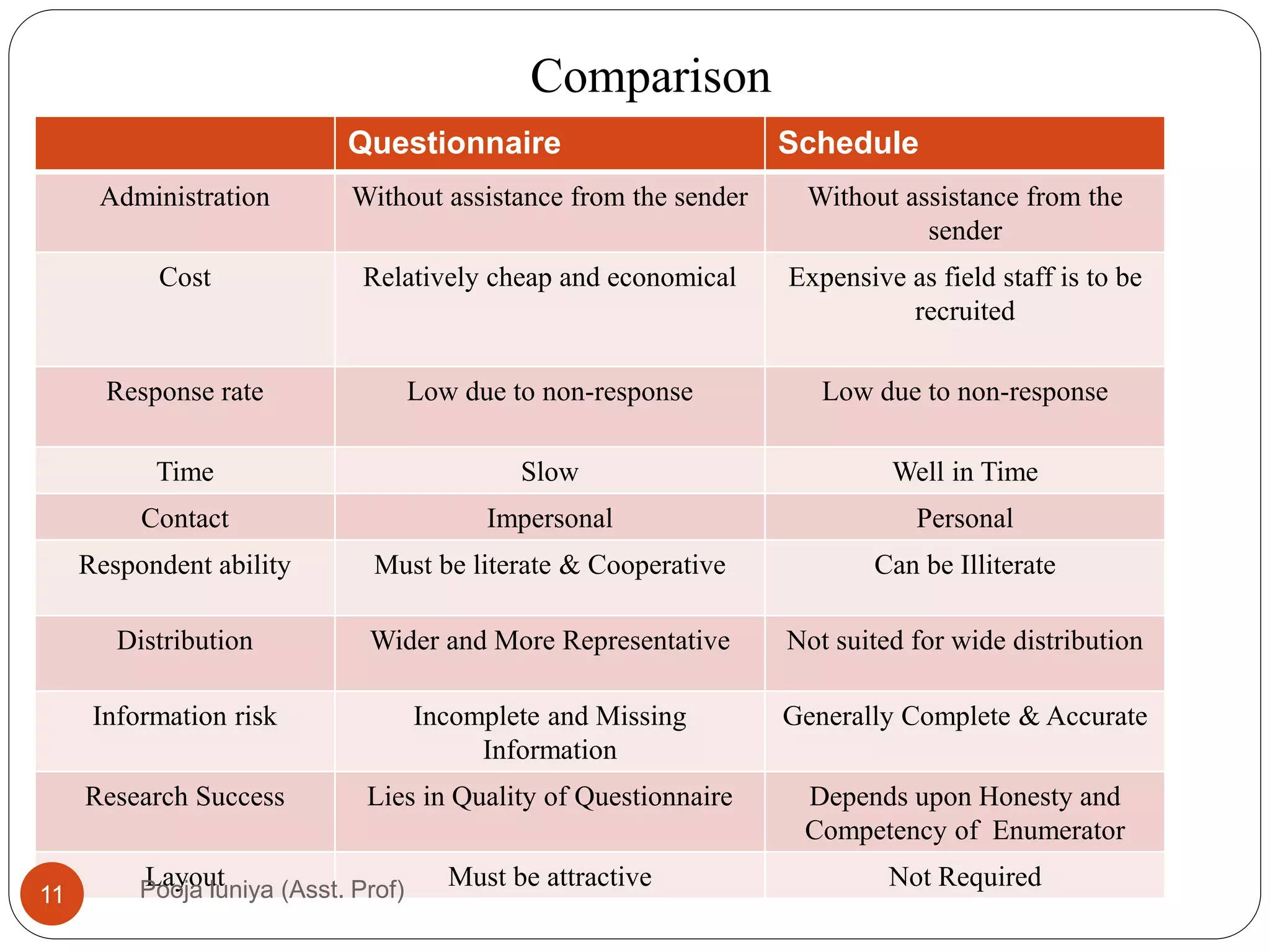
This document discusses data collection methods, including secondary and primary data. Secondary data refers to data that has already been collected for other purposes, and can help identify problems, define research questions, and interpret primary data. However, secondary data may not be directly relevant or accurate for the current research problem. Primary data is originally collected by the researcher specifically for the research problem and can be qualitative or quantitative. Common primary data collection methods include surveys, interviews, and observations. Surveys are a widely used quantitative method that involve distributing questionnaires via mail, email, telephone or online. They have advantages of being low-cost and allowing large samples, but suffer from low response rates.