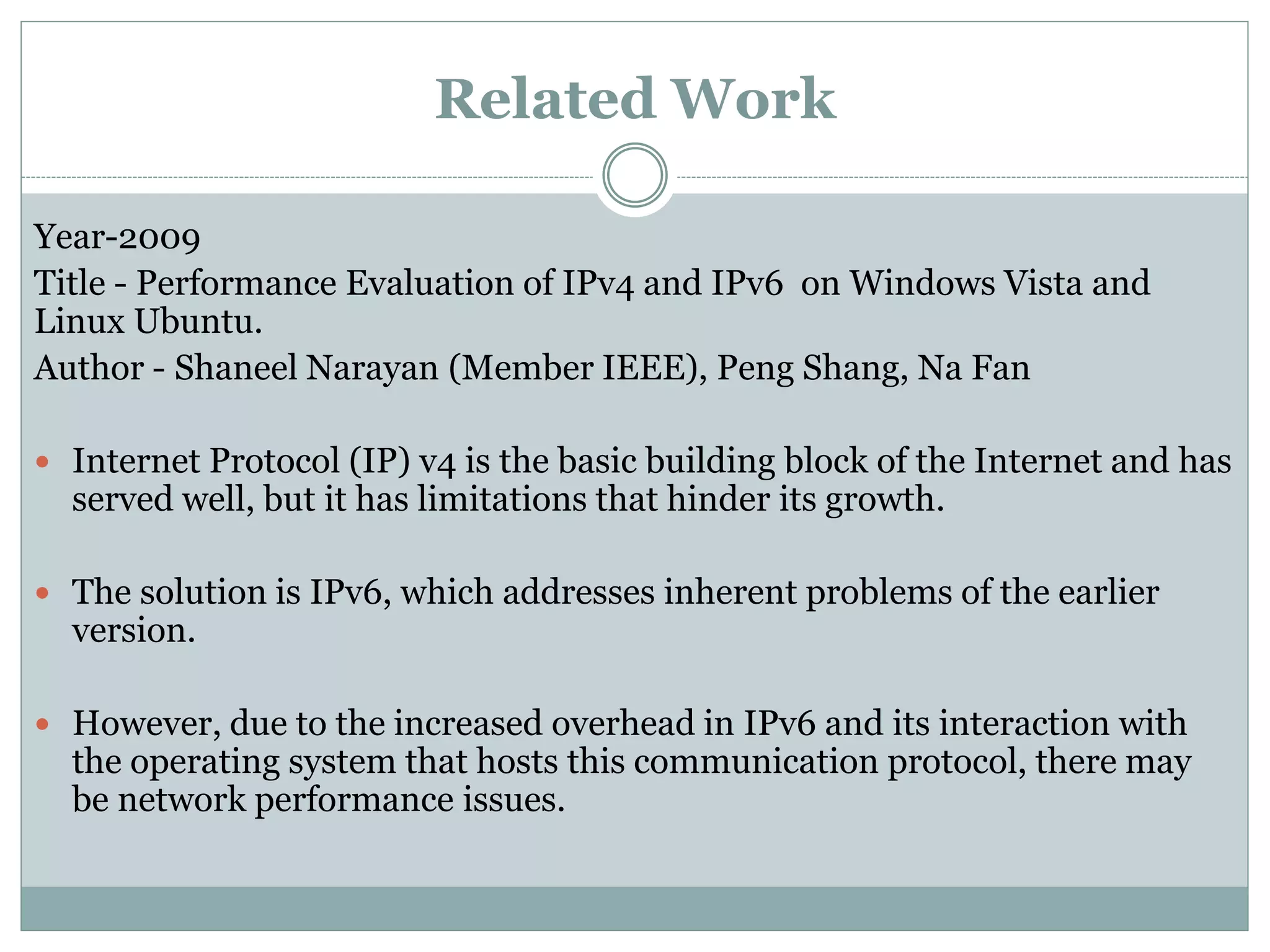
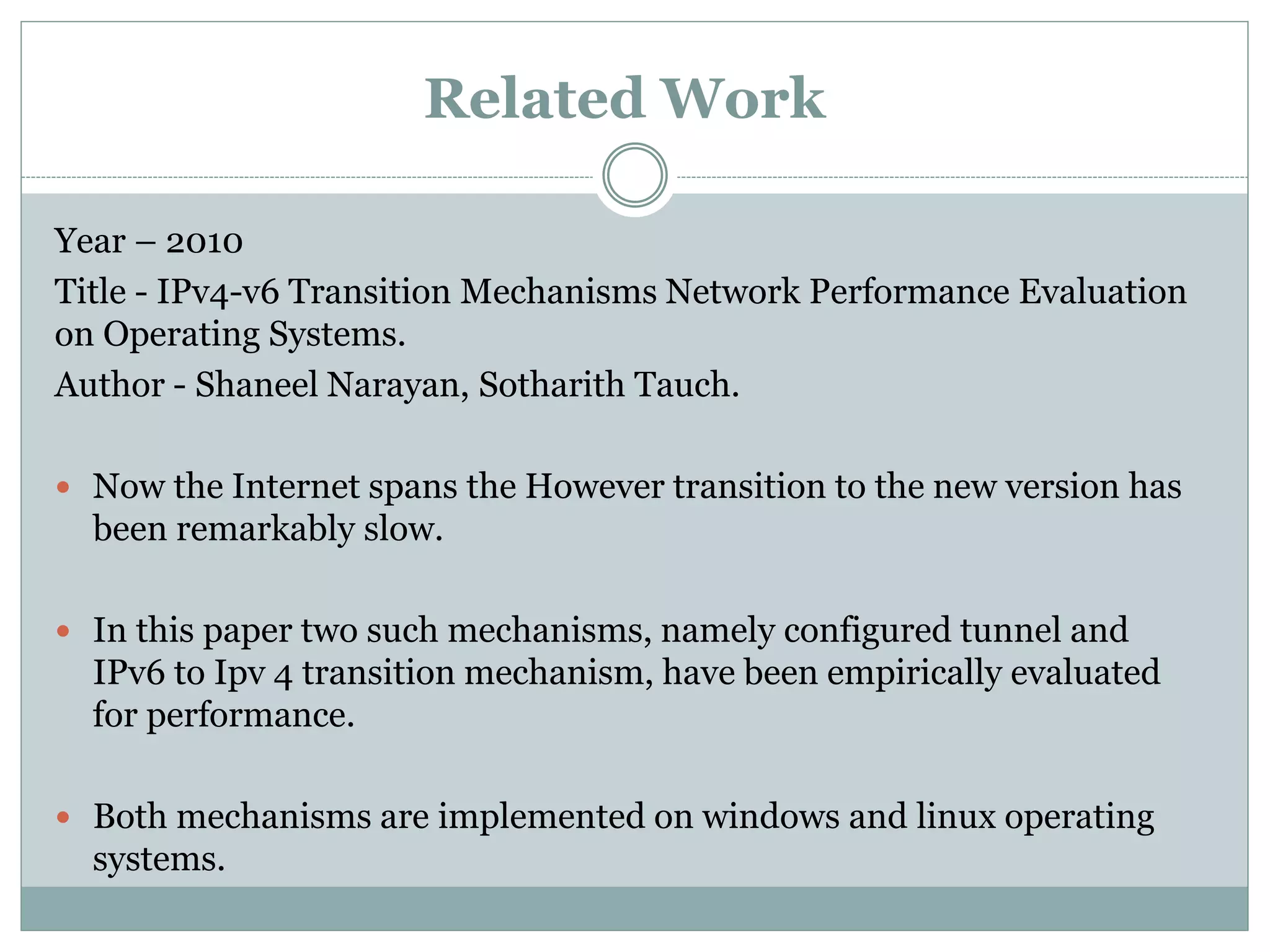
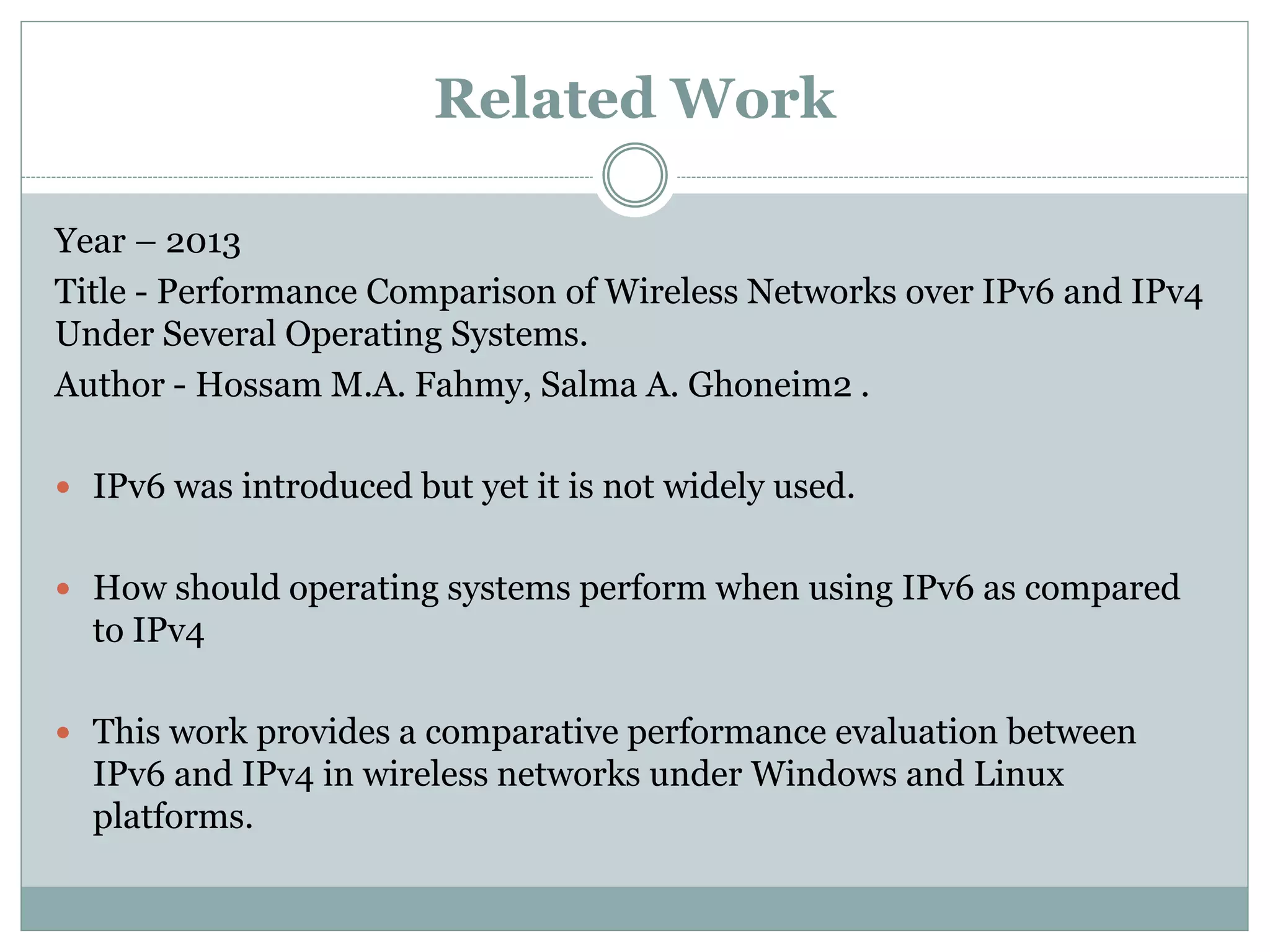
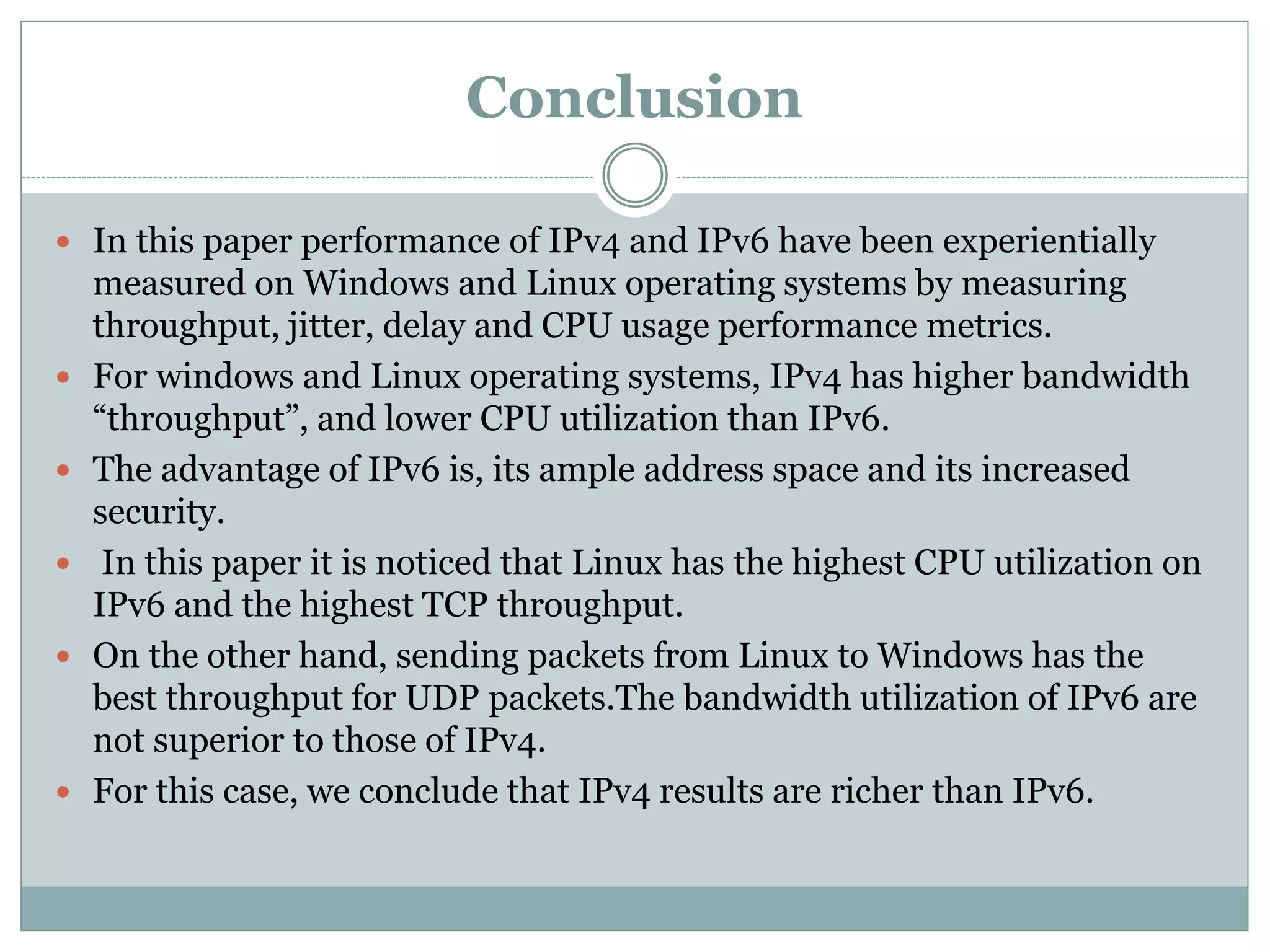
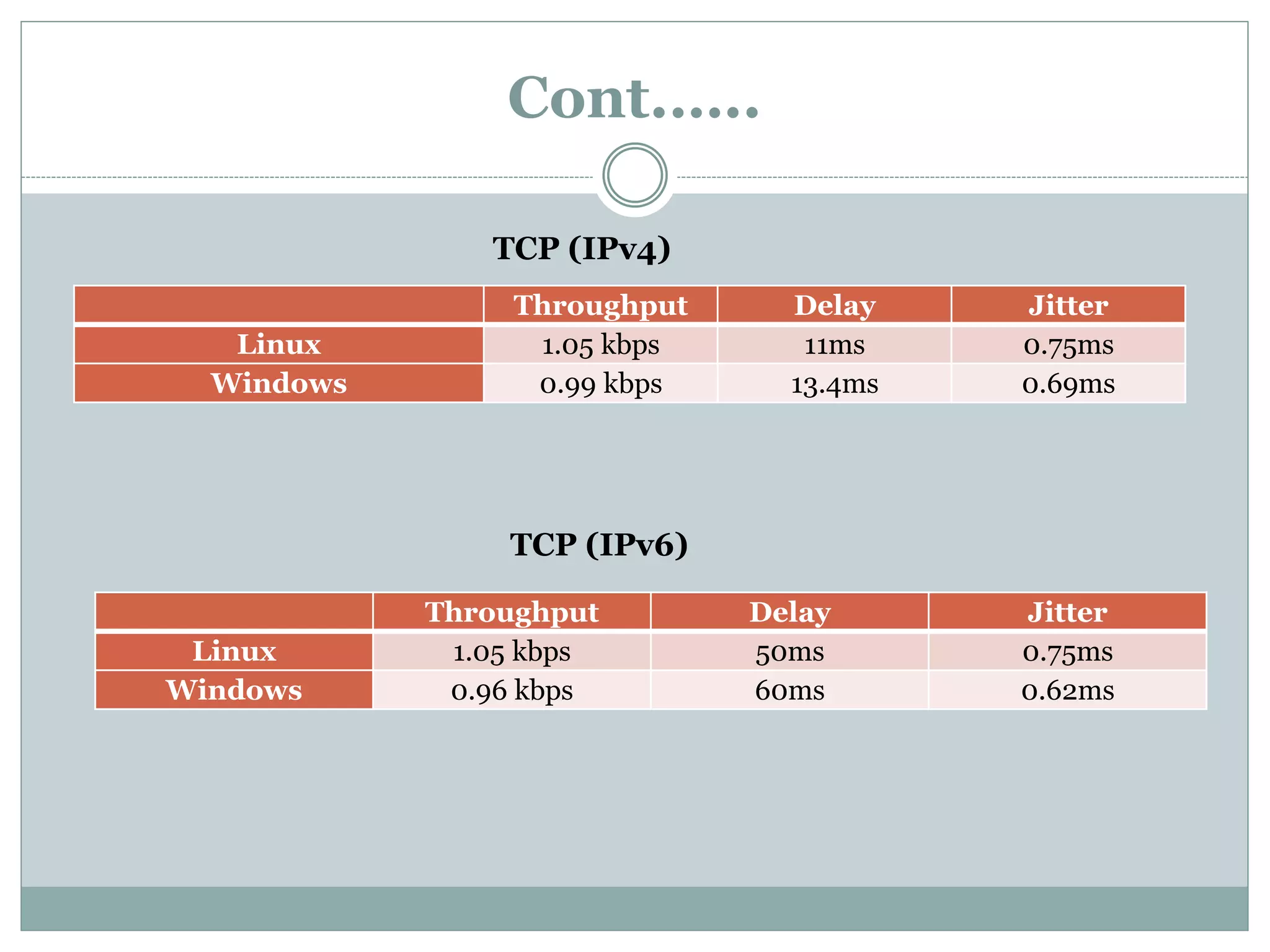
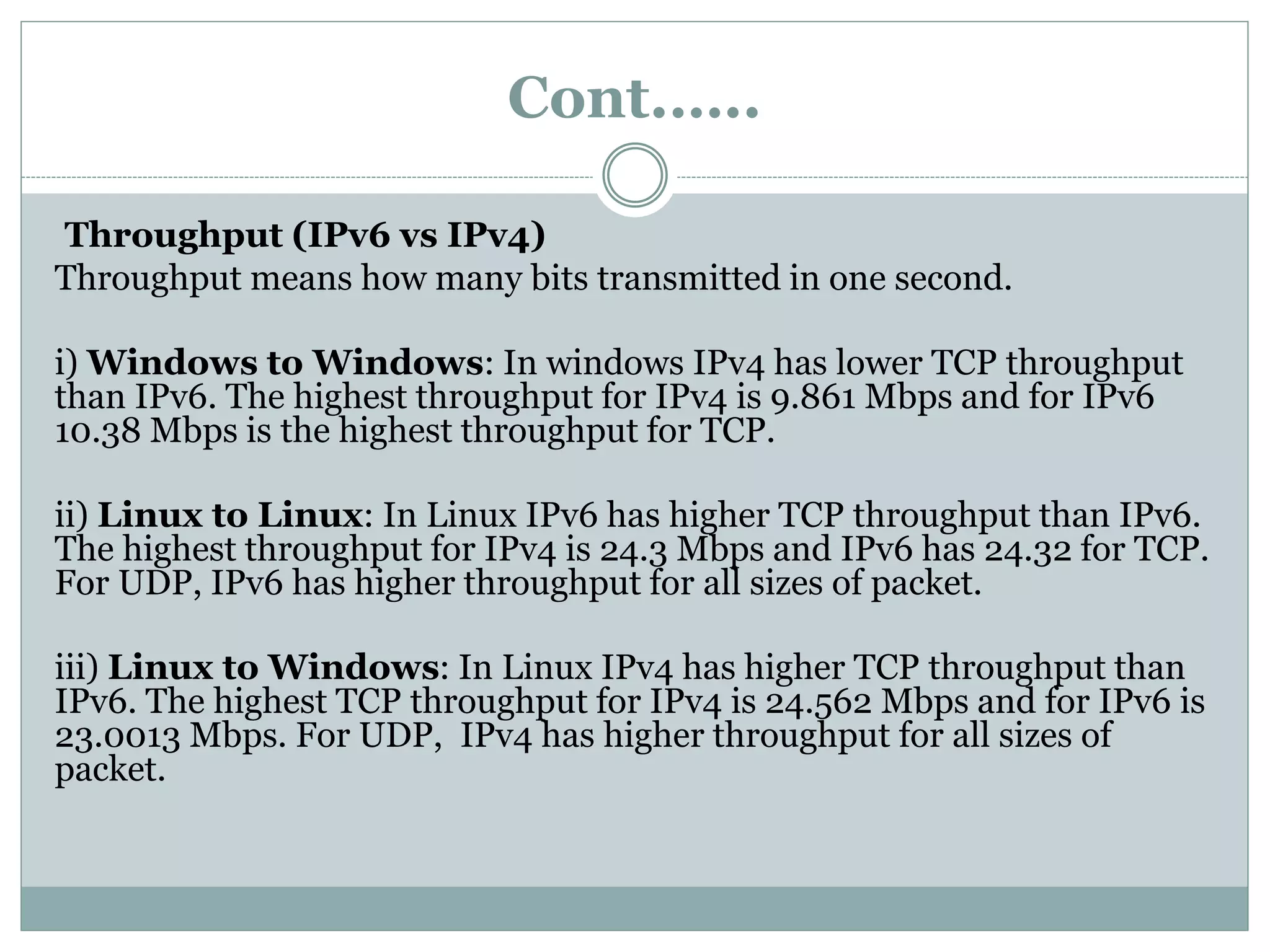
This document provides a comparative study of IPv4 and IPv6 performance on Windows and Linux operating systems. It introduces IPv4 and IPv6, compares their key differences, and experimentally measures performance metrics like throughput, delay, jitter and CPU usage for IPv4 and IPv6 on Windows and Linux. The results show that for Windows and Linux, IPv4 generally has higher throughput and lower CPU usage than IPv6. However, IPv6 has advantages like a larger address space and increased security. Linux typically shows the highest CPU usage and TCP throughput for IPv6. The document also reviews several related works comparing IPv4 and IPv6 performance on different operating systems.





![Cont.…..
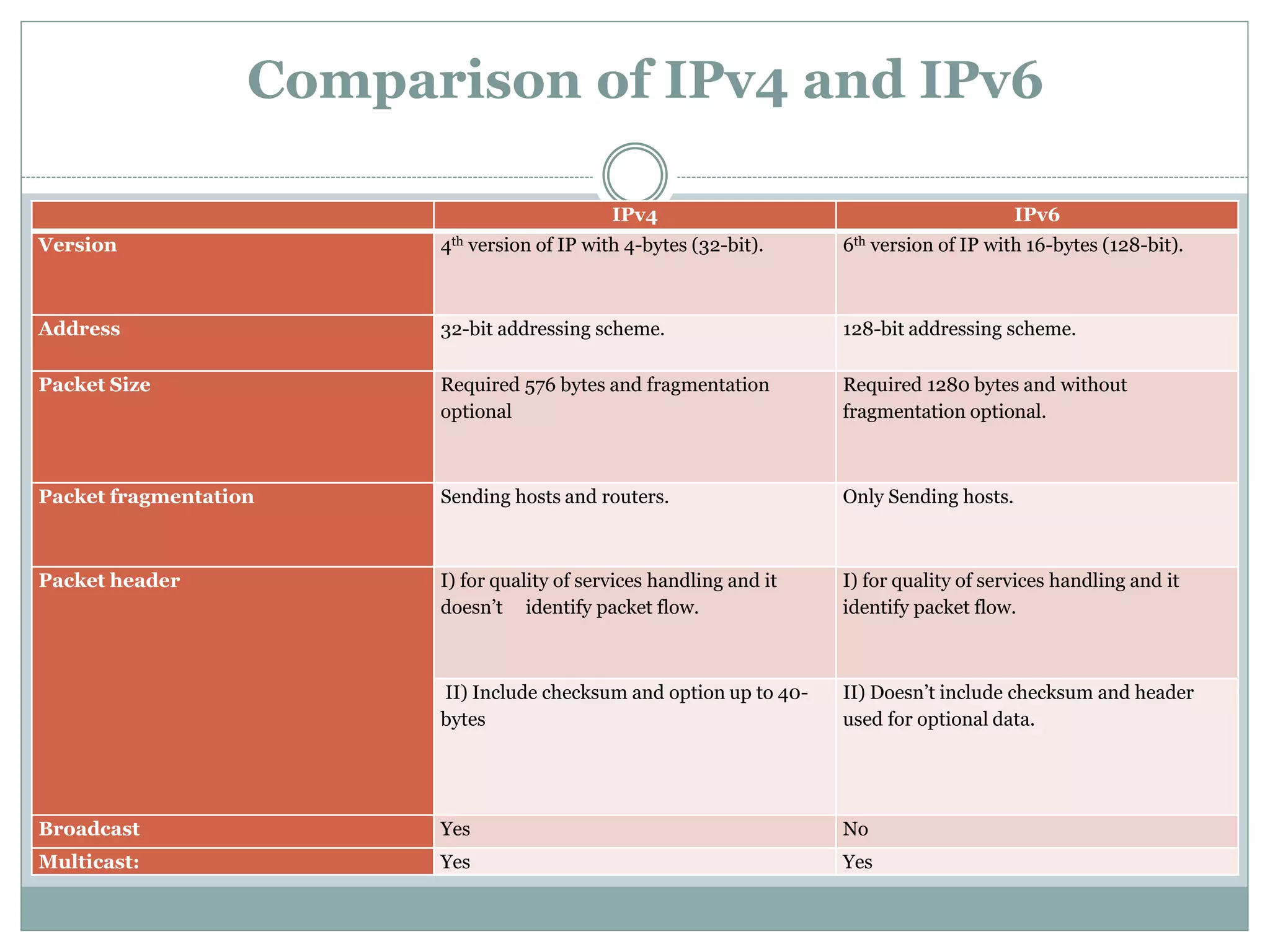
CPU Utilization (IPv4 vs IPv6)
CPU utilization is measure of CPU usage percentage. CPU utilization is
a metric that managed for efficient system performance. [5]
i) Windows to Windows: IPv4 has higher CPU Utilization, for all
packet sizes. CPU Utilization at packet size 640 bytes For IPv4 it is
20.577 % and for IPv6 it is 15.944 % at packet size 128 bytes.
ii) Linux to Linux: For all packet sizes, IPv6 has higher CPU
utilization than IPv4. CPU Utilization at packet size 128 bytes For IPv4
it is 7.04 % and for IPv6 it is 21.51 % at packet size 896 bytes.
iii) Linux to Windows: IPv6 has higher CPU Utilization than IPv4
for all packet sizes. CPU Utilization at packet size 128 bytes For IPv4 it
is 8.76% and for IPv6 it is 9.774 % at packet size 1152 bytes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/research-3-copy-150524171642-lva1-app6891/75/Comparative-study-of-IPv4-and-IPv6-on-Windows-and-Linux-11-2048.jpg)