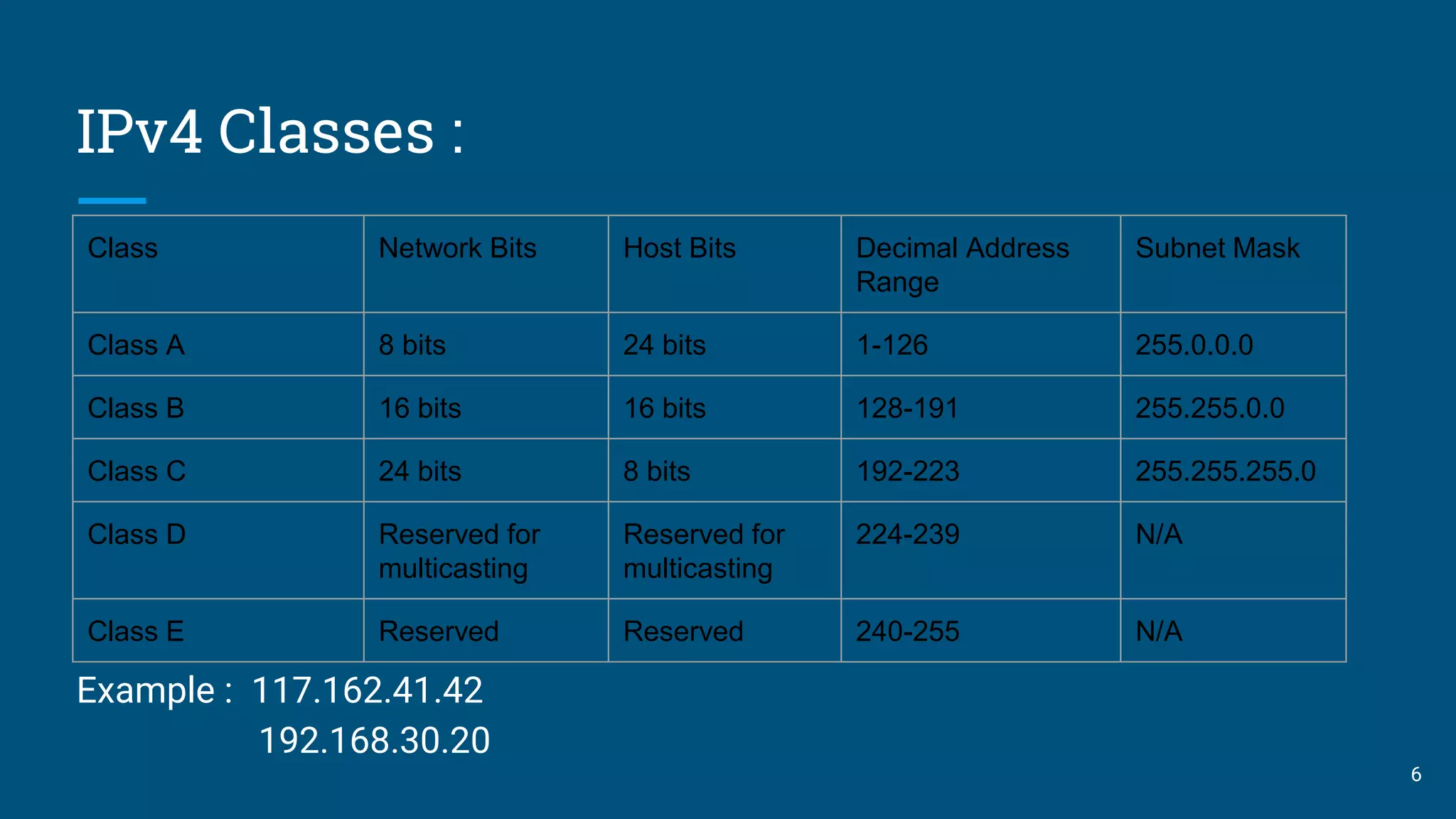
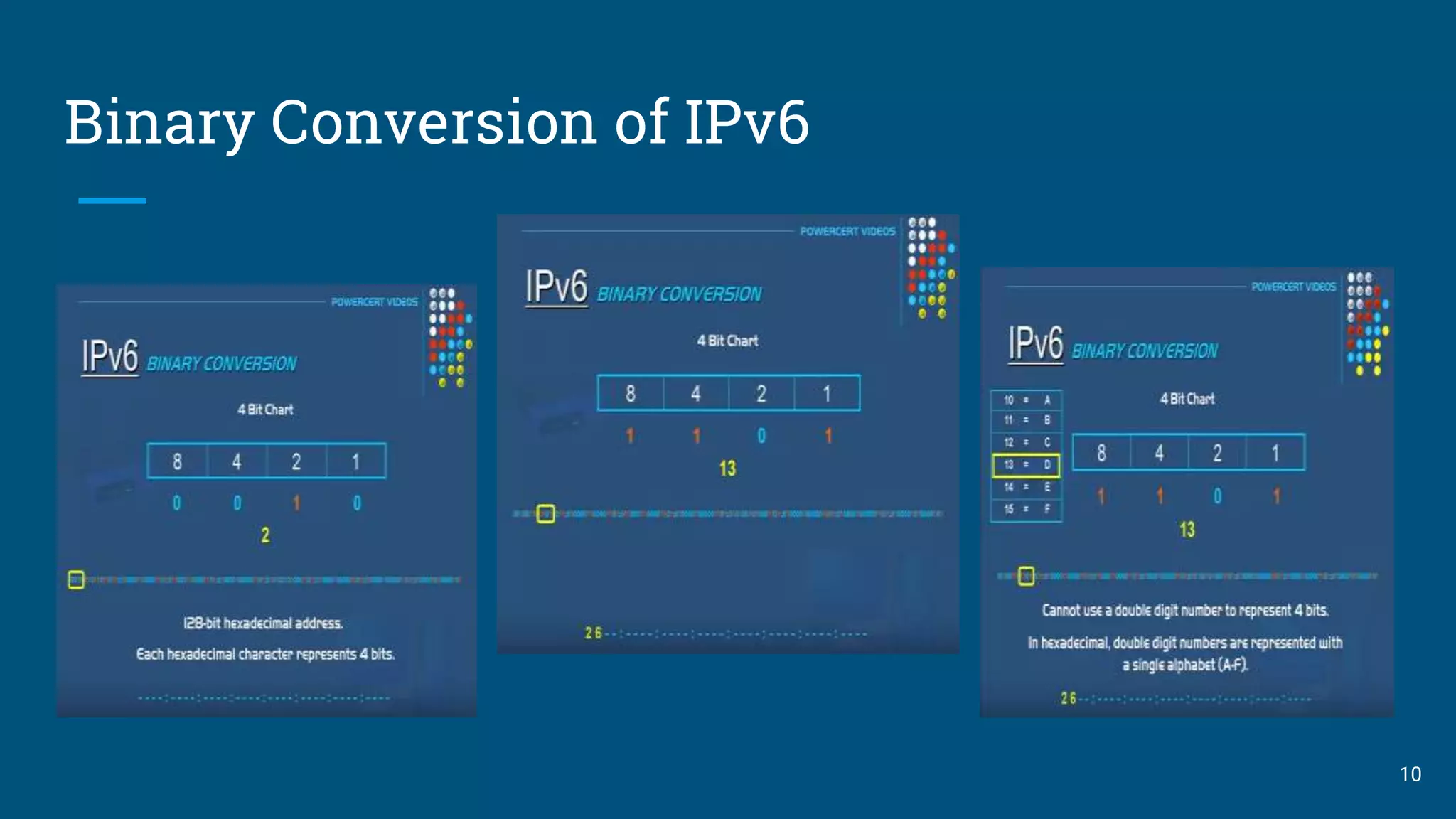
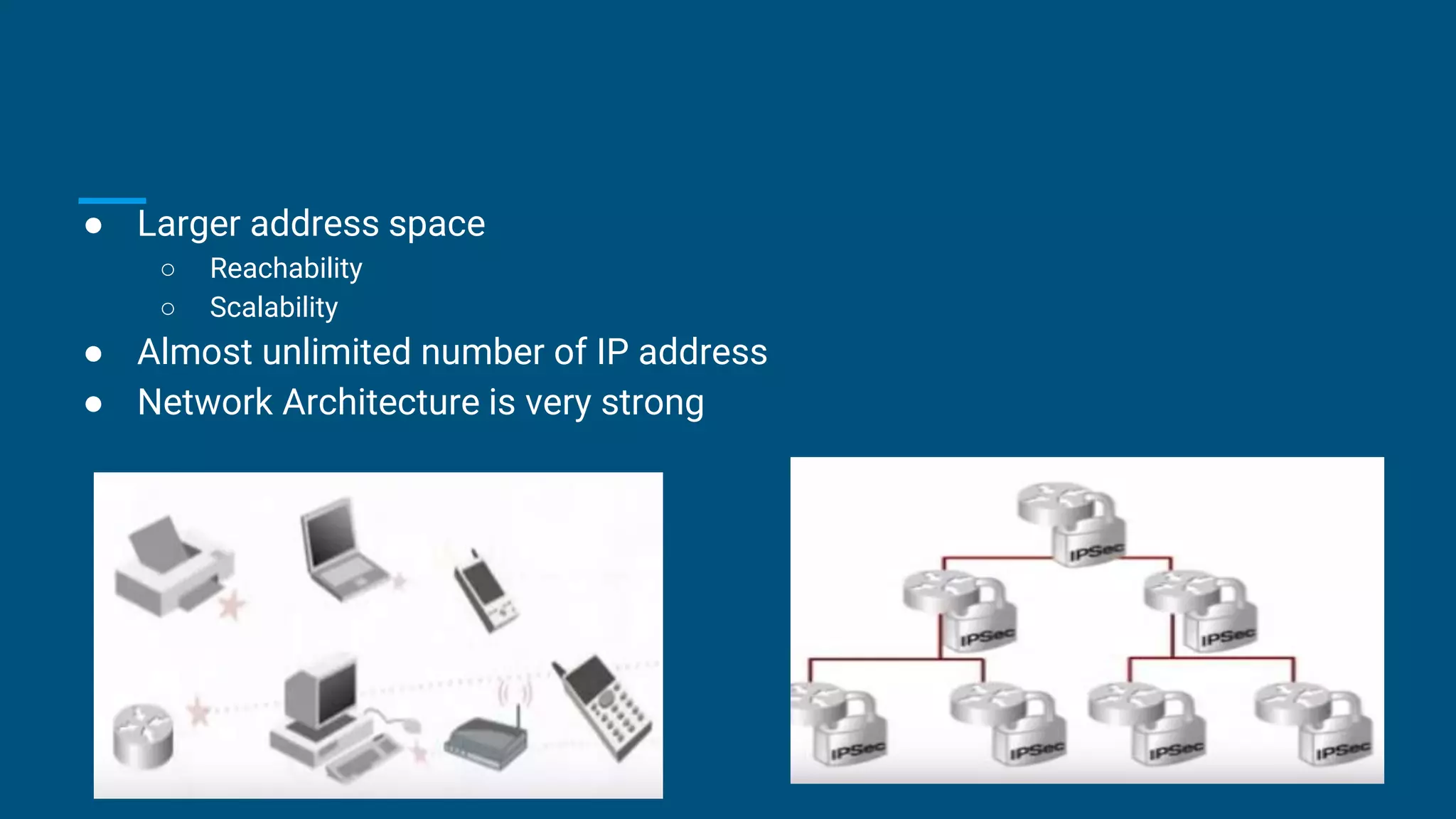
This presentation compares IPv4 and IPv6. It begins with introductions of the group members and defines IP as an Internet Protocol address assigned to devices connected to a network. It then discusses the evolution of IP versions from IPv1 to the current IPv6. Key details provided include that IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses limiting its capacity while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses allowing for vast expansion. The presentation outlines advantages and limitations of IPv4 and reasons for the development of IPv6, including the growing shortage of IPv4 addresses. It clarifies that IPv4 and IPv6 are not compatible but can co-exist on networks using dual stack technology.