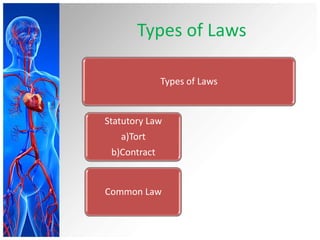
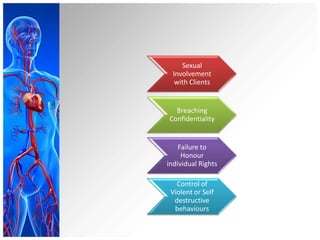
This document provides an overview of trends and issues in psychiatric mental health nursing. It discusses the history and evolution of the field from institutionalization to deinstitutionalization. Current trends include expanded roles for psychiatric nurses in primary care, collaboration, education, and community-based care. Legal issues addressed include informed consent, restraints, seclusion, and liability concerns. Ethical principles of autonomy, beneficence, and justice are considered in the context of common dilemmas around treatment refusal, privacy, and dual relationships.