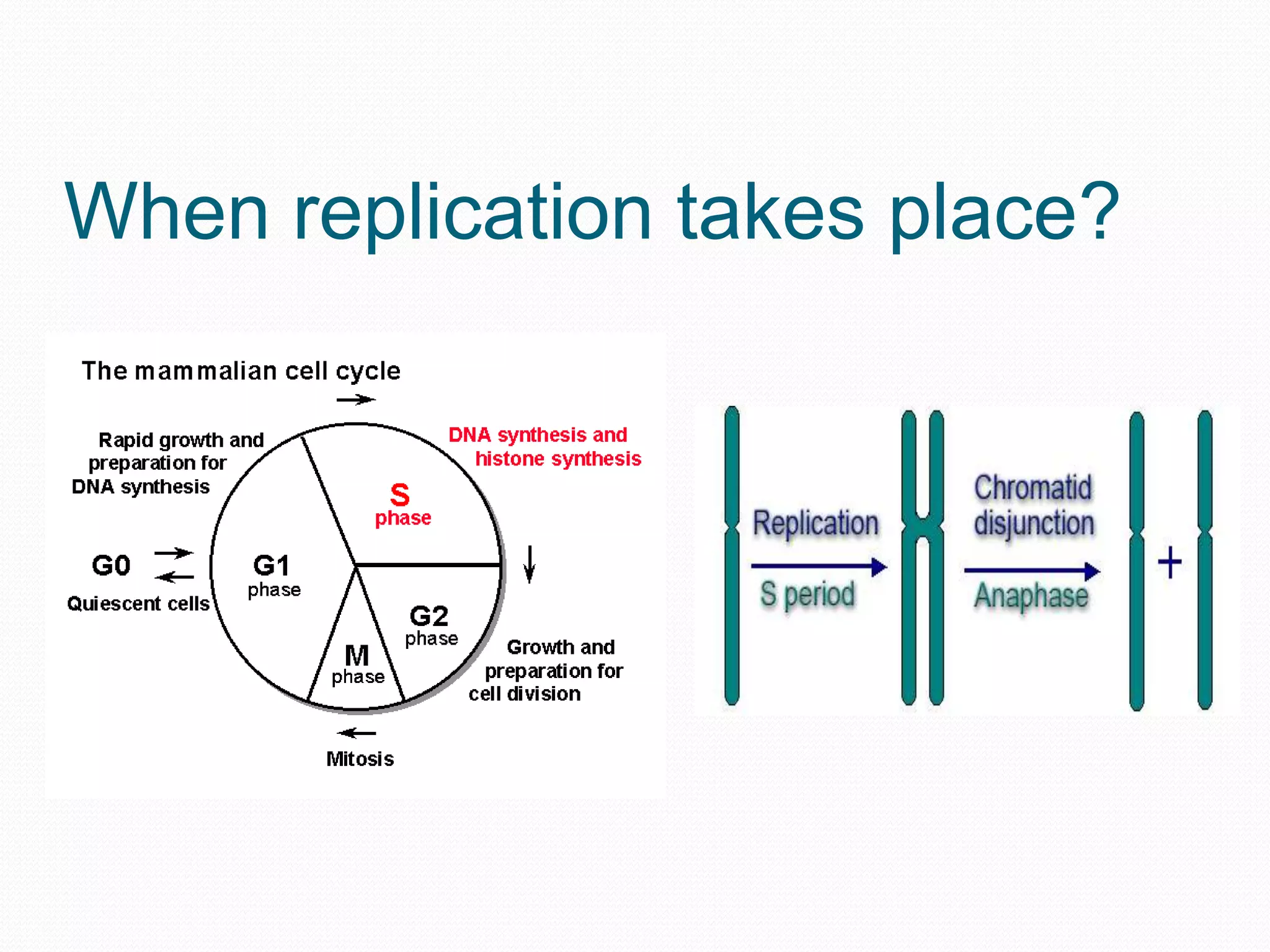
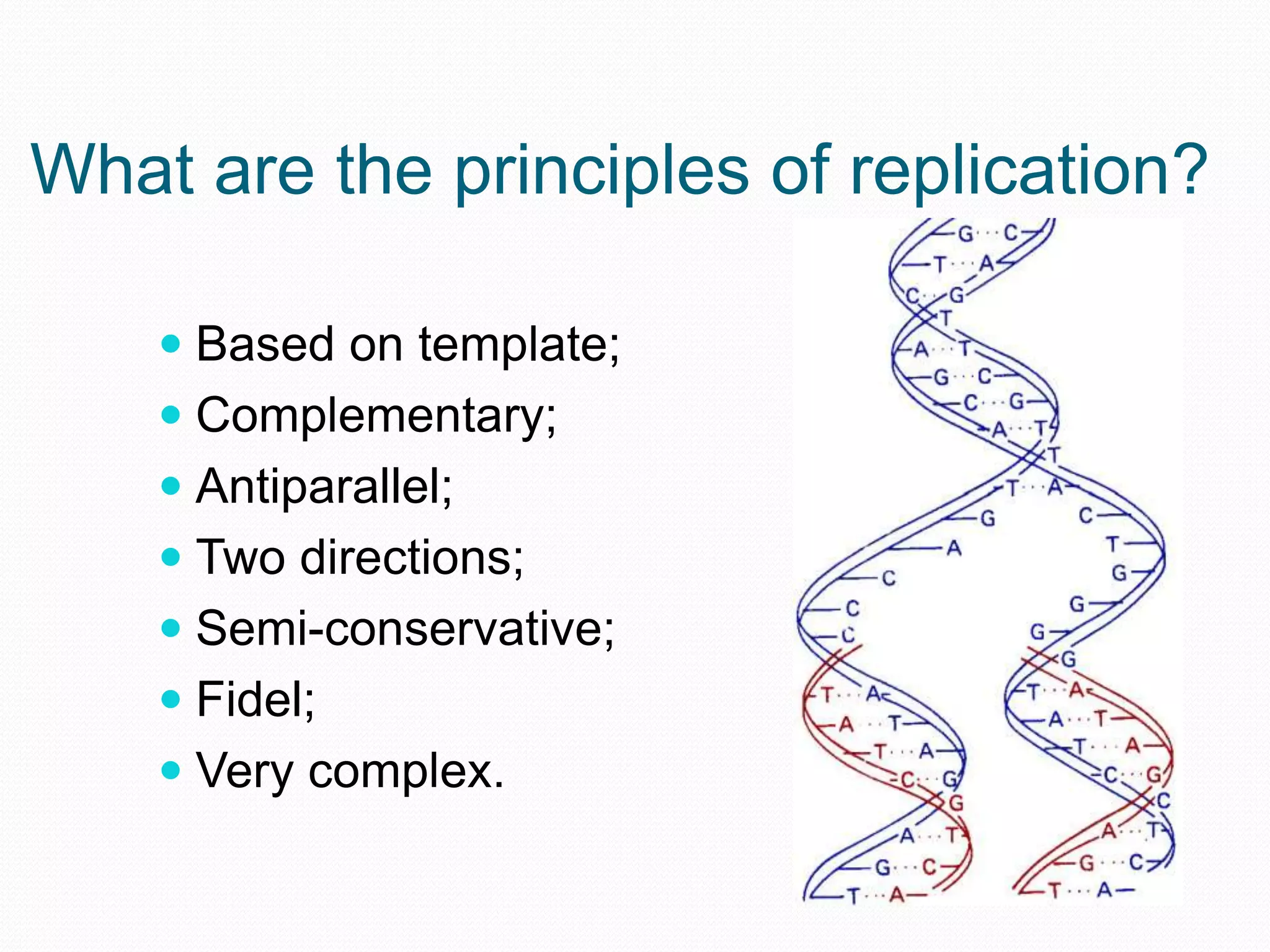
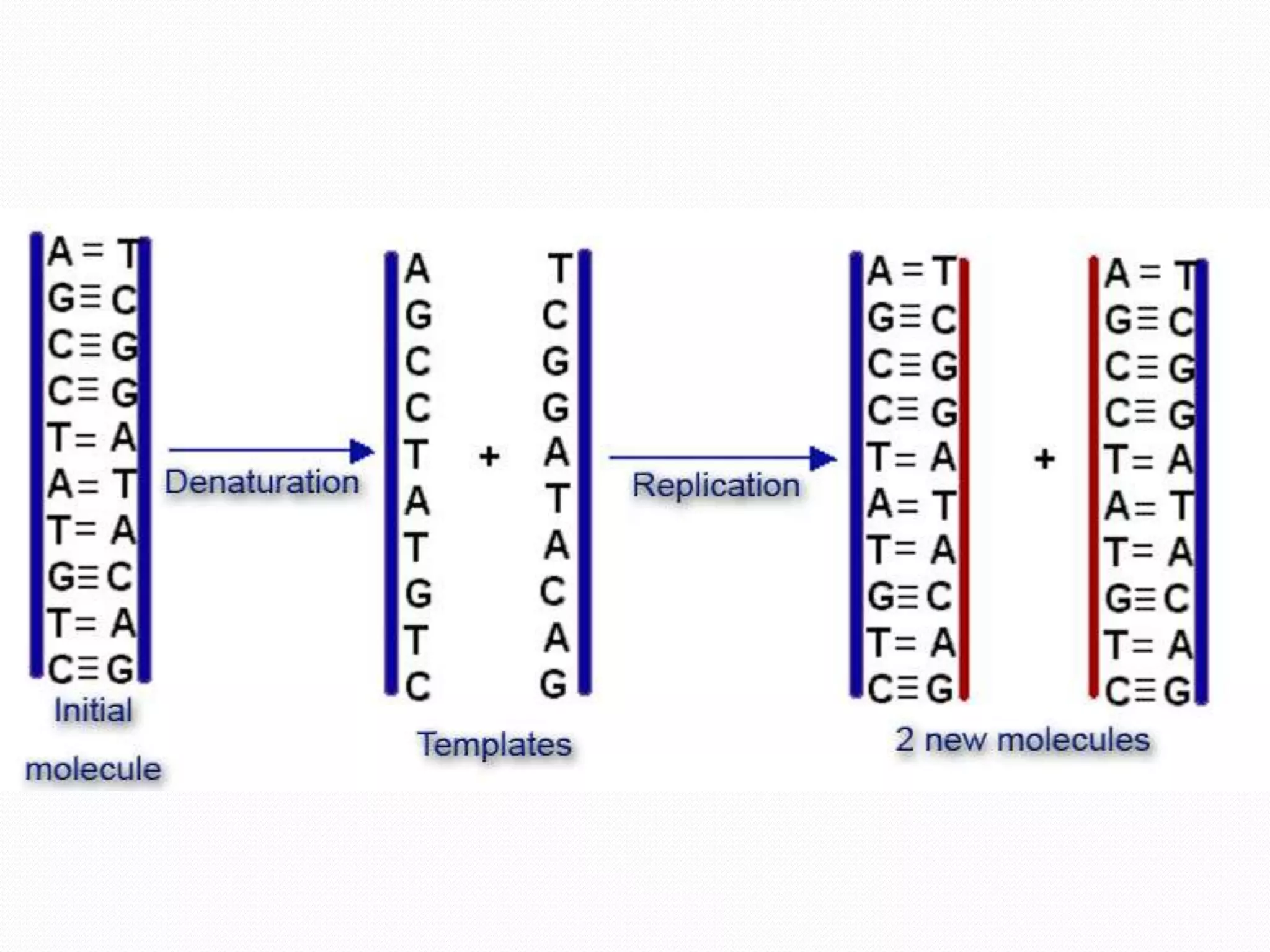
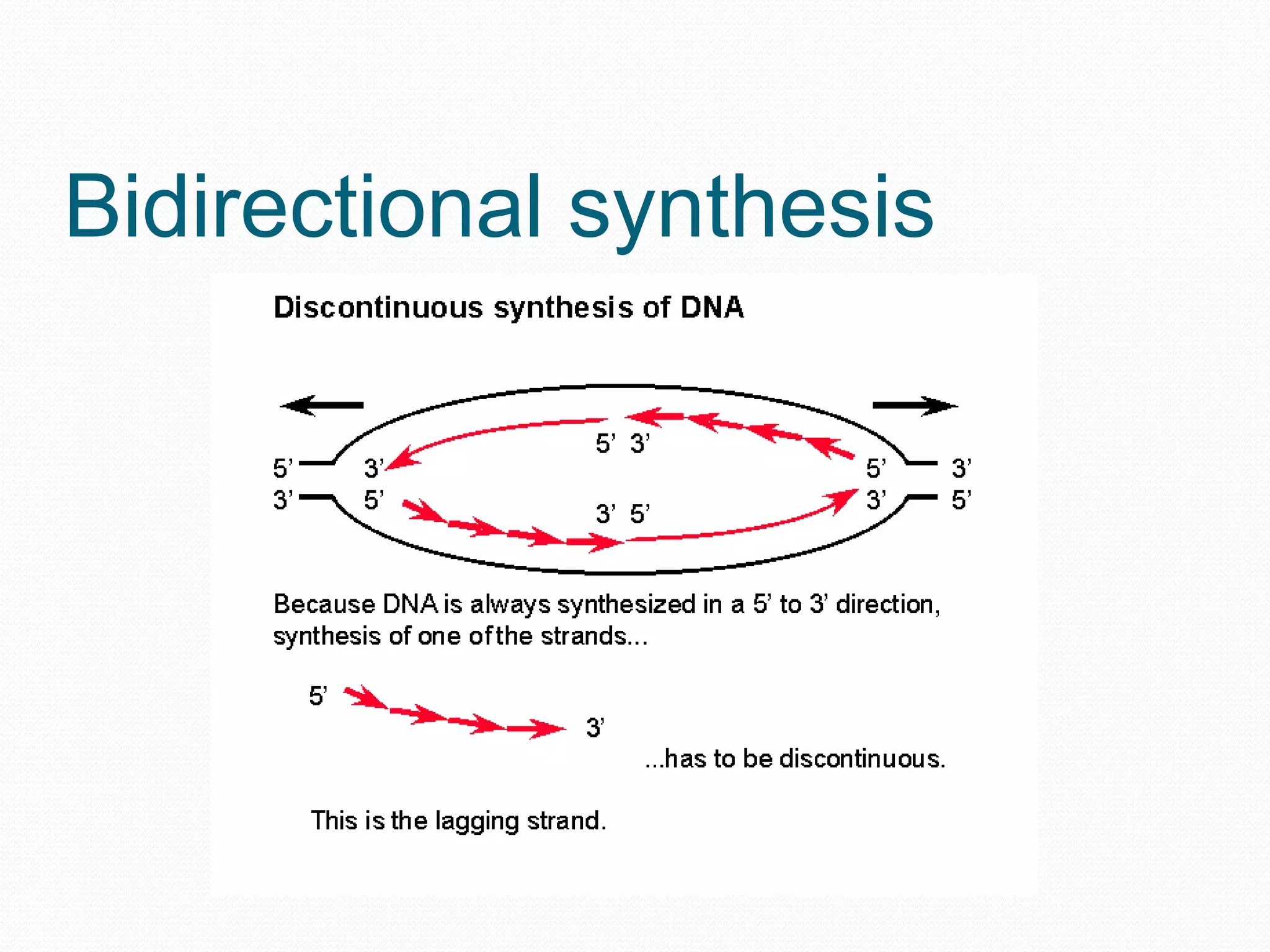
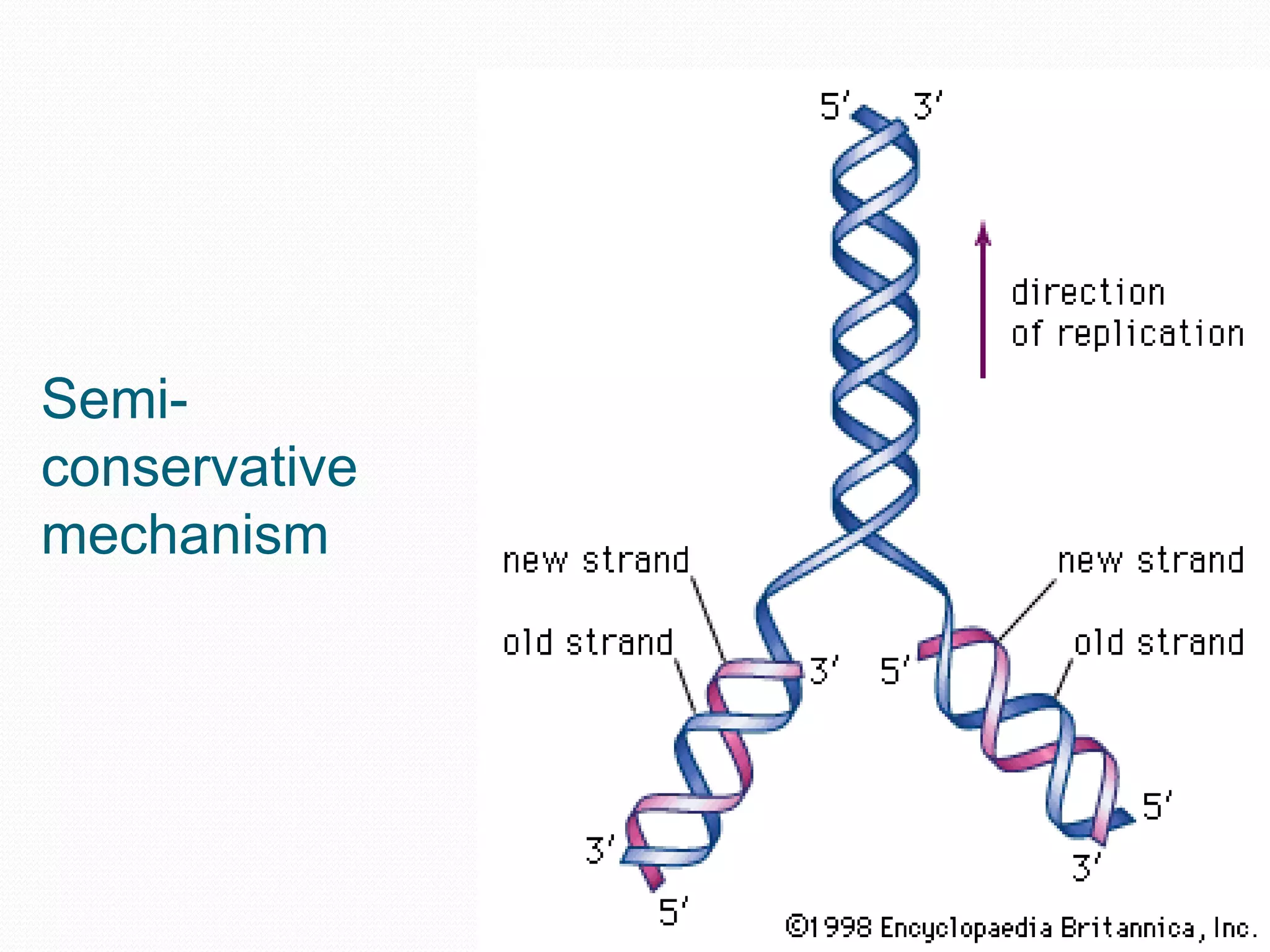
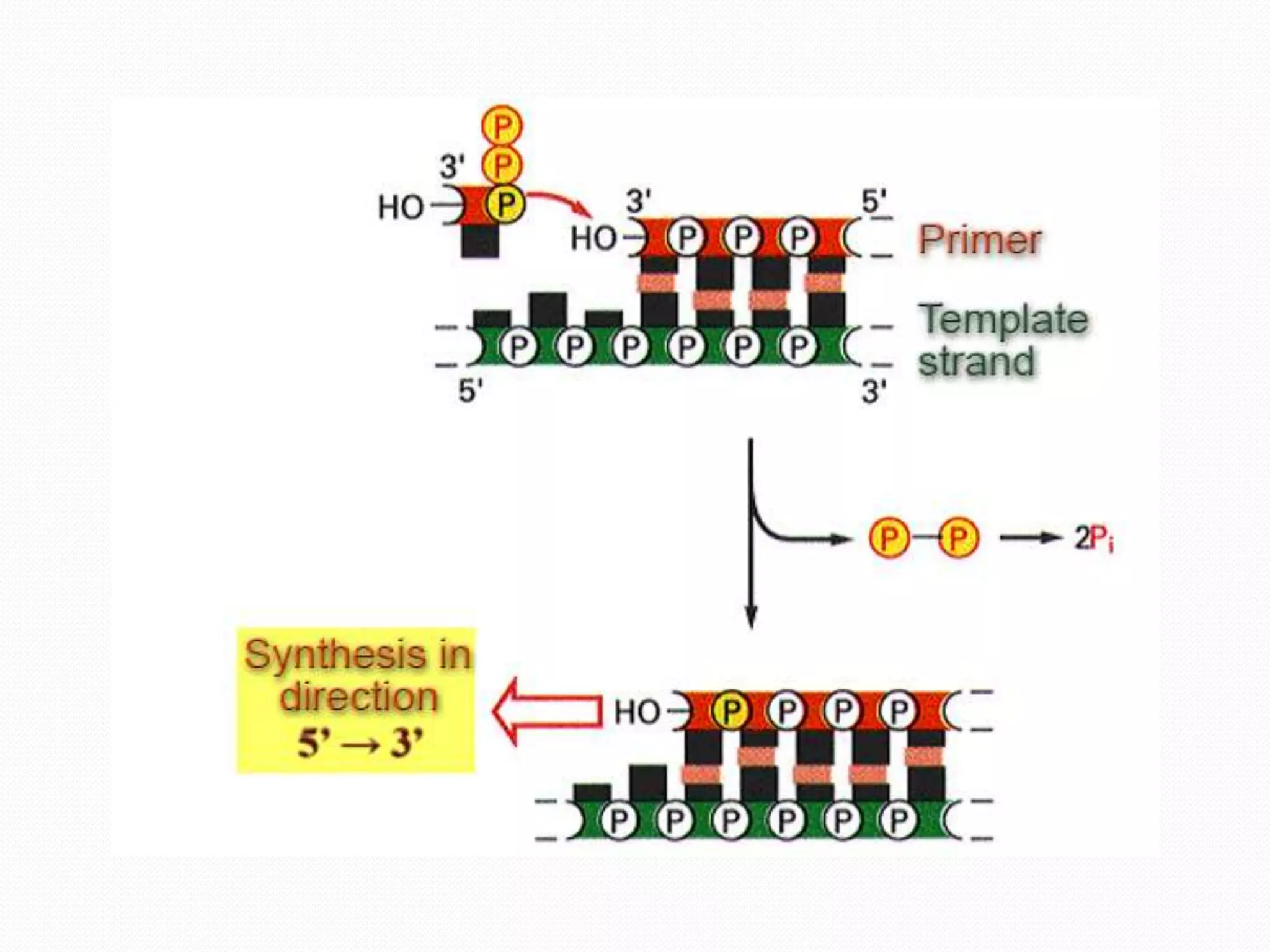
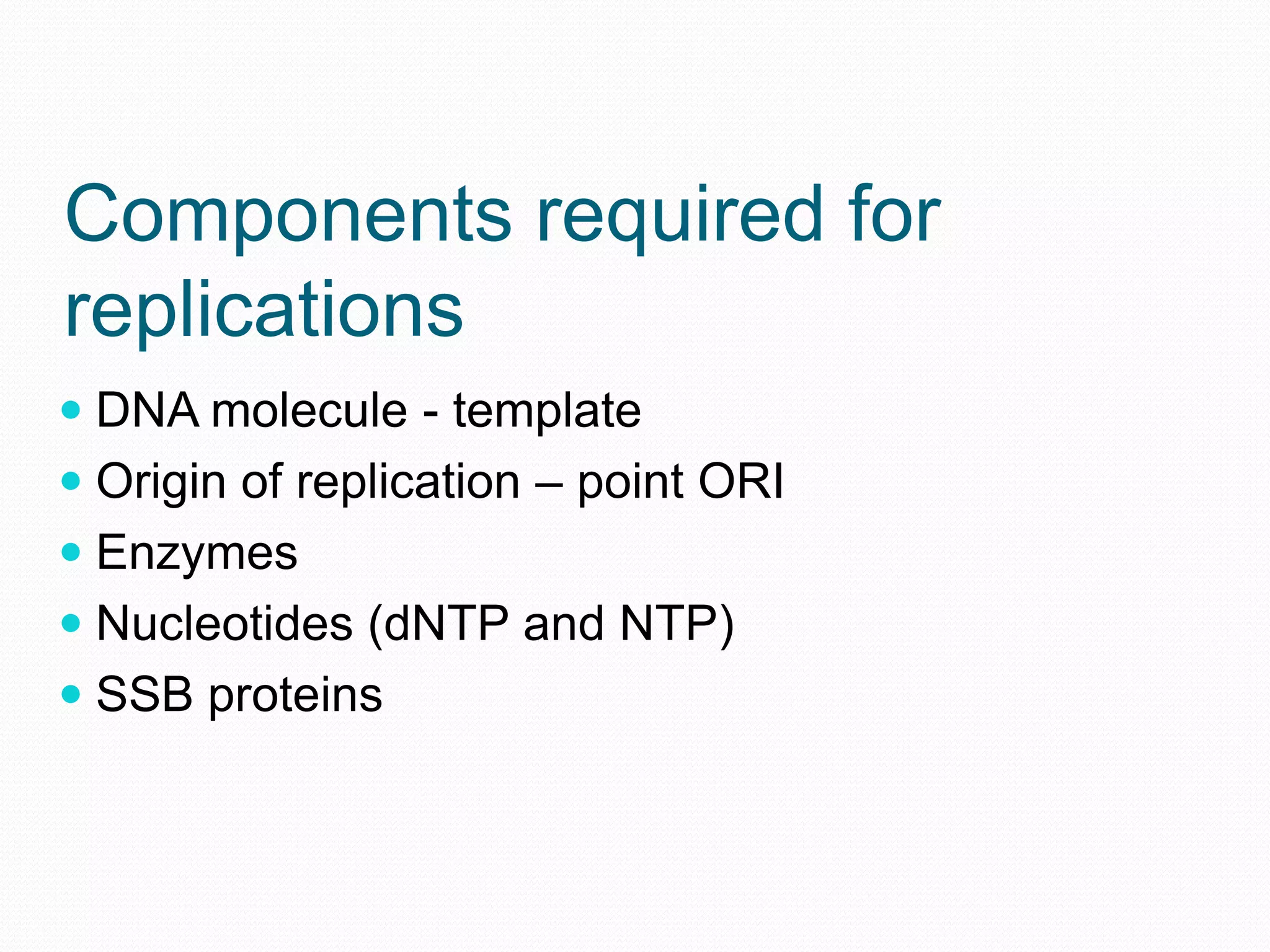
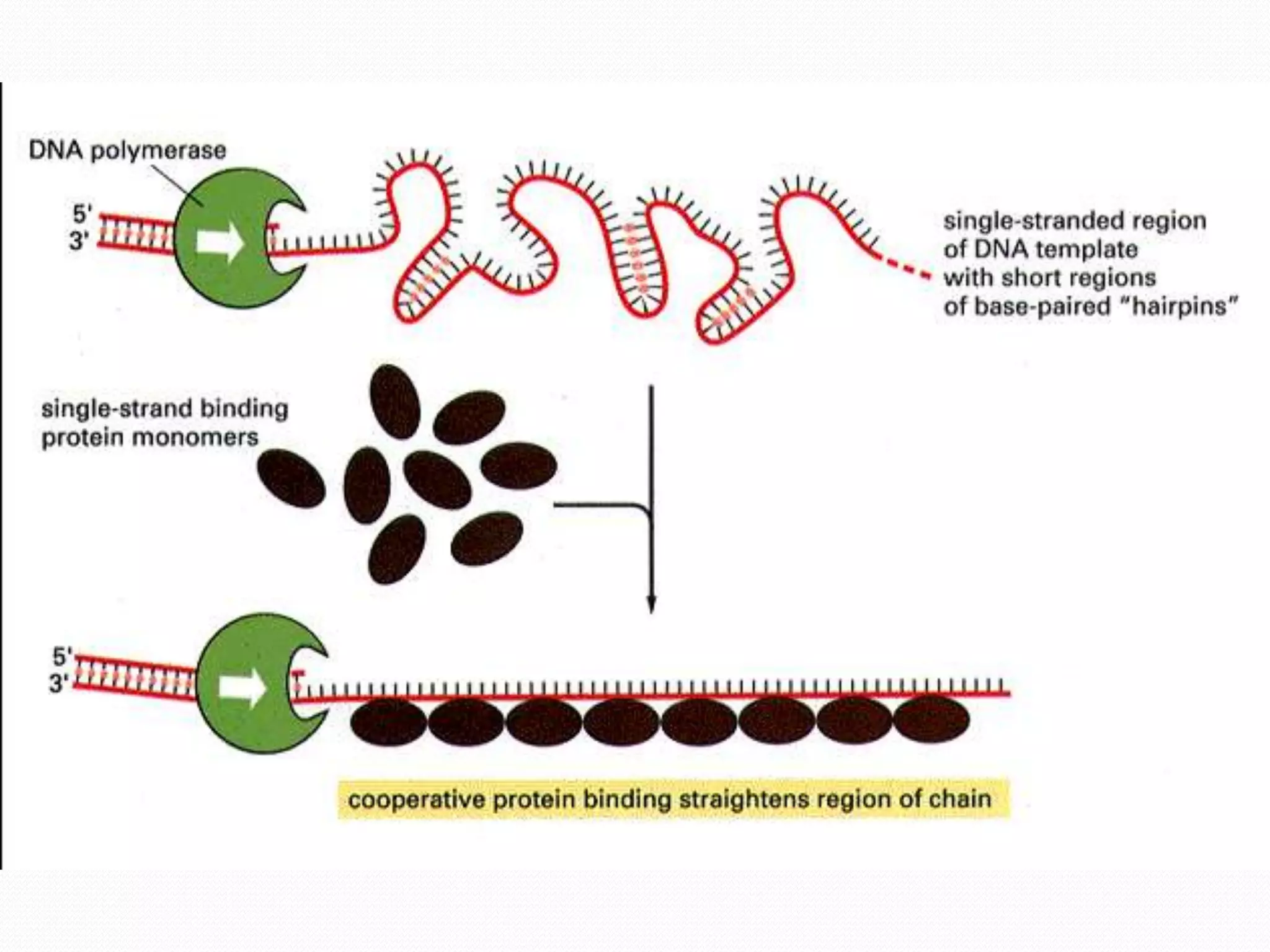
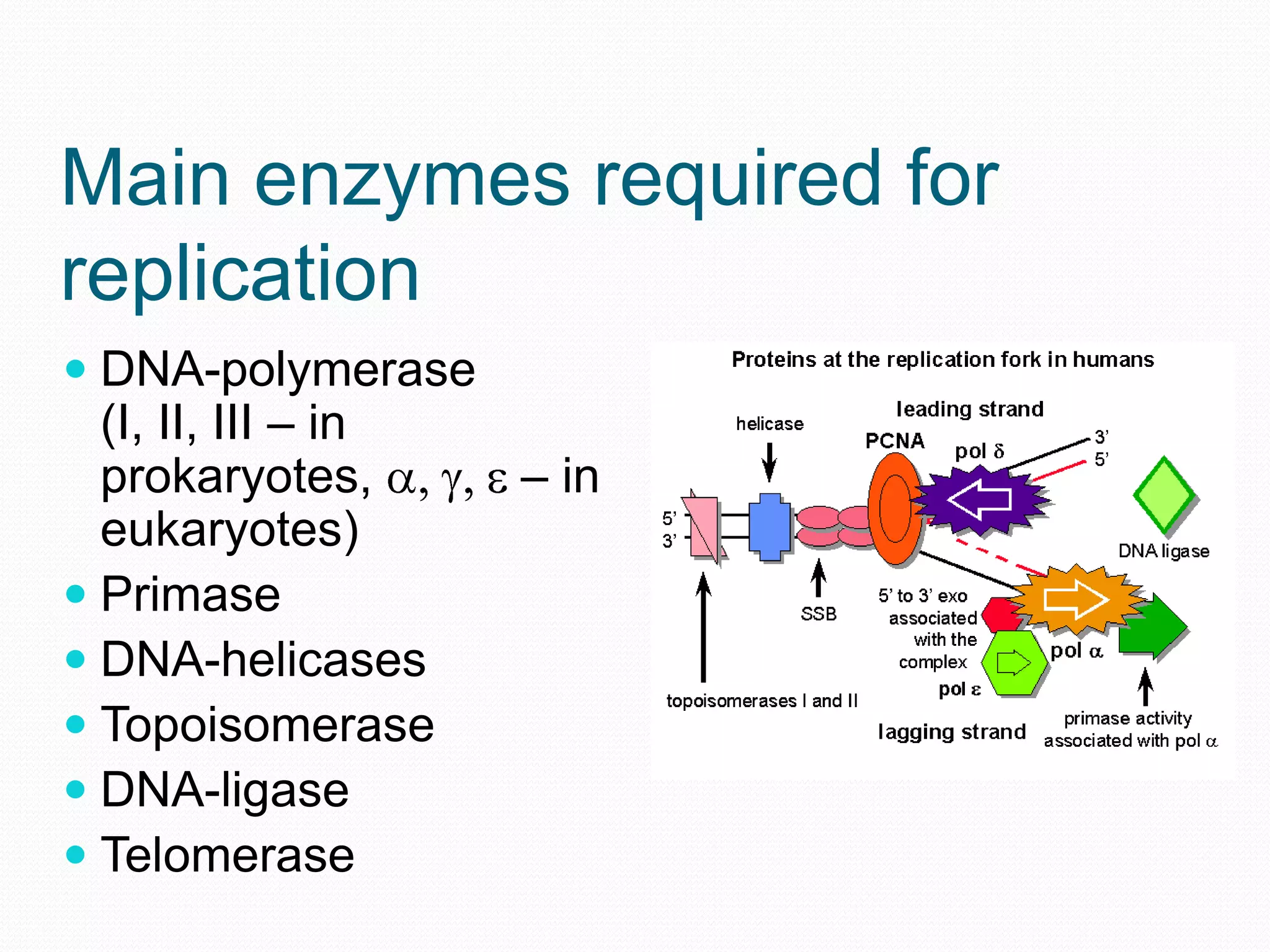
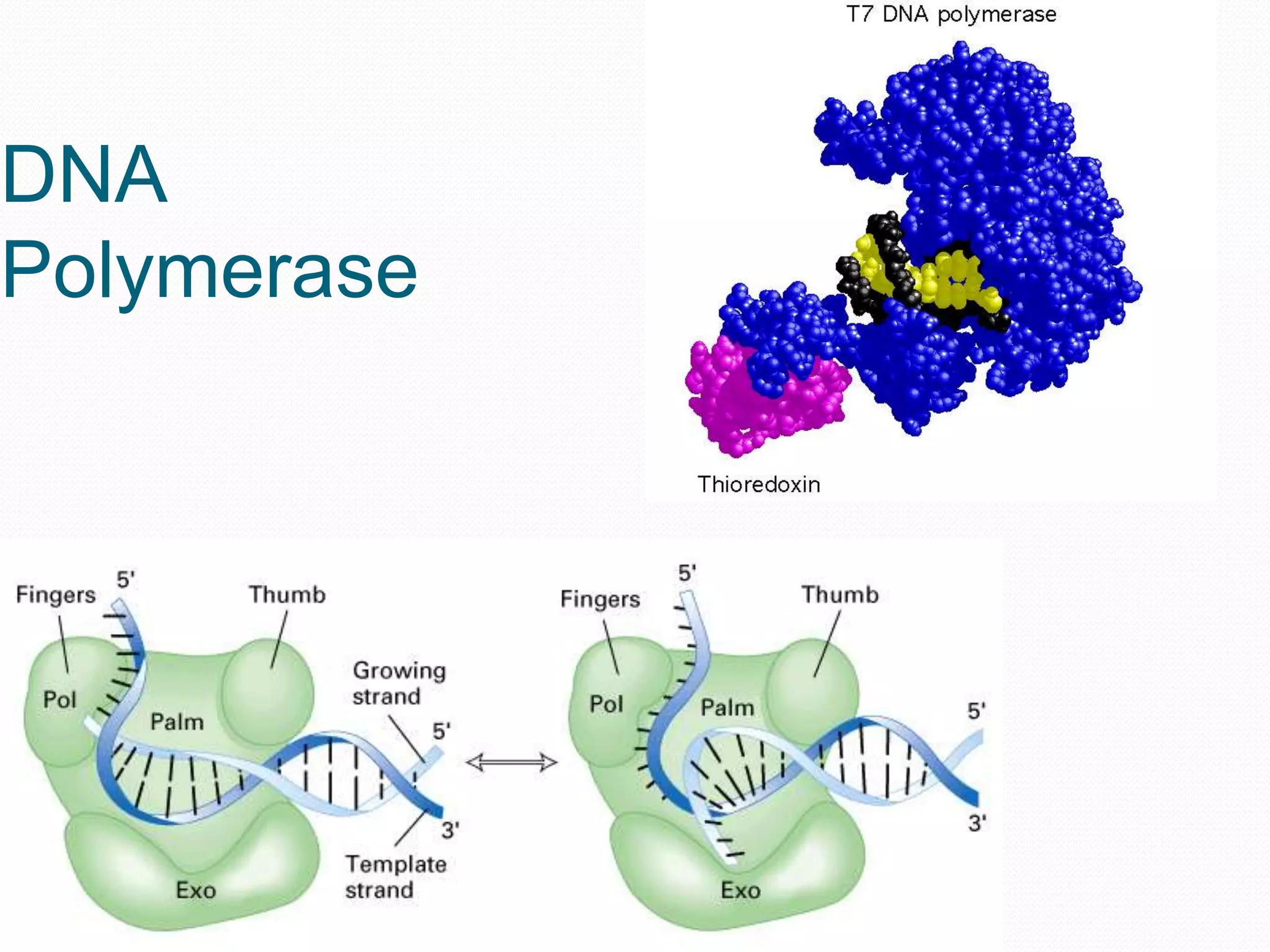
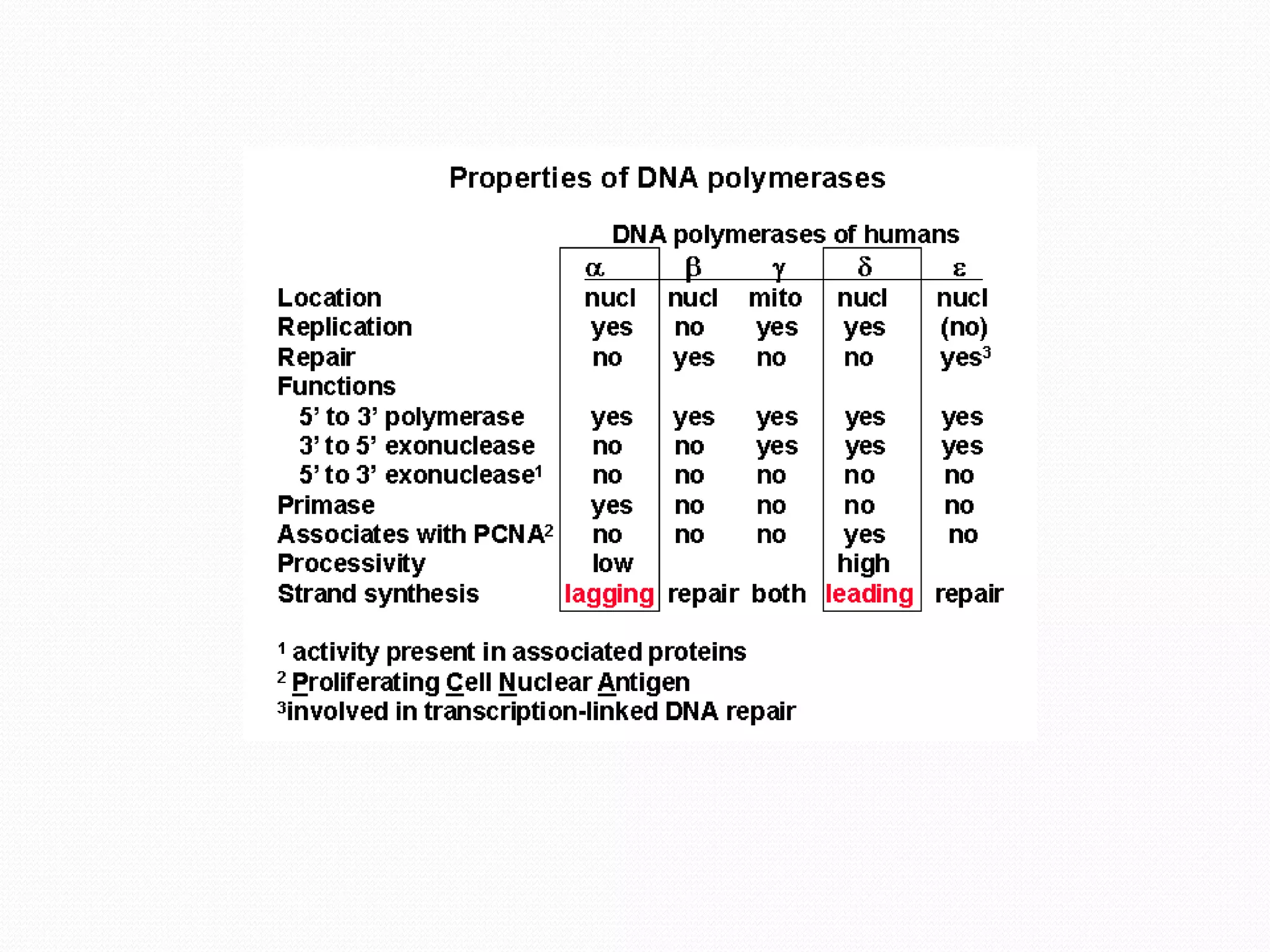
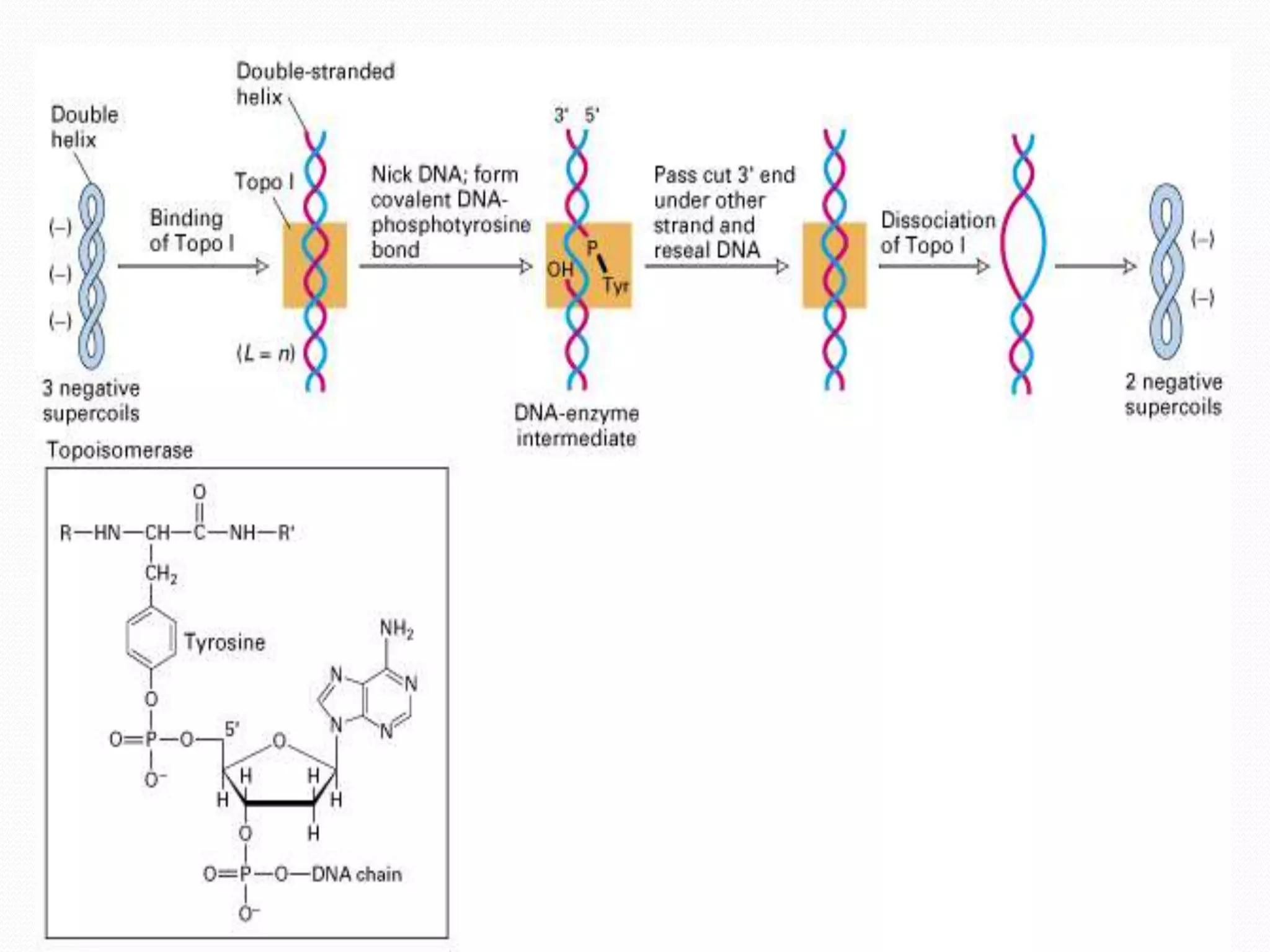
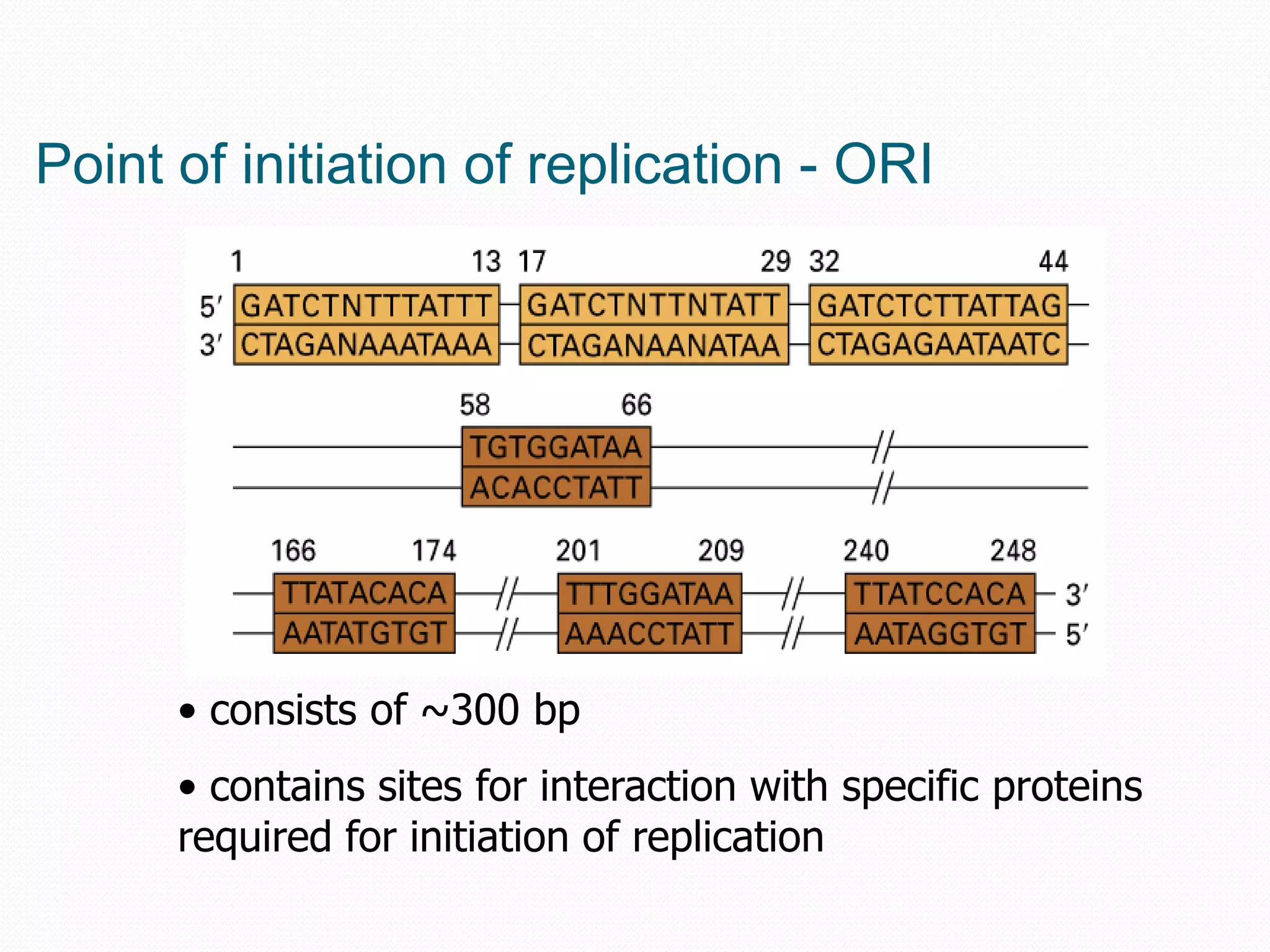
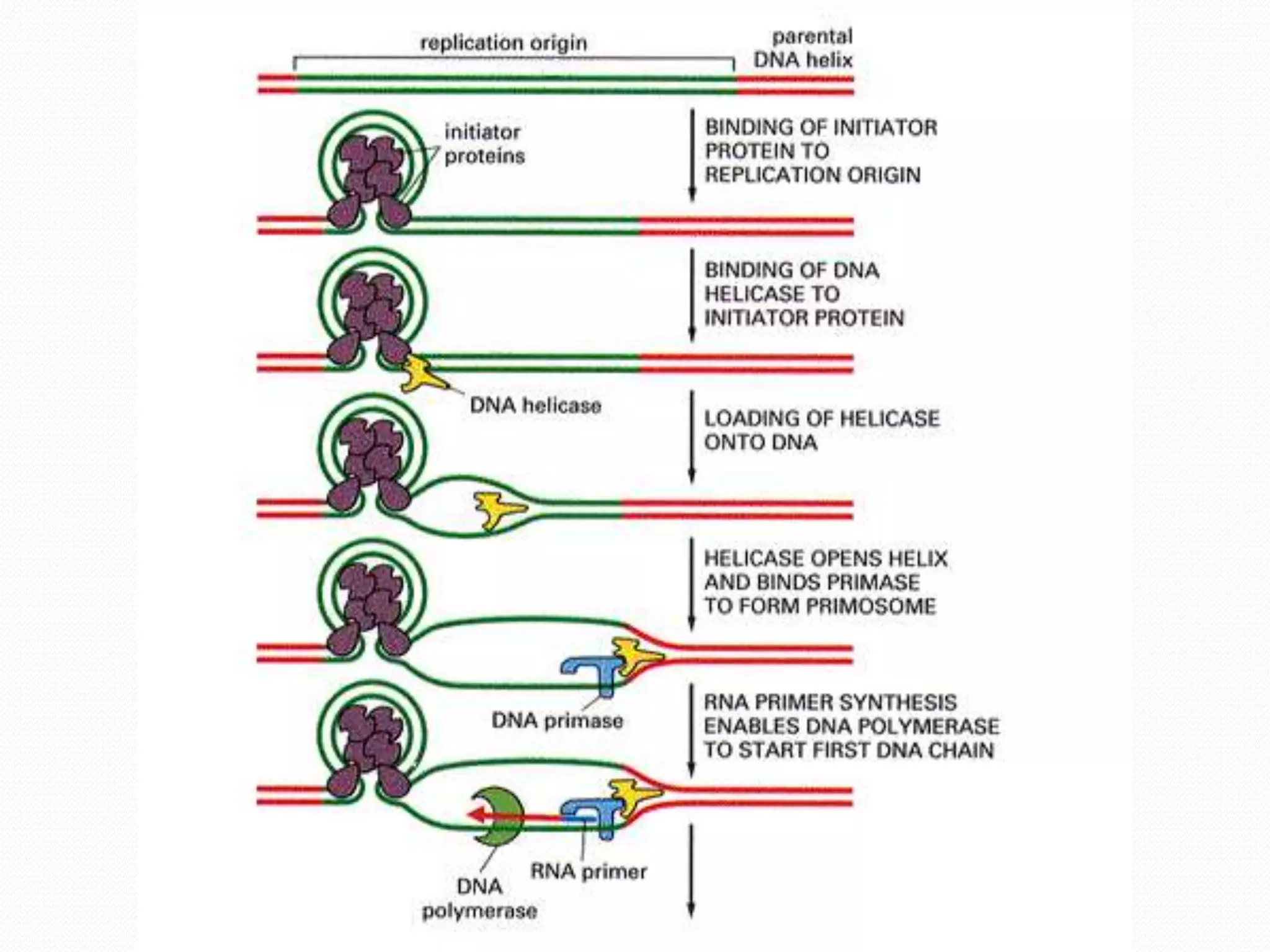
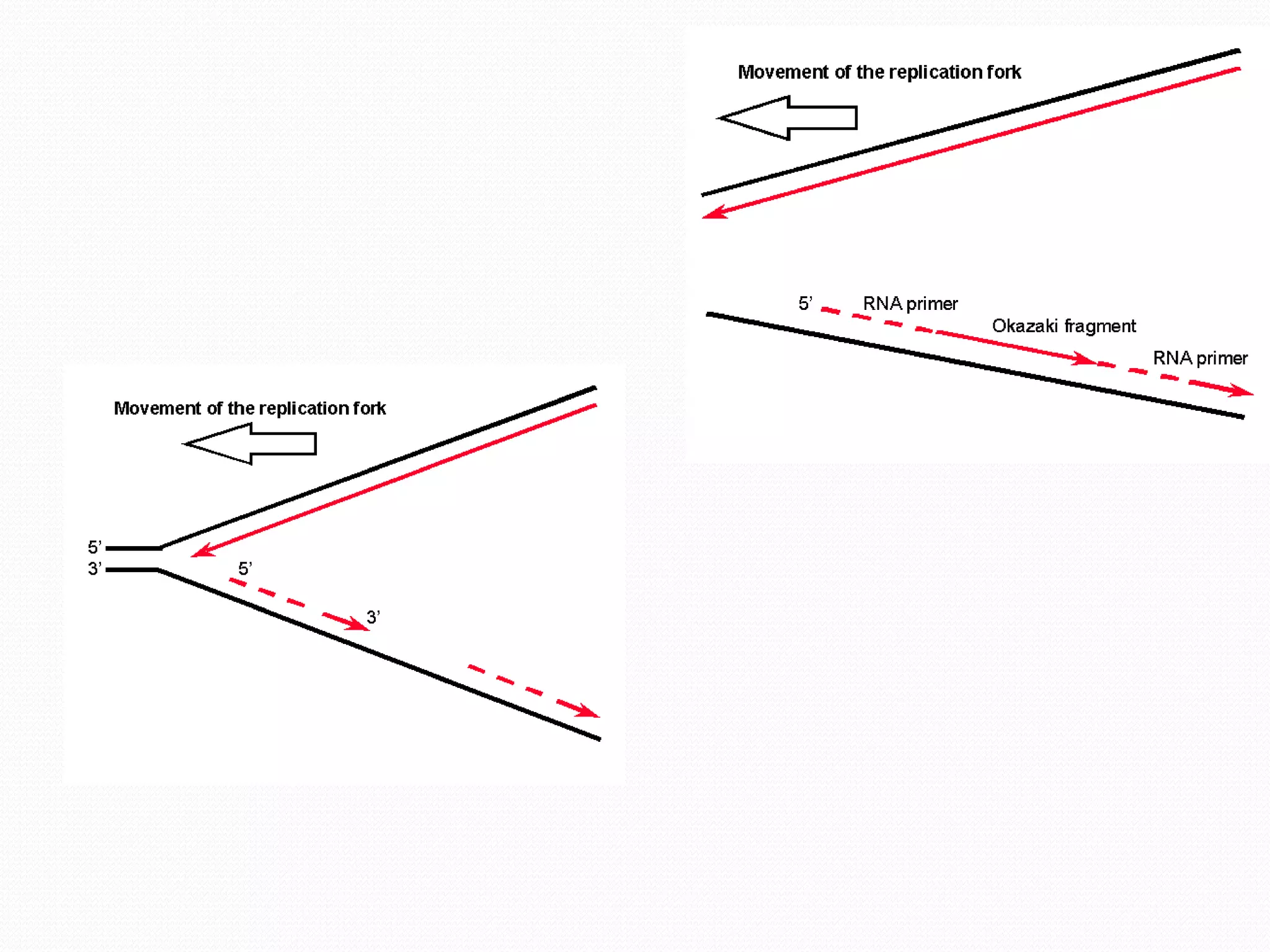
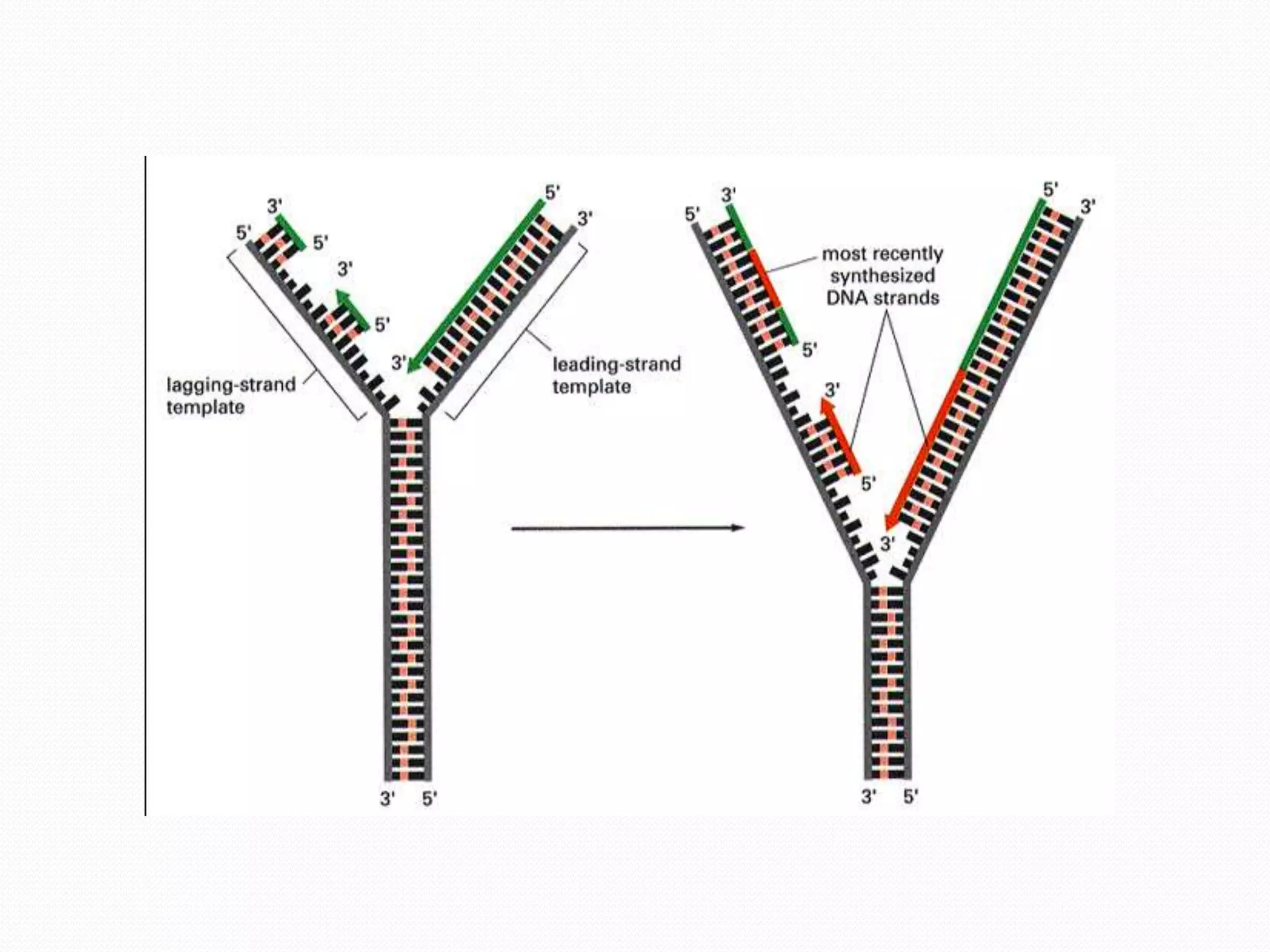
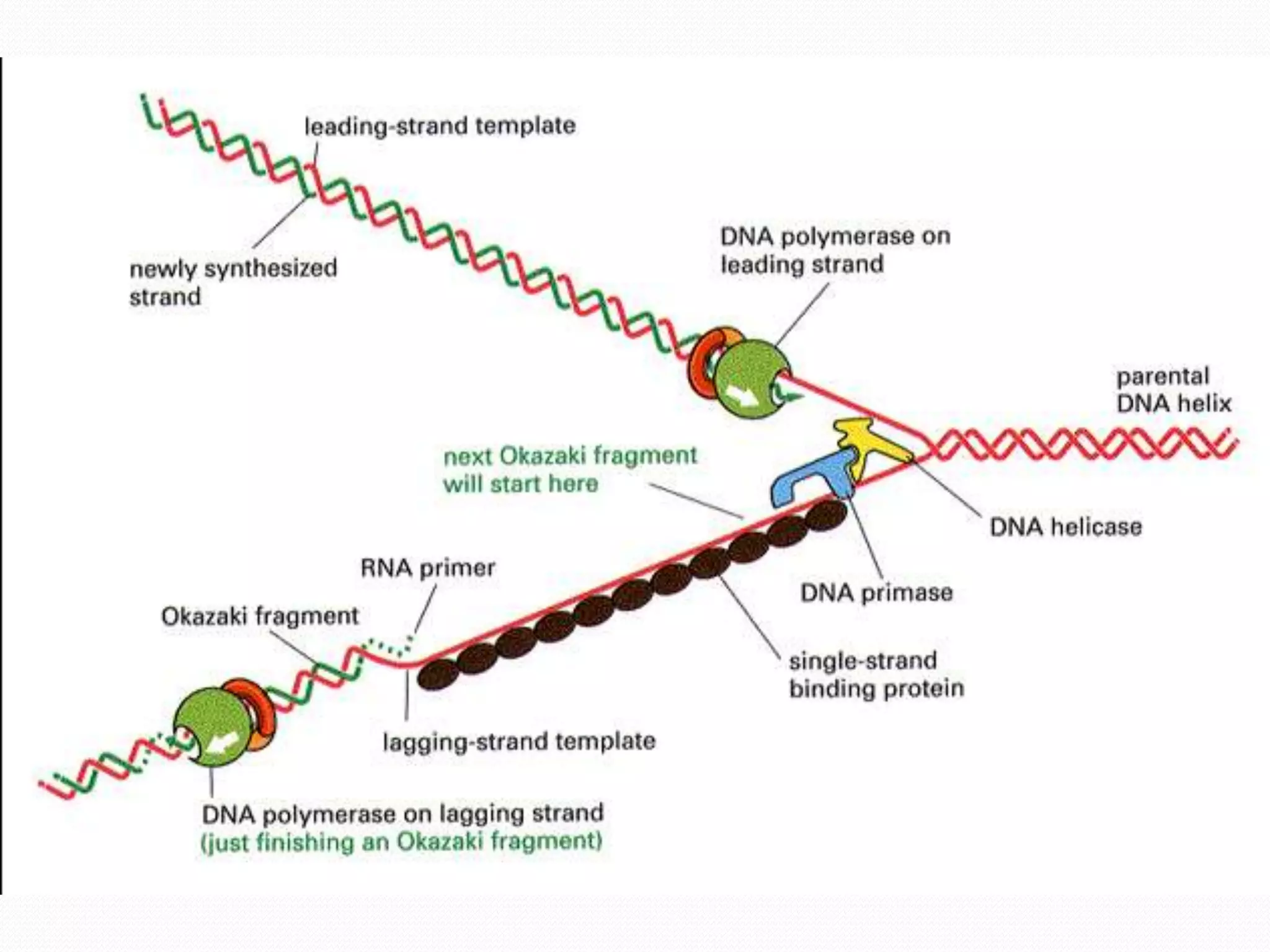
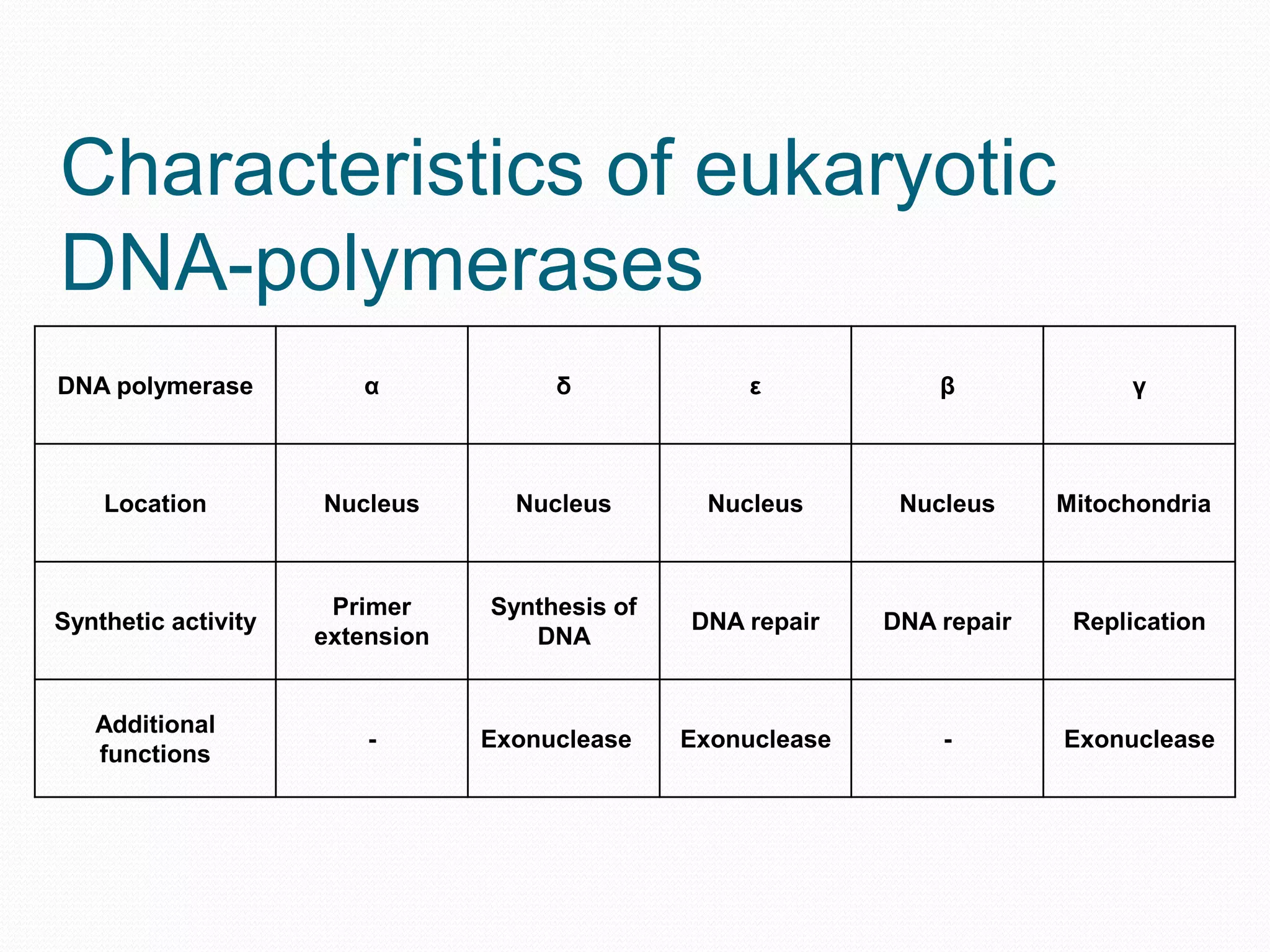
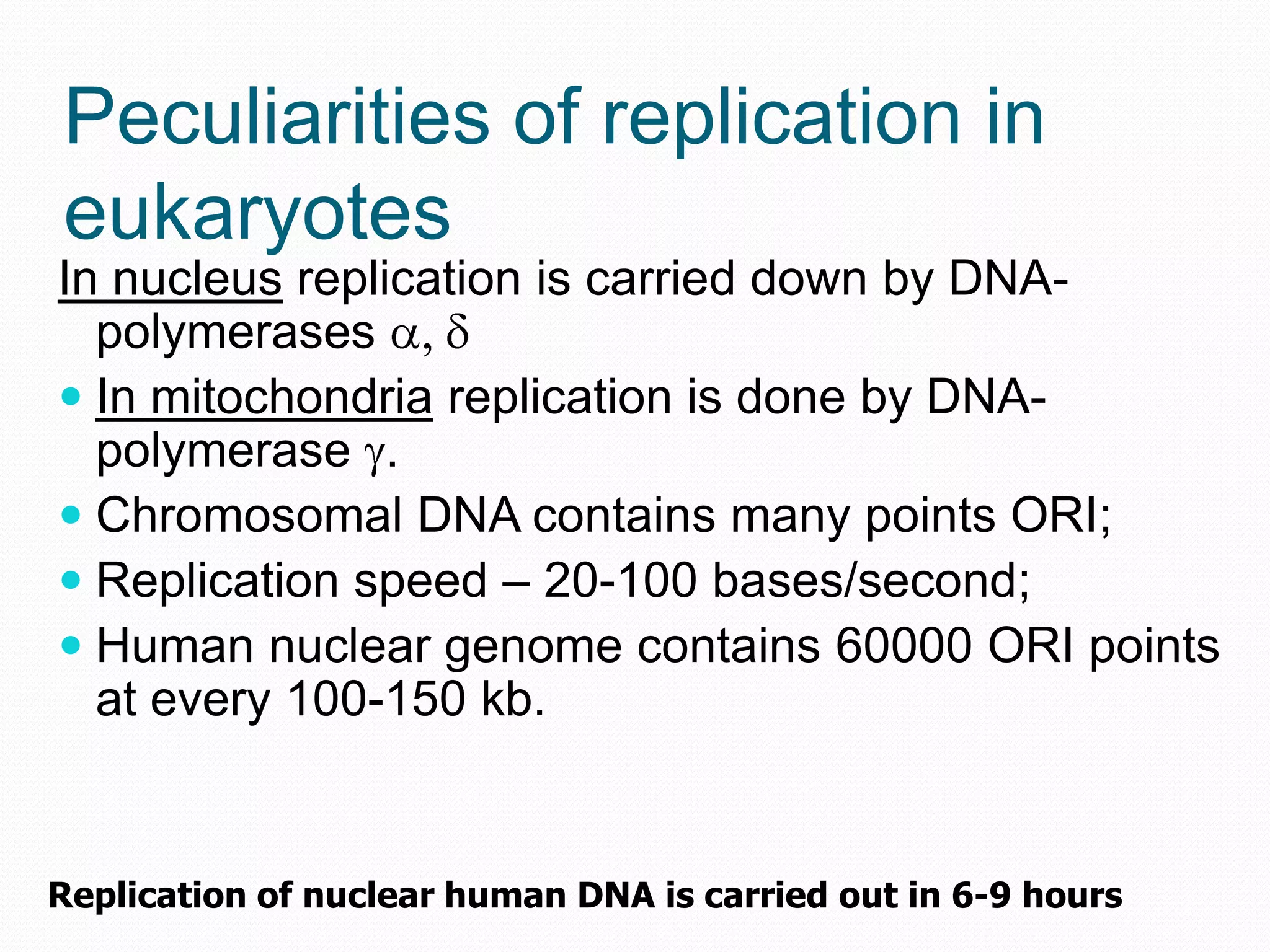
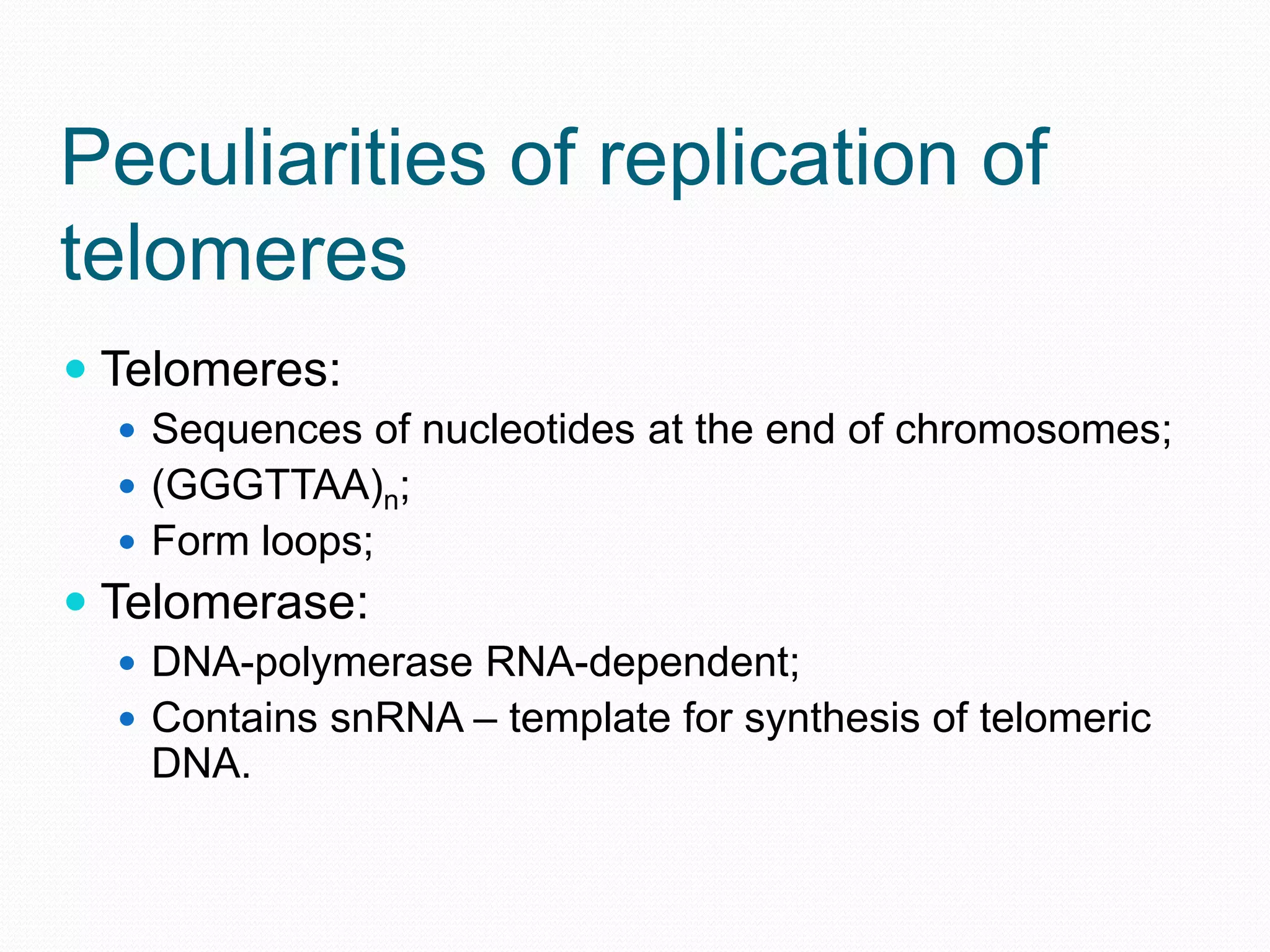
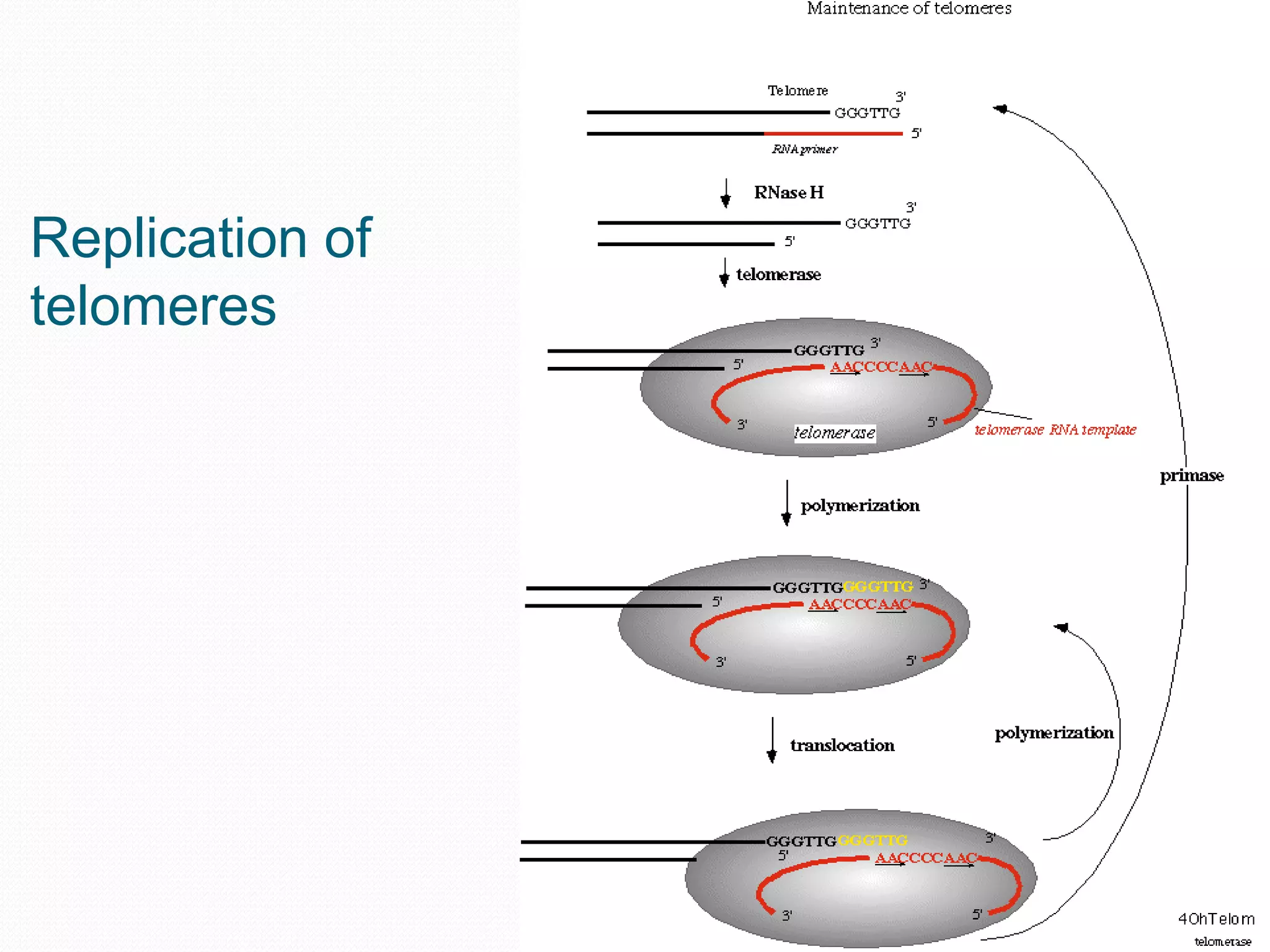
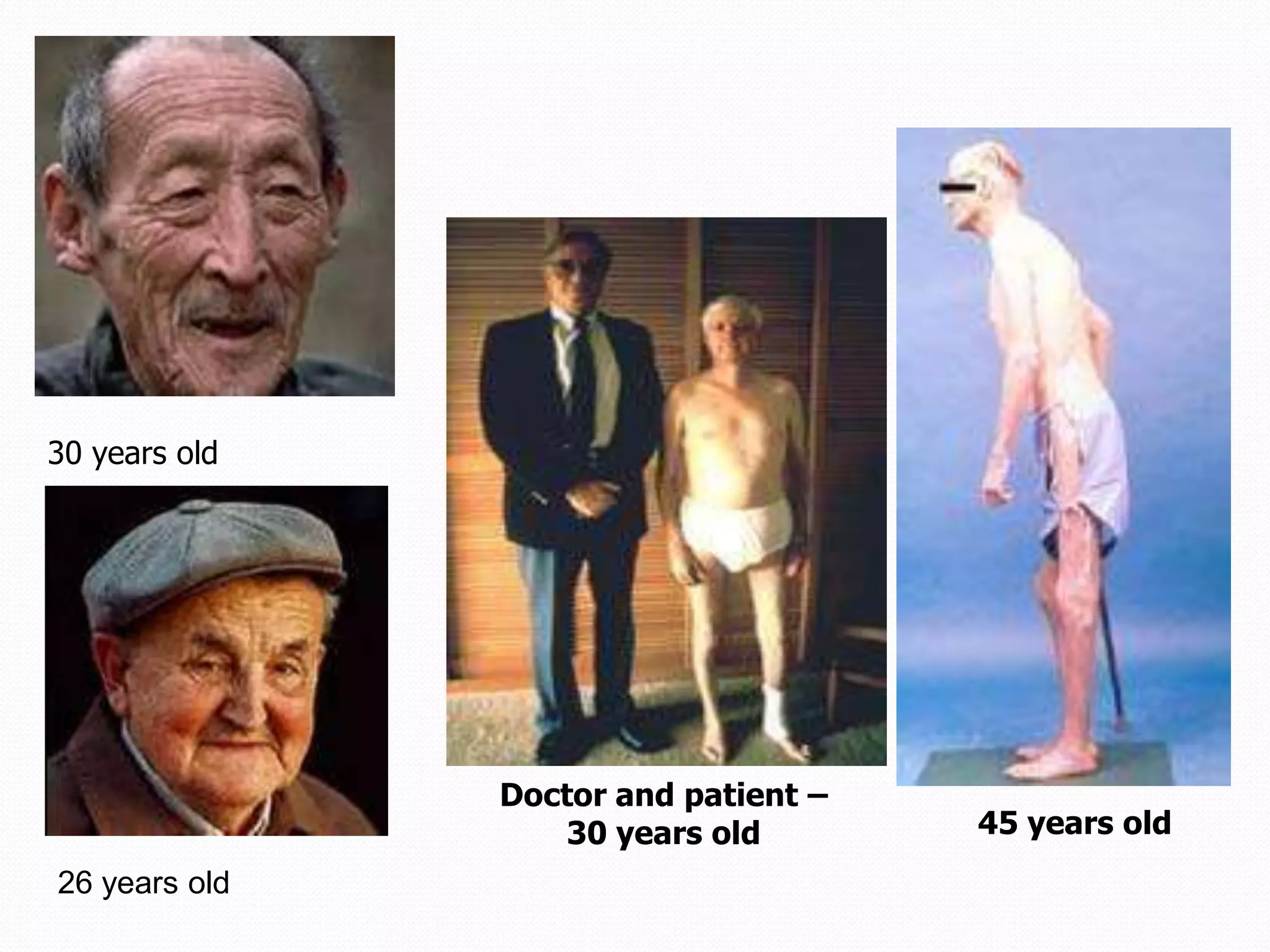
Replication is the process by which DNA duplicates itself for transmission to daughter cells. It ensures exact transmission of genetic information from one cell generation to the next. Replication involves semi-conservative synthesis of new DNA strands based on existing DNA templates. It requires specific enzymes and occurs through initiation, elongation, and termination steps. Initiation begins at an origin of replication and results in unwinding and denaturation of the DNA helix. Elongation then extends the new strands bidirectionally until replication forks from adjacent origins meet and terminate the process.